Source: 3D Printing Industry article
H.C. Starck Tantalum and Niobium, a metal powder manufacturer based in Germany, has announced the launch of a new range of powders developed specifically for metal additive manufacturing processes. Sold under the brand name AMtrinsic, the new powder selection will consist of tantalum and niobium metals, as well as their alloys, which offer highly resistant properties, ideal for ‘high-tech applications’ that involve high temperatures, electric currents and chemical contact.
“We see the introduction of our new Additive Manufacturing brand AMtrinsic as an important milestone in our new business development activities,” comments Melanie Stenzel, Head of Marketing and New Business Development.
The advantages of tantalum and niobium
H.C. Starck Tantalum and Niobium, a division of the JX Nippon Mining & Metals Group, is dedicated to the conversion of metal ores and secondary materials into tantalum and niobium-based powders. The company supplies the metal powders for applications such as capacitors, semiconducting materials, and SAW devices for a variety of industries, including aerospace and defense.
Both tantalum and niobium are often paired together due to their chemical similarity. The two metals provide high melting points, chemical and corrosion resistance, and thermal and electrical conductivity. This combined set of properties make tantalum and niobium suited towards fields such as chemical processing, superconductors, energy and high-temperature environments. For example, tantalum is often employed within capacitors in electronic equipment, like DVD players, video game systems and computers.
When processed with additive manufacturing, alloys containing tantalum and niobium offer further advantages. They reportedly allow the development of new intrinsic material properties that can deliver improved performance in challenging applications. For example, tantalum and niobium can be used as an alternative material in medical implants, as they can provide optimization for mechanical and biological performance parameters. Their chemical and corrosion resistance makes them useful in sterile/lab environments as well.
Developing tantalum and niobium alloys for additive manufacturing
H.C. Starck is not alone in developing tantalum and niobium powders for additive manufacturing processes. In 2018, Global Advanced Metals (GAM), a leading producer of tantalum metal powders, announced a partnership with Carpenter Technology subsidiary LPW Technology, to help process tantalum for use in powder bed fusion (PBF) additive manufacturing. Speaking at the time about the collaboration, Ben Ferrar, LPW COO explains that working out the metal’s compatibility with additive manufacturing is key:
“This work will further develop understanding of the factors affecting tantalum powder spheroidization and how it performs in the AM process, adding assurance to metal AM producers of the material compatibility for AM production.”
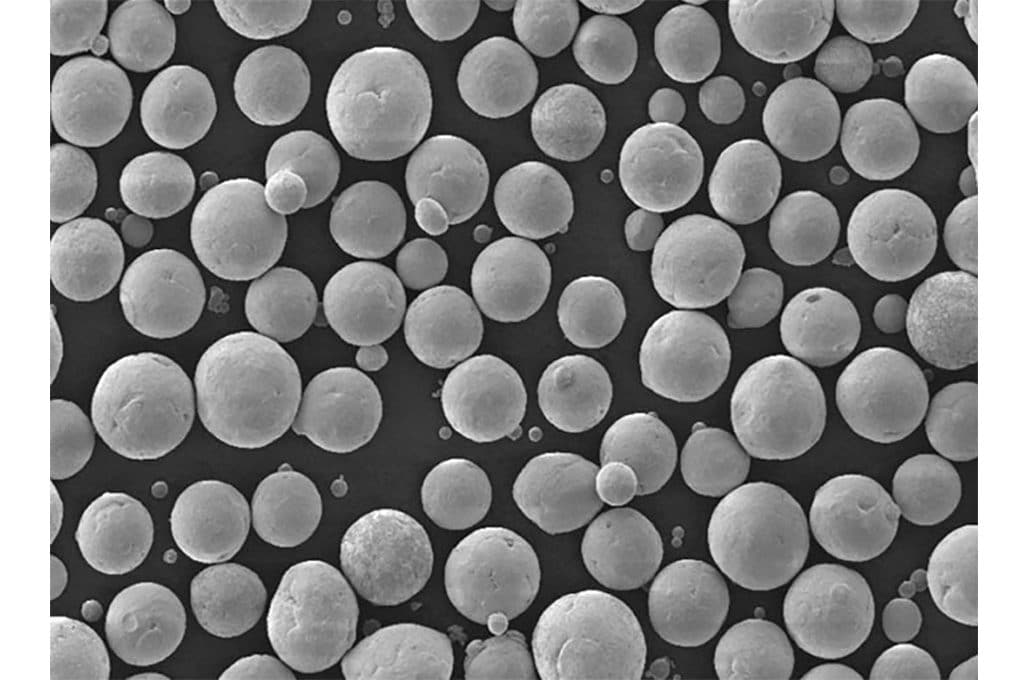
featured image: spherical niobium powder for additive manufacturing. Image credit: H.C. Starck Tantalum and Niobium