source: KEMET Electronics Portugal, S.A.; ESA SPCD 2018 Symposium
EPCI e-symposium library article
Solid electrolytic tantalum capacitors using conductive polymers as the solid cathode electrolyte have been commercially available since the mid 1990’s and continuously adopted by increased demand applications. This cathode system offers numerous advantages over traditional manganese dioxide based solid electrolytic capacitors, including lower ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance), improved surge current resistance, benign failure mode and lower voltage derating requirements.
For the past several years KEMET has worked with European Space Agency support to develop and release to market the T583 Series, as detailed in specification ESCC3012/005. Following the last application requirements KEMET started the development of single digit equivalent series resistance product. This paper presents the latest in line electrical characterization and ETP (Evaluation Test Plan) results.
published by EPCI under approval of ESA SPCD 2018 organizing committee.
Title:Ta SMD capacitors with Polymer Counter Electrode for Space Applications Update 2018
Author(s): Ana Tomás(1), Cristina Mota-Caetano(1), Dr. Denis Lacombe(2), Leo Farhat(2)
Organisation(s): (1)KEMET Electronics Portugal, S.A. Road Werner von Siemens1, Évora, 7005-639, Portugal
(2)ESA/ ESTEC European space Agency, Keplerlaan 1 NL 2200AG, Noordwick ZH, The Netherlands
Symposium: ESA SPCD 2018
Reference: Evaluation and Qualification 1.
ISBN: N/A
e-Sessions Applications: Aerospace
e-Sessions Scope Components: Capacitors
e-Sessions Topics: Technology, Specification & Qualification
INTRODUCTION
The general trend of new market and design in applications require ever lower ESR, high capacitance and high reliability. To achieve such capabilities, we directed our efforts on the multi-anode approach, taking entire advantage of its cumulative charge storage characteristics, cathode material and geometry of the paths within its elements.
The deepest capacitive element is the one that defines the worst or highest resistive connection to these elements and is the first element to stop responding at increasing frequencies, continuing to the outermost capacitive elements. In this way, the KEMET Multianode design composed by a three-pellet structure will allow us to reduce the resistance connecting these capacitive elements to the external contacts of the device, reducing the penetration depth to the deepest capacitive element by one-third compared to the single anode structure. Therefore the three pellets in paralel
will act as resistors in paralell, offering an effective resistance of one-third of each individual element. See featured image.
In addition, the use of low resistivity conductive polymer as material for the cathode system will turn it in the perfect combination for low ESR and high capacitance, with better performance in frequency and the inherent benefit of “no ignition” known to polymer technology.
To support the market requirement for an ultra-low ESR with maximum capacitance for POL (‘Point of load’) solutions KEMET started a new project to release the EIA 7343-43 330uF10V with ultra-low ESR targeting ESR≤15mOhm. This new PNR (Part Number) has a similar base design and manufacturing process as the previously qualified EPPL (European Preferred Part List) T583 Series under detailed Specification ESCC3012/005, building on the knowledge and technology of the earlier design, with the main difference being the assembly of multiple anodes – 3 in
this specific case.
This paper will be sharing preliminary results and evaluation test program data of prototype batch with PNR: T584X337M010AHE010P000.
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERIZATION
Similar to the single anode qualification, 3 additional standard conformity check procedures tests were carried out to provide a more complete characterization of the parts produced, prior to moving to the ETP Phase. These tests were:
- SSST Test (Step Stress Surge Test);
- Cap and ESR over a range of frequencies;
- Electrical characterization over a range of temperatures.
SSST is a low resistance, high current test that subjects the components to increasing voltages until failure. This is a destructive supplementary test that is a good indicator of dielectric stability.
This test consists of determining the voltage at which the dielectric breaks down under high surge current conditions. This behavior will give us a prediction on the reliability of the parts for the application voltage defined.
The PNR evaluated presented a very good SSST behavior within expectation, with the first failure approximately two times higher than the rated voltage, consistent with the behavior of the single anode.
EVALUATION TEST PROGRAM
The Evaluation Test program for the multianode samples was reviewed and established with our ESA partners. The agreed upon test plan for the multianode design took the performance during ETP testing and electrical characterization for the previously EPPL qualified single anode design (ESCC3012/005) as a baseline. To achieve the for the most relevant and quickest path to qualification the following test plan was defined:
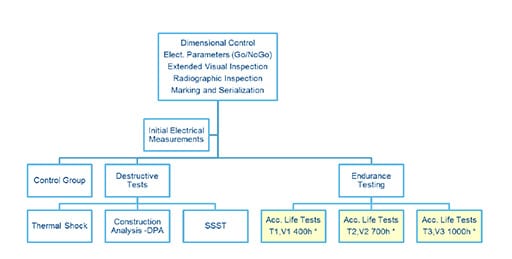
Multianode T584X337/010 Agreed Evaluation Test Program (ETP) .
Anomalous Charge Current
ACC is a phenomenon where higher current flows into a capacitor while charging than is predicted by i = c *dv/dt. ACC increases the time required to fully charge a capacitor at a constant current, but ACC is not caused by degradation of the capacitor’s dielectric. ACC occurs when the capacitor is in a “dry state”, with higher impact at lower temperatures. Anomalous Charge Current phenomenon occurs at voltages below rated for only certain designs with specific design criteria, material sets and conductive polymer formulations necessary to achieve specific design goals
(higher reliability, smaller size, higher voltage, etc.).
ACC is observed only if the applied voltage exceeds a ‘threshold’ voltage. Below this voltage, charging obeys i = c * dv/dt. To illustrate ACC, the current required to charge a T584X337/010 at 0, 25 and 45°C at a voltage ramp rate of 120V/sec was measured. The charging current and applied voltage are plotted versus time in Figure below. Below an applied voltage of approximately 5 volts the charging current for the 3 curves is generally flat and very close to the theoretical charging current of 39.6 mA. At applied voltages above 5 volts the charging current measured at 0°C is
observed to increase relative to the theoretical line.
The deviation is less noticeable at 25 and 45°C. For higher voltage ramp rates, the theoretical charging currents are higher and deviations from the theoretical charging current become less noticeable. The potential impact of ACC on circuit performance is dependent on many factors, including circuit design, circuit voltage, and voltage ramp rate. In Space and Military applications, where conservative derating rules are applied, this phenomenon is normally not observed and does not impact the final application.
Constant voltage ramp test to illustrate ACC
… read more at the full paper link below…
CONCLUSION
With Evaluation Test Program report, and upon on-going Construction Analysis completion, it is KEMET’s intent to apply for EPPL-part2, with a new detailed Specification for T584 Series based on existing released 3012/005 (T583 Series). Pilot Series for QPL (Qualified Part List) will then be manufactured and qualified accordingly to close the process.
KEMET will continue its development efforts qualifying needed components of SMD Tantalum technology for space applications with increasing harsh environmental conditions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The developed work and quick definition for this new series of Ta SMD Polymer Multianode Cap -T584, was only possible through a good support and partnership with ESA technical department.
REFERENCES
[1] A. Tomás, C. M. Caetano, D. Lacombe, L. Farhat, “Ta SMD capacitors with Polymer Counter Electrode for Space Applications”, 1st Passive Components Networking Symposium, Brno, Czech Republic, September, 2017.
[2] A. Tomás, “Electrical Characterization MAT Polymer Tantalum Capacitors (Based on type T583) Report” unpublished.
[3] Technical Update, T530 Multiple Anode Polymer- Tantalum Andes, “The Lowest ESR, Surface-Mount, High-CV Capacitor, http://www.kemet.com/Lists/FileStore/T530TechUpdate.pdf
[4] Y.Freeman, G.F. AlapatW. R. Harrell, I. Luzinov, P. Lessner, J. Qazi, ECS Journal of Solid State Science and Technology, 2 (11), N197 (2013)
[5] Y. Freeman, Tantalum and Niobium-Based Capacitors, (Springer, 2018)
[6] Y. Freeman, W. R. Harrell, I. Luzinov, B. Holman, P. Lessner, Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 156 (6) G65 (2009)
[7] ESCC3012/005, <https://escies.org/specfamily/view>.
[8] www.kemet.com;
read the full technical paper in pdf here:
and presentation here: