Dennis Zogbi, Paumanok Inc. publishes on TTI Market Eye circuit protection components 2023 market analysis.
Navigating Regulatory Demands in the Digital Age
Circuit protection components, though not intrinsically enhancing system functionality, are an imperative requirement due to stringent regulations outlined by esteemed bodies such as IEEE, IEC and UL. These mandates ensure the inclusion of protective components at crucial points, ranging from power transmission grids to the intricate I/O ports of advanced computing devices. This meticulous redundancy continues to play a pivotal role in shielding sensitive semiconductor layers from an array of threats, including electrostatic discharge, line switching transients and lightning-induced coupling to exposed exterior lines.
Market Dynamics: A 2023 Overview
As we step into 2023, the landscape of circuit protection components has witnessed significant transformations. Manufacturers catering to applications in digital electronics, power distribution, automotive and specialized high-tech sectors have embarked on a journey characterized by rapid innovation and transformative challenges. Notably, specific components closely tied to the automotive and connected device sectors have undergone pronounced shifts. The chip varistor, surface mount TVS diode, blade fuse and NTC thermistor components, intricately entwined with the automotive sector, have witnessed transformative shifts in their roles and applications.
Sector Transformation and the Path to Resilience
The circuit protection landscape has evolved significantly in response to transformative trends, particularly those propelled by Industry 4.0 and the proliferation of advanced connectivity. The automotive sector, traditionally a stronghold for these components, is now embracing electrification, autonomy and connectivity, prompting a recalibration of component requirements. Amid this transformation, the legacy wireless handset sector has transitioned into a hub for emerging technologies, accentuating the importance of chip varistors and surface mount TVS diodes for advanced connectivity, 5G technology and beyond.
Innovative Technologies and New Growth Trajectories
Amidst these transformations, innovative technologies such as 5G, IoT and smart cities are driving new growth trajectories for circuit protection components. As 5G networks continue to expand, the demand for components that protect against transient voltages, such as varistors, SAD diodes, SMD gas tubes and polymeric ESD protection, has surged. Furthermore, the “stay at home” trend has catalyzed the demand for computer-related circuit protection, revitalizing components like varistors and avalanche diodes.
Revolutionizing Power-Related Markets
In 2023, power-related markets have undergone a revolution, driven by the imperatives of sustainable energy and carbon neutrality. Markets catering to power transmission and distribution have witnessed unprecedented growth, propelled by climate change initiatives and a global shift towards renewable energy systems. This has fueled demand for specific circuit protection components, including power thyristors, AC line gas discharge tubes, industrial-grade fuses, film snubber capacitors, disc varistors and valve block arresters.
Adapting to Change: Customer Premises Equipment
While circuit protection components have been resilient in navigating change, customer premises equipment markets have also adapted to evolving trends. The “stay at home” trend, an enduring consequence of the pandemic, has driven demand for IoT devices, game consoles and smart home systems. However, this has also prompted shifts in demand for specific components. As home appliances, HVAC systems, lighting ballasts and smoke detectors remain central to the home ecosystem, the market has experienced slight downturns driven by housing market dynamics.
Specialty Markets: A Spectrum of Possibilities
In the realm of specialty markets, 2023 has witnessed a spectrum of possibilities. The demand for circuit protection devices in the space and medical sectors continues to grow, underscoring the critical role these components play in cutting-edge applications. However, the mining, oilwell and semiconductor manufacturing equipment sectors have faced fluctuations driven by commodity prices and market dynamics.
Decoding Circuit Protection Component Categories
The following chart offers a Paumanok IMR taxonomy for circuit protection components as one does not exist in the Harmonized Tariff Schedule (HTS) of international trade and therefore this product line remains extremely important. The content is pulled from multiple ecosystems to accomplish a similar task not fundamental to the performance of the product line but rather a solution in search of a frequent and destructive problem for electrical and electronic systems. See Figure 1.
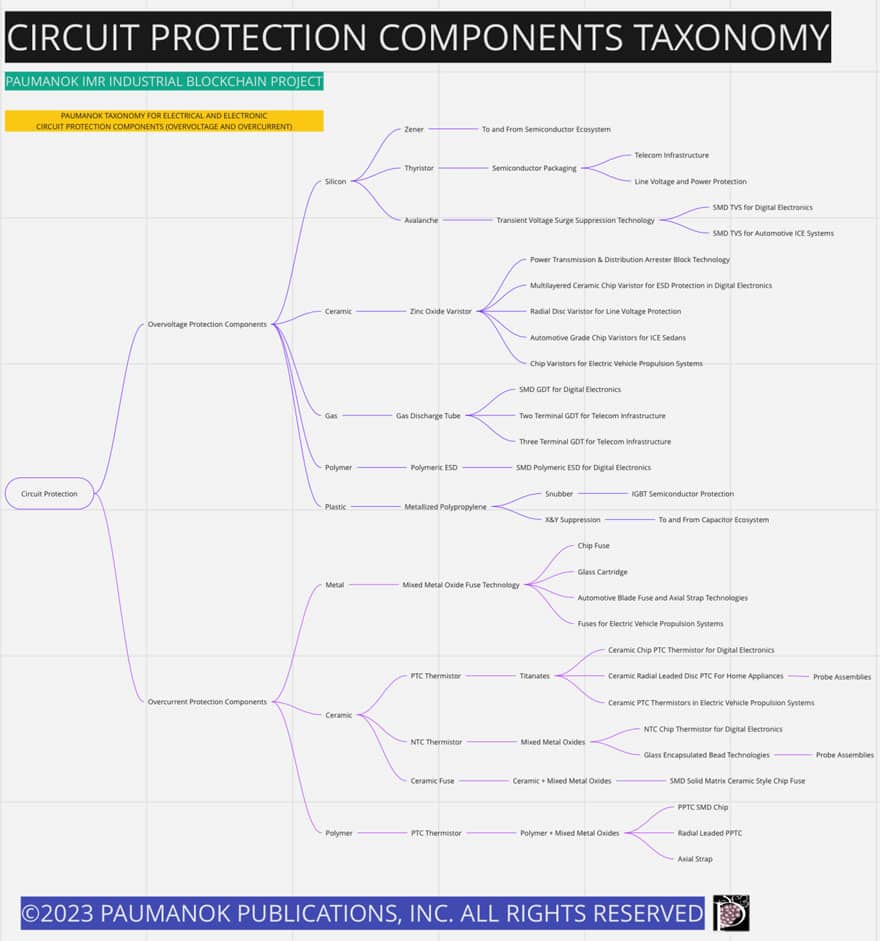
Over the past 40 years, semiconductive layers have become thinner and more precise and their technology has moved at a pace that exceeds protective component technologies. The total circuit protection solution is based upon redundancy of circuit protection against known transients such as lightning or load switching. This article also contains information on areas of expansion in capacitance and inductance as tools for additional circuit protection.
Overvoltage Protection Components
Zener Diodes: These diodes continue to be a cornerstone in voltage regulation, allowing current flow in both directions when a specific reverse breakdown voltage is surpassed. As connectivity and high-speed data transmission become paramount, Zener diodes remain a robust solution against electrostatic discharge in electronic systems.
Silicon Avalanche Diodes: Characterized by their rapid response and resistance stability, avalanche diodes play a vital role in protecting circuits from harmful high voltages. In the era of IoT and connected devices, their ability to respond swiftly to transient events is paramount.
Thyristors: As power systems evolve to embrace renewable energy and decentralized grids, thyristors continue to act as efficient switches for various applications. Their role in preventing power supply failures and optimizing energy utilization remains pivotal.
Metal Oxide Varistors: Varistors have adapted to the changing landscape, finding applications in wireless handsets, automotive electronic subassemblies and emerging technologies. Their volumetric efficiency and resilience in harsh environments continue to set them apart.
Gas Discharge Tubes: Evolving applications, including cable modems and station class protectors, have invigorated this technology. The ability to mitigate signal distortion in the era of high-definition data transmission remains a valuable trait.
Polymeric ESD Protection: As electronics become increasingly miniaturized and interconnected, polymeric ESD suppressors have risen to the occasion. Their ability to neutralize fast-rising ESD transients without introducing capacitance aligns seamlessly with the demands of modern high-tech systems.
Overcurrent Protection Components
Fuses: In the dynamic landscape of 2023, fuses have become integral to ensuring system safety and reliability. As systems become more complex and interconnected, fuses play a pivotal role in preventing overcurrent events from compromising critical components.
PTC Thermistors: With the proliferation of electronic systems in diverse applications, PTC thermistors continue to serve as guardians against overcurrent events. Their adaptability in various applications, from inrush current limiting to temperature sensing, reflects their versatility.
NTC Thermistors: In the age of data-driven insights, NTC thermistors have assumed a new role as temperature sensors, enabling precise monitoring and control. Their application in diverse fields, including automotive electronics, highlights their growing importance.
Unveiling Additional Circuit Protection Devices
Amid the realm of circuit protection, a multitude of passive components extend the frontier of safeguarding electronics. Our meticulous analysis and assessment have identified these underappreciated champions that warrant a spotlight:
Plastic IGBT Snubber Capacitors: Among the unsung heroes are polypropylene plastic dielectric film capacitors, adept at shielding IGBT semiconductors from overvoltage surges. Though targeting a specific niche, this unique capacitor, engineered for overvoltage protection, generates microfarads at elevated voltages, amplifying its utility across diverse scenarios.
Plastic X and Y Interference Suppression Capacitors: Polypropylene plastic dielectric film capacitors take center stage for noise suppression in domains spanning lighting, power supply and line voltage circuits—such as the high-voltage landscape of EVx propulsion. Innovations in OPP film within the Japanese realm propels the evolution of this application.
MLCC Ceramic Chip Capacitors: Multilayered ceramic chip capacitors navigate beyond convention to embrace the mantle of circuit protection. Expanding their spectrum, these capacitors integrate variations of ceramic dielectric materials, including barium titanate, to rival chip varistors within ultra-compact case sizes.
SLC X&Y Capacitors: Single-layered ceramic capacitors emerge as formidable contenders for X&Y suppression roles, lauded for their adeptness at managing soaring voltages—a testament to their robust capabilities.
Ferrite Beads: Noise suppression finds a loyal ally in ferrite beads, witnessing significant adoption across the notebook computer and consumer electronics segments, where their presence significantly elevates system integrity.
Inductor Coils: Handsets, notebook computers and kindred devices experience a boost in performance courtesy of ceramic chip coils. Employed for noise suppression, these components epitomize the fusion of innovation and practicality.
Bi-Metallic Switches: The saga of circuit protection expands to encompass bi-metallic switches, instrumental in safeguarding home appliances against inrush currents. The deployment of diverse metal alloys—a trend echoing in fuses, resistors and circuit breaker markets—resonates as a hallmark of adaptability and versatility.
Cable Connectors: Cable connectors offer premium products with built in circuit protection on each power, telecom or data line. These products are vertically integrating components into their product lines to generate added protection and addition premiums.
Other Circuit Protection Components and Devices: Our 35 years of research in circuit protection also notes the following unique product lines as additional examples of circuit protection components and devices: Delay lines, static isolators, with the following products the vertical integration of the circuit protection component into a more complex module, connector, rack mounted box or line voltage device. For example, plug-in modules for central office; station class telecom arresters, utility grade lightning arresters, plug-in surge protectors and suppressors.
Conclusion: Expanding Horizons in Circuit Protection
The world of circuit protection extends beyond the conventional confines, revealing an ecosystem teeming with diverse components and devices that collectively fortify electronic systems against the vagaries of voltage fluctuations, transient events and electromagnetic interference. These unsung components—each equipped with a unique set of capabilities—complement the broader spectrum of circuit protection, underscoring the industry’s ceaseless quest for resilience, innovation and operational integrity. As we continue to explore the dynamic landscape of electronic protection, these sister components and related devices stand as a testament to the field’s ceaseless evolution and relentless pursuit of enhanced reliability.
As we stand at the cusp of technological innovation and disruption in 2023, the circuit protection components market embodies adaptability, resilience and transformation. The sector, once seen as conventional, has embraced innovation and new applications, reflecting the ever-changing needs of modern high-tech industries. Amidst evolving regulatory demands, transformative market dynamics and emerging technologies, circuit protection components continue to serve as the bedrock of system reliability and operational integrity.