Source: Microwave and RF news, Knowles Precision Devices
Any engineer knows that capacitors are a fundamental building block in RF/microwave systems. Bypass networks are one example—they require capacitors to bypass ac signals to ground. For such cases, rules-of-thumb or approximate equations can be used to select the best capacitor for the job. However, those approaches may not always be valid. In the technical paper, “Choosing blocking capacitors – it’s more than just values,” Knowles Precision Devices discusses real-world capacitor performance and then presents measurement results of various capacitor bypass networks.
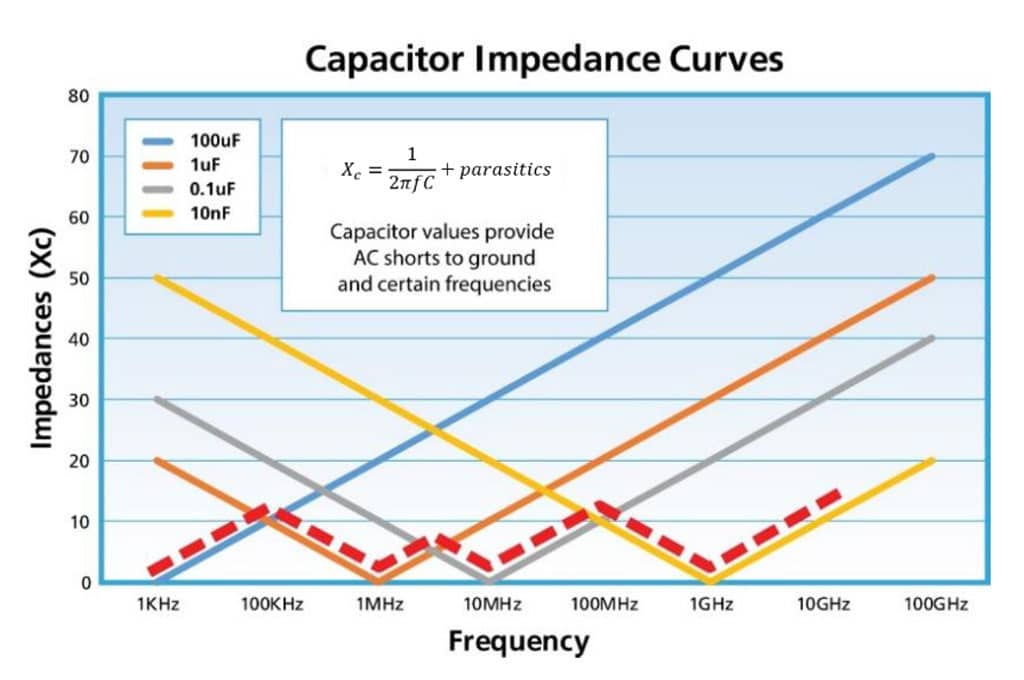
For bypass applications, the paper explains that capacitor values are chosen to provide a low-resistance ground path for unwanted noise signals. It then presents the familiar mathematical expression of capacitor reactance. This equation allows one to determine the theoretical capacitor values needed to provide a low-resistance path to ground for a signal at a given frequency.
In practice, actual capacitors are modeled as a combination of capacitors, inductors, and resistors. A low impedance is realized at a capacitor’s first self-resonant frequency. Above the resonant frequency, the impedance rises as the frequency increases. The paper illustrates this by presenting impedance plots of several capacitors with different values. Furthermore, a common approach to enable broadband RF isolation involves shunting three or four capacitors, each with different values, to ground. Oftentimes, designers employ this method by simply following the recommendations from a manufacturer’s datasheet.
The paper continues by breaking down the parasitic inductance that’s present in a capacitor. It’s noted that increasing a capacitor’s contact pad size can reduce the parasitic inductance. Mention is made of a new manufacturing process that allows for larger pad areas in capacitor footprints without compromising the voltage rating.
Real measurements are shown of the V-Series capacitors, demonstrating how one of them can offer broadband performance that’s typically achieved by bypass networks with multiple capacitors. Additional measurement results compare the performance of a traditional capacitor bypass network with a V-Series capacitor by itself, as well as with a UX-Series capacitor in combination with a V-Series capacitor.
Read more at the technical paper here.