Vladimir Azbel published on his LinkedIn blog an article on hydrogen impact to features of tantalum capacitors.
Tantalum capacitors (TC) are polarized devices designed to operate in forwarding bias only. The application of reverse voltage, depending on the working conditions of the TC, can cause not only an increase in leakage currents but also lead to destruction.
The study of the influence of exploitation conditions on the behavior of DCL, TC (see table 1), when a reverse voltage is applied, It was conducted under conditions of humidity (see fig 1a), and at a temperature of 75C in the air (see fig 1b), and vacuum (see fig 1c), ( TC and electrical date perform NASA)
From the experimental data obtained, it follows that during the test, at conditions of humidity, besides more intensity increasing of DCL, destruction of the anode was observed, which did not occur in a dry environment. The mechanism of DCL degradation under moisture conditions is associated with the generation and diffusion of hydrogen protons into the anode, proposed in work (1). To confirm the proposed mechanism, the TC, after tested, were subjected to stripping, which made it possible to separate the anode. The anode is a product, a sintered tantalum powder, that has been anodized.
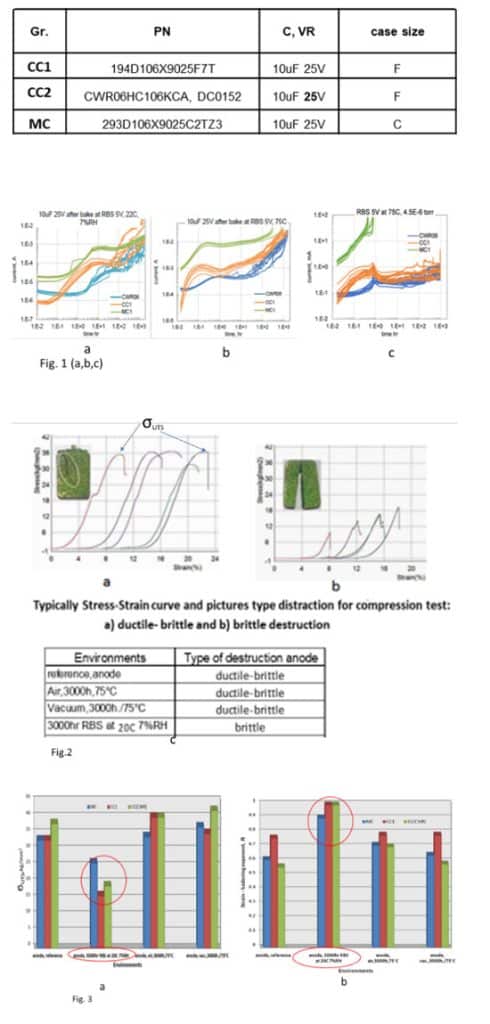
It is known from materials science that hydrogen introduced into a metal product will reduce its mechanical characteristics plasticity and ultimate tensile strength (σUTS) and affect the type of its destruction. To determine the mechanical characteristics of the anode, they were subjected to compression loading to failure and the stress-strain curve was recorded.
Figures 2a and 2b show the typical form of the stress-strain curve and the type of anode failure after testing in various environments(see Fig.2c) Strength values (σUTS) were determined from the stress-strain curve, and the plasticity values were calculated by the strain-hardening exponent of an index (na), [ 2]
From the data on the influence of test conditions on the tensile strength (see Fig.3a) and the na index (plasticity) (see Fig.3b) of test anodes, it can be seen that, under moisture conditions, strength and plasticity decrease, and the fracture has a brittle fracture type when compressed. In metal products, such changes indicate the presence of hydrogen, which was not observed in other tests (see Fig. 2c) and is a confirmation of the mechanism proposed in the work (1)
Note: The value of the strain hardening exponent lies between 0 and 1. A value of 0 means that a material is a perfectly plastic solid, while a value of 1 represents a 100% elastic solid. Most metals have a n value between 0.10 and 0.50.
1. A. Teverovsky “Kinetics of Moisture Sorption and Reverse Bias Degradation in Chip Tantalum Capacitors”, NASA Electronic Parts and Packaging (NEPP) Program PCND Sept 2017
2. A Rajeshkannan* and S Narayan “Strain hardening behavior in sintered Fe–0.8%C–1.0%Si–0.8%Cu powder metallurgy preform during cold upsetting” Proc. IMechE Vol. 223 Part B: J. Engineering Manufacture
featured image source: AVX Corporation