This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog discusses role of supercapacitors in backup power and load management applications.
Supercapacitors, also known as electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), store energy electrostatically rather than via chemical reactions like traditional batteries. Their unique characteristics make them ideal for applications requiring short bursts of power and/or durability over time.
With built-in high-power characteristics, supercapacitors are critical in power electronics, where engineers are looking for short-term power peaks.
Supercapacitors are also popular in low-power applications, like security installations. In these cases, batteries provide insufficient performance over time; in contrast, supercapacitors can efficiently handle those quick bursts of energy when needed and endure many more charge/discharge cycles than batteries over time.
Key Takeaways
- Supercapacitor applications include backup power and load management, providing energy quickly and reliably.
- They excel in situations requiring short bursts of power and durability, unlike traditional batteries.
- Supercapacitors serve critical roles in electronic circuits for memory backup and power failure safeguards.
- They effectively assist in high load situations and enhance hybrid energy storage systems in microgrids.
- With evolving technology, supercapacitors will remain essential for efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
Supercapacitors in Electronic Circuits
Supercapacitors play two main functions in electronic circuits. In battery-powered devices, they provide backup power in the event of disconnection (Figure 1a). They also provide alternating current (AC) voltage for devices with heavy switching currents (Figure 1b). In that case, supercapacitors protect the device’s memory, for example, from large voltage drops.
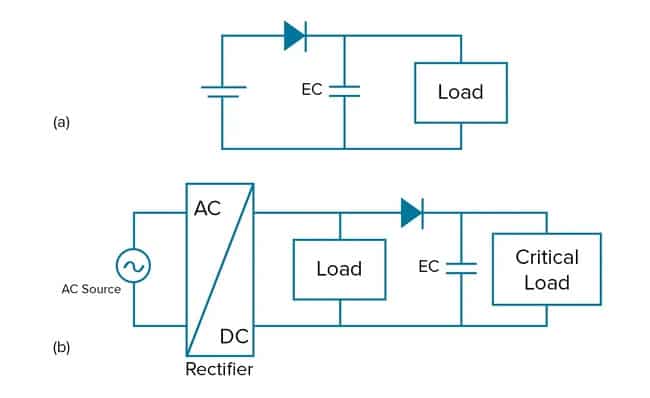
The following examples demonstrate how supercapacitors assume these functions in real-time clock backups, power failure backups, high load assist systems and hybrid energy storage systems to enhance efficiency and reliability.
Real-Time Clock Backup
In real-time clock backup, also known as memory backup, solid-state drives have many advantages over hard-disk drives, including low power consumption and high reliability. By design, write speed is their main weakness, and that’s remedied using protected cache memory (SDRAM). SDRAMs need backup power, and supercapacitors are an excellent choice because of their fast response time, high power density and low maintenance requirements – see Figure 2.
Power Failure Backup
Power supply backups, otherwise known as uninterruptible power supplies (UPS), offer emergency power when a system’s primary power source fails. In these cases, telecommunications, industrial and other electrical equipment can be subject to malfunction or data loss. To successfully provide uninterrupted power, the backup supply must be able to start up reliably and instantaneously – see Figure 3.
High Load Assist
Supplementary systems help maintain a system’s primary energy storage system (ESS). In some cases, like the camera flash on a smartphone, peak lower load is significantly higher for a short period of time. Supercapacitors are ideal secondary sources to handle those power bursts while leveraging a low-power, more cost-effective battery as the primary energy source – see Figure 4.
Hybrid Energy Storage Systems
Some energy storage systems combine supercapacitors with batteries to form hybrid energy storage systems (HESS). These are common in applications like the photovoltaic (PV) microgrids found in homes and neighborhoods. Microgrids are weak electrical grids, so they’re sensitive to load generation changes. A HESS decreases the impact of variations in load – See Figure 5.
As technology continues to evolve, supercapacitors will remain a critical component in meeting the demand for more efficient, reliable and sustainable energy solutions.
Supercapacitors, also known as electric double-layer capacitors (EDLCs), store energy electrostatically rather than chemically. Unlike batteries, they deliver short bursts of power, recharge quickly, and endure many more charge/discharge cycles.
hey are commonly used for backup power in battery-powered devices and to stabilize voltage in circuits with heavy switching currents, protecting memory and sensitive components from voltage drops.
ey applications include real-time clock backup, power failure backup (UPS), high load assist systems such as camera flashes, and hybrid energy storage systems (HESS) in photovoltaic microgrids.
hey provide efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy storage, making them critical for evolving technologies that demand quick response, durability, and hybrid integration with batteries
Using Supercapacitors in Power Management Applications
- Identify the application
Determine whether the need is for backup power, voltage stabilization, high load assist, or hybrid energy storage.
- Select the right supercapacitor
Choose a supercapacitor with suitable power density, voltage rating, and cycle life for the target application.
- Integrate into the circuit
Connect the supercapacitor in parallel with the primary power source to provide backup or peak load support. Ensure proper balancing circuits if multiple capacitors are used.
- Test for performance
Verify that the supercapacitor delivers the required burst power, stabilizes voltage, and supports the system during power interruptions.
- Optimize for long-term reliability
Monitor charge/discharge cycles, ensure thermal stability, and combine with batteries in hybrid systems for maximum efficiency.