Circuit protection components help to keep our electrical systems safe. Learn about different types of circuit protection devices in this article.
Circuit protection components don’t make the systems do more, but keep safe operation of the devices following rules such as IEEE, IEC, and UL standards. These parts go everywhere electricity is used, from the big power lines to the tiny parts inside computers. They stop bad things like static shocks or lightning from breaking the tiny, important parts that run our electronics.
There are two very basic categories of circuit protection depending to what critical electrical parameter to protect from – voltage or current:
- Overvoltage Protection Components
- Overcurrent Protection Components
Overvoltage Protection Components
Zener Diodes: These diodes continue to be a cornerstone in voltage regulation, allowing current flow in both directions when a specific reverse breakdown voltage is surpassed. As connectivity and high-speed data transmission become paramount, Zener diodes remain a robust solution against electrostatic discharge in electronic systems.
Silicon Avalanche Diodes: Characterized by their rapid response and resistance stability, avalanche diodes play a vital role in protecting circuits from harmful high voltages. In the era of IoT and connected devices, their ability to respond swiftly to transient events is paramount.
Thyristors: As power systems evolve to embrace renewable energy and decentralized grids, thyristors continue to act as efficient switches for various applications. Their role in preventing power supply failures and optimizing energy utilization remains pivotal.
Metal Oxide Varistors: Varistors have adapted to the changing landscape, finding applications in wireless handsets, automotive electronic subassemblies and emerging technologies. Their volumetric efficiency and resilience in harsh environments continue to set them apart.
Gas Discharge Tubes: Evolving applications, including cable modems and station class protectors, have invigorated this technology. The ability to mitigate signal distortion in the era of high-definition data transmission remains a valuable trait.
Polymeric ESD Protection: As electronics become increasingly miniaturized and interconnected, polymeric ESD suppressors have risen to the occasion. Their ability to neutralize fast-rising ESD transients without introducing capacitance aligns seamlessly with the demands of modern high-tech systems.
Select voltage protection based on hazard level, frequency of occurrence, and sensitivity of equipment
- Voltage protection will absorb transient energy during abnormal high-voltage conditions.
- Reaction time and energy-handling capability varies based on technology.
- Using multiple technologies together can help maximize features and benefits.
Overcurrent Protection Components
Fuses: play a crucial role in maintaining the safety and reliability of complex, interconnected systems by preventing overcurrent events from damaging critical components.
PTC Thermistors: With the proliferation of electronic systems in diverse applications, PTC thermistors continue to serve as guardians against overcurrent events. Their adaptability in various applications, from inrush current limiting to temperature sensing, reflects their versatility.
NTC Thermistors: In the age of data-driven insights, NTC thermistors have assumed a new role as temperature sensors, enabling precise monitoring and control. Their application in diverse fields, including automotive electronics, highlights their growing importance.
Additional Circuit Protection Devices
Multitude passive components can be used in addition in a function of circuit protection as safeguarding electronics components:
IGBT Snubber Capacitors: Among the unsung heroes are polypropylene plastic dielectric film capacitors, adept at shielding IGBT semiconductors from overvoltage surges. Though targeting a specific niche, this unique capacitor, engineered for overvoltage protection, generates microfarads at elevated voltages, amplifying its utility across diverse scenarios.
X and Y Interference Suppression Safety Capacitors: Polypropylene plastic dielectric film capacitors take center stage for noise suppression in domains spanning lighting, power supply and line voltage circuits—such as the high-voltage landscape of EVx propulsion. Innovations in OPP film within the Japanese realm propels the evolution of this application.
MLCC Ceramic Chip Capacitors: Multilayered ceramic chip capacitors navigate beyond convention to embrace the mantle of circuit protection. Expanding their spectrum, these capacitors integrate variations of ceramic dielectric materials, including barium titanate, to rival chip varistors within ultra-compact case sizes.
SLC X&Y Capacitors: Single-layered ceramic capacitors emerge as formidable contenders for X&Y suppression roles, lauded for their adeptness at managing soaring voltages—a testament to their robust capabilities.
Ferrite Beads: Noise suppression finds a loyal ally in ferrite beads, witnessing significant adoption across the notebook computer and consumer electronics segments, where their presence significantly elevates system integrity.
Inductor Coils: Handsets, notebook computers and kindred devices experience a boost in performance courtesy of ceramic chip coils. Employed for noise suppression, these components epitomize the fusion of innovation and practicality.
Bi-Metallic Switches: The saga of circuit protection expands to encompass bi-metallic switches, instrumental in safeguarding home appliances against inrush currents. The deployment of diverse metal alloys—a trend echoing in fuses, resistors and circuit breaker markets—resonates as a hallmark of adaptability and versatility.
Cable Connectors: Cable connectors offer premium products with built in circuit protection on each power, telecom or data line. These products are vertically integrating components into their product lines to generate added protection and addition premiums.
KEY OVERCURRENT PROTECTION TECHNOLOGIES COMPARISON
| Technology | Key Features and Protection Characteristics | When / Where Typically Used | Surge Energy Rating Range | Typical Voltage Clamping Speeds | Typical Capacitance/ Insertion Loss | Mounting/Size/ Packaging Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fuses | Completely stops current flow, which helps to identify faults; Wide range of options | Ultimate protection for sensitive/ expensive/critical components | Low through Very High | Not applicable | Series impedance measured in nH | Very extensive range of options |
| PPTC Devices | Resettable; No device replacement needed after most common overcurrent events | Where overcurrent events may occur often, and continuous uptime desired | Low through High | Not applicable | Series resistance measured in ohms | Surface Mount, Radial Leaded, Axial Strap |
| Battery Mini-Breakers | Resettable overtemperature and overcurrent protection in high-capacity Lithium-Ion, LiP and prismatic cells | Typically used in overtemperature protection (72°C to 90°C) | Low through High | Not applicable | Not applicable | Axial Strap |
| Battery Protectors | Non-resettable overcurrent and overcharge protection | Protects the Battery Fuel Gauge IC from overcurrent and overvoltage events | Low through High | Not applicable | Not applicable | Surface Mount |
| Protection ICs | Significant flexibility by integrating robust circuit protection, sensing, and control in a single chip | Heavy-use consumer electronics, data communications, and industrial applications | Low through Medium | Fast | Series resistance measured in mohms | Surface Mount |
| Circuit Breakers | Hydraulic-magnetic circuit breakers are considered temperature stable and are not appreciably affected by changes in ambient temperature. Their overcurrent sensing mechanism reacts only to changes of current in the circuit being protected | OE requiring precise overcurrent protection and resettability | Low through High | Not applicable | Series resistance and impedance measured in ohms | Extensive range of options |
KEY OVERVOLTAGE PROTECTION TECHNOLOGIES COMPARISON
| Technology | Key Features and Protection Characteristics | When / Where Typically Used | Surge Energy Rating Range | Typical Voltage Clamping Speeds | Typical Capacitance/ Insertion Loss | Mounting/Size/ Packaging Options |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Layer Varistors (MLVs) | Compact and capable of handling significant surges for their size | ESD and EFT suppression in smaller and portable electronics | Low through Medium | Moderate | High | Miniature Surface Mount |
| Metal-Oxide Varistors (MOVs) | Capable of withstanding very high energy transients; Wide range of options | Appliance, industrial, and very high energy suppression applications | Medium through Very High | Moderate | High | Radial Leaded, Industrial Terminal |
| GDTs | Switches that turn to on state and shunt overvoltage to ground using a contained inert gas as an insulator | Protection of telecom equipment from lightning surges | Medium through High | Fast | Low | Surface Mount, Axial Leaded, 2/3 Lead Radial |
| Polymer ESD Suppressors | Extremely low capacitance; Fast response time; Compact size | ESD suppression; Ultra-fast reaction; Low signal distortion | Low | Moderate | Low | Miniature Surface Mount |
| PLED LED Protectors | Shunt function bypasses open LEDs; ESD and reverse power protection | High brightness outdoor LED lighting applications | Low | Very Fast | Medium | Miniature Surface Mount |
| TVS Diode Arrays | Low capacitance/ low clamping voltage; Compact size | ESD suppression; Low distortion; Ideal for I/O interfaces and digital and analog signal lines | Low through Medium | Very Fast | Low | Extensive range of surface mount options |
| TVS Diodes | Fast response to fast transients; Wide range of options: No wear out mechanism | Semiconductor protection; Telecom I/O interfaces, electronics, industrial equipment, and automotive electronics | Medium through High | Fast | Medium | Axial Leaded, Radial Leaded, Surface Mount |
| Thyristors | Designed to comply with stringent telecom/datacom networking and industrial AC power surge protection standards; No wear out mechanism, precise trigger voltage, and very low Vt | Telecom/datacom and networking applications, industrial equipment | Medium through High | Very Fast | Medium – Low | Extensive range of surface mount and through-hole options |
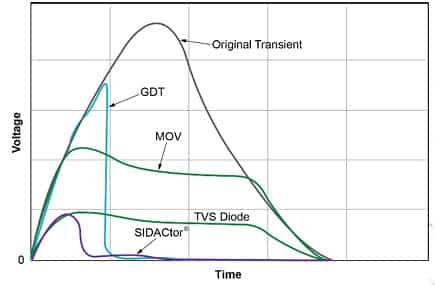
ESD Protection Benchmarking
The figure below compares various circuit protection devices’ capability for ESD protection / high frequency suppression