This post based on Knowles Precision Devices blog explains how MLCC ceramic capacitors are used and enable implantable deep brain stimulators (DBS).
A deep brain stimulator (DBS), also known as a neuro-stimulator, is a medical device that uses electrical stimulation to treat neurological disorders such as Parkinson’s disease, essential tremor, dystonia, and obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD).
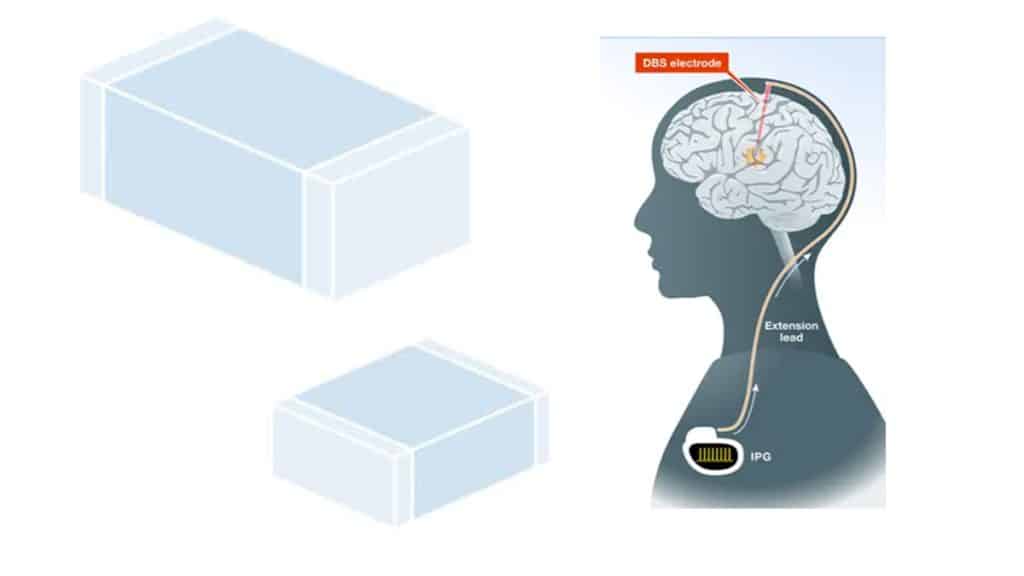
The DBS is typically implanted under the skin near the collarbone or in the abdomen, and connected to a thin wire, or lead, that runs under the skin to the targeted area of the brain as shown in Figure 1.
The Critical Role Capacitors Play in a DBS
Capacitors are essential components in making sure a DBS functions correctly and safely. There are many roles capacitors must serve within the different parts of a DBS including the following:
- Decoupling and Filtering – These capacitors help separate the power supply and other electronic components, preventing interference or crosstalk. Capacitors act as filters by absorbing noise and high-frequency signals, ensuring a clean and stable power supply for the DBS system. Switched capacitors are popular for filter designs because of their extremely accurate frequency response along with good linearity and dynamic range.
- Surge Protection – Capacitors can offer a degree of surge or transient protection in the DBS. They can absorb and dissipate energy spikes or voltage surges that may occur due to external factors such as electrostatic discharge or electromagnetic interference (EMI). This protects the sensitive electronics and prevents damage to or malfunctioning of the DBS.
- Voltage Filtering and Stability – Capacitors help maintain a stable voltage level in the DBS circuitry. They act as filters by smoothing out voltage variations and reducing noise or ripple on the power supply lines. This ensures a consistent and reliable power source for the device, minimizing potential fluctuations that could affect the stimulation output.
- Energy Storage – Capacitors in a DBS are primarily responsible for storing electrical energy. They are charged by the device’s power supply and hold the energy until it is needed to deliver electrical stimulation. When the stimulation pulses are generated, the capacitors discharge their stored energy to produce the required electrical impulses. Flying Capacitors are a good choice for this because through charging and discharging, the charge-pump inverter allows for an inverse voltage to be realized from a stable positive supply.
- Power Delivery – Capacitors enable the delivery of high-current pulses during the stimulation process. As electrical energy is discharged from the capacitors, it flows through the circuit and reaches the electrodes implanted in the brain. The capacitors provide the necessary power for generating electrical pulses that stimulate specific areas of the brain to alleviate symptoms.
DBS Design Challenges that Impact Capacitors Selection
As with any device implanted in the human body, there are a number of design challenges engineers must navigate when selecting any component, including capacitors, for a DBS. One big challenge is the size constraints associated with devices implanted inside the human body. Implantable devices need to be made as unobtrusive as possible, which is why developers are constantly working to further miniaturize these systems.
Additionally, for any electronic device implanted inside the human body, safety is paramount, and these devices must be designed for high reliability and longevity. Patients cannot face risks such as an internal shock resulting from a malfunctioning component or needing to undergo another surgery to replace a component that wore out far too soon.
In general, MLCCs are well-suited for the many capacitor roles required in a DBS, plus they are also capable of addressing the many unique challenges of developing electronic systems for implantable medical devices. The qualities that make MLCCs an excellent fit include the following:
- Compact Size: Can be manufactured in small sizes, allowing them to fit within the space constraints of DBS devices without compromising functionality.
- High Capacitance Values: Can store and release the electrical energy required for effective stimulation in a DBS.
- Low Equivalent Series Resistance (ESR): Can efficiently deliver the required electrical energy to the DBS without significant power loss.
- Wide Voltage Ratings: Can withstand the voltage levels required in DBS applications.
- Fast Charging and Discharging: A high charge and discharge rate is ideal for the rapid and precise stimulation required in DBS therapy.
- Temperature Stability: Ensures reliable performance across a range of environmental conditions, including the human body.
- High Dielectric Strength: Robust dielectric materials provide a high dielectric strength, which ensures the capacitors can withstand voltage stresses without breakdown.
Meeting DBS Design Constraints
Beyond designing MLCCs to include all the qualities discussed above, at Knowles Precision Devices, we also take the time to ensure our MLCCs are ready to meet the reliability and regulatory requirements implantable medical devices face. To do this, we work closely with medical device innovators to create source control drawings (SCD) that govern every aspect of the capacitors we supply. The SCD’s provide an engineering description, qualifications, and acceptance criteria for the delivery of specialized components for critical applications. The two main SCD specifications we follow for medical components are MIL-PRF-55681 and MIL-PRF-1234.