Chinese company Shenzhen Toomen New Energy developed and producing hybrid lithium ion “power capacitors” that can store as much energy as lithium batteries, but with much higher charge/discharge rates, a safe operating temperatures, long lifespans and no risk of explosion.
The highest density cells were getting between 200-260 Wh/kg, every bit the equal of today’s leading commercial lithium batteries but with a higher charge and discharge rate, and no risk of explosion. The power-focused variants were delivering densities of 80 and 100 Wh/kg, and were charging and discharging at 10 and 20C.
How do they work?
The power capacitor cells design is sitting halfway between a regular carbon-based supercapacitor and a lithium battery cell. Capacitors charge statically and thus charging and discharging quickly. Batteries use chemical reactions to store and release charge, which makes them slower, gives them a higher energy density and also their tendency to catch fire and explode due to dendrite formation..
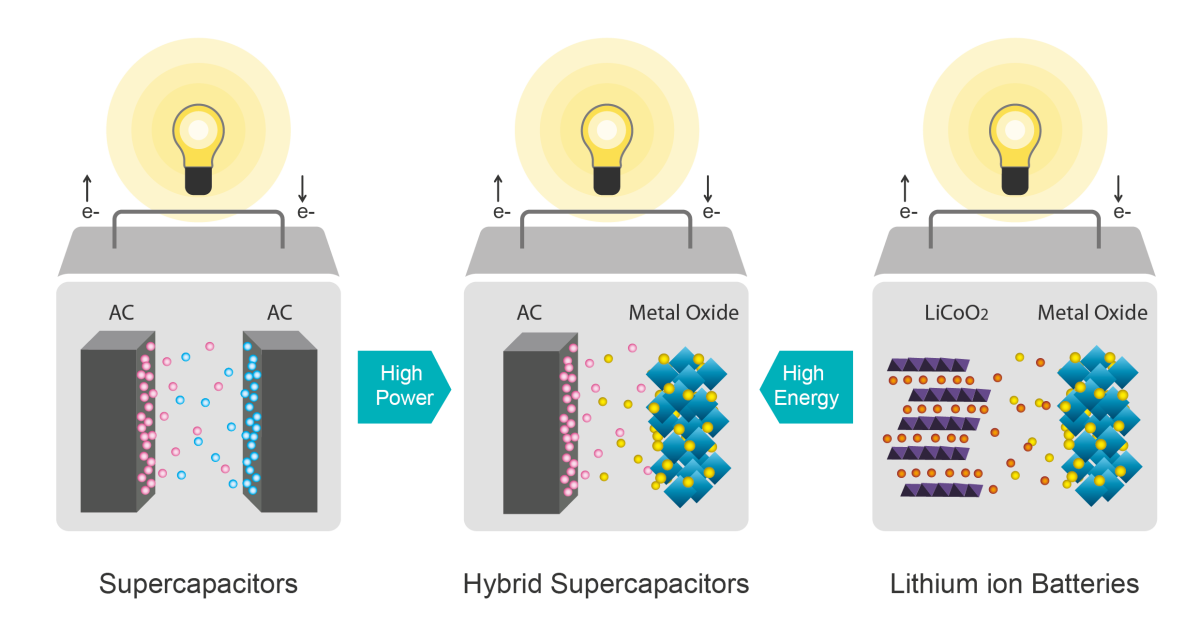
Toomen’s powercapacitors have one “activated carbon” electrode made from a variant of graphene, and the other is based on a lithium compound, but compared with lithium-ion, there’s no active lithium in there. There’s no chemical reaction; the charges are stored statically, like a supercapacitor. One electrode has some battery effect, but what you don’t have is a free flow of lithium ions floating in the battery that can form potentially dangerous dendrites.
There are currently two variants, one that prioritizes energy density and the other delivering maximum power rates. The high density cells are currently offering between 200-260 Wh/kg, with rated power densities around 300-500 W/kg. The high power cells are getting 80-100 Wh/kg, with power densities around 1,500 W/kg, peaking at up to 5,000 W/kg.
A new prototype pouch cell under development feature even higher volumetric density more than twice the volumetric density of the highest density cylindrical cells at up to 973 Wh/liter.
To put those numbers in context, a current model commercial ultracapacitor like the DuraBlue from Maxwell offers a much, much lower energy density of just 8-10 Wh/kg but a sky-high power density around 12,000-14,000 W/kg. A good lithium battery, on the other hand, typically offers 150-250 Wh/kg and power-wise is somewhere around the 250-350 W/kg area. So while it’s clearly a trade-off between power and energy storage, the Toomen power capacitors certainly offer power advantages at the high density end of the scale, and huge density advantages at the high-power end of the scale.
a small Belgian company Altreonic – Kurt.Energy is already making sales into the automotive, energy storage and solar markets, with the key driver being the Toomen cells’ ability to work flawlessly across wide range of temperatures. Munich University is evaluating the power capacitors for a possible role in deep space, where temperatures can reach -200 ºC (-328 ºF) that’s under testing for some time.
Source: Kurt.Energy