Dennis Zogbi, Paumanok Inc. publishes on TTI Market Eye his mid-year global market and materials update on passive electronic components.
This article highlights passive electronic components leadtimes and material pricing trends.
Mid-Calendar-Year Report Highlights:
- Capacitor, resistor and inductor lead times declined in July 2022, as did key materials prices – especially that of nickel and copper – clearly showing a global economic recession.
- Declines in specific product groupings suggest weakness in the computer, handset and automotive ICE markets.
- Minor positive market activity was noted in infrastructure and mission critical end-markets.
- We expect global improvement in the September 2022 quarter to support the seasonal rate of growth for the holiday electronics build and to support higher variable costs to produce electronic components.
- We view the ongoing data as an attempt for the markets to return to normalcy following back-to-back supply chain issues stemming from the 2019 pandemic.
Capacitors
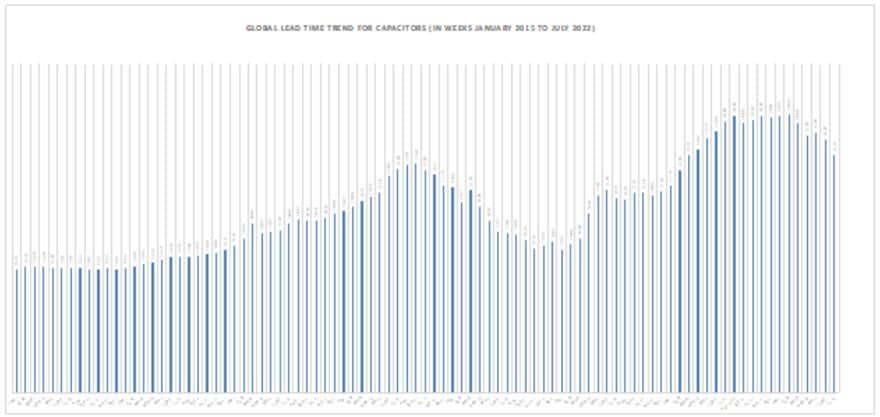
Capacitor lead times and demand declined sharply in July of 2022. Weakness was noted in MLCC, tantalum and plastic film, while aluminum electrolytic capacitors remained somewhat turbulent due to salient issues with materials supply, showing a clear correction in the global capacitor markets for July 2022 (see Figure 1).
MLCC Ceramic Capacitors
MLCC lead times showed weakness again in July of 2022, after a clear slowdown in June 2022. Ultra-small parts such as the 0201, 0402 and 0603 (EIA case sizes) consumed in handsets showed signs of end-market weakness, as did the supply chain for the larger 1206, consumed in computer electronics. Other product types, such as the 0805 and larger 1210 case sizes, remained steady and unchanged on a month-to-month basis. MLCC market demand has remained at elevated levels since a pre-pandemic supply chain shortage rocked the market in 2019 and drove up value in the ceramic supply chain that remained steadfast throughout the turbulence of the pandemic. MLCCs contain four key choke point metals that are impacted by tensions in Eastern Europe. These include nickel, copper, titanium and palladium, which are cornerstone metals supporting ceramic dielectric materials, electrodes and termination ecosystems.
Aluminum Capacitors
Sharp declines in lead times were noted for the SMD V-Chip and radial leaded aluminum electrolytic capacitors in July 2022 related to the supply chain for notebook and desktop computers. Meanwhile, there was an increase in lead times for the large can aluminum capacitors and for the EDLC Supercapacitor. The combined data suggests weakness in the computer channel but strength in the infrastructure channels for power transmission and distribution. The aluminum electrolytic capacitor supply chain has been impacted by additional pressures with the processing of bauxite and alumina impacted by Eastern European tensions creating price disruptions in anode and cathode foil supply. Meanwhile, competition between manufacturers in the Far East has become even more intense as rumors of consolidation fuel the rumor mill in primary intelligence source.
Tantalum Capacitors
Tantalum capacitor lead times showed signs of deep weakening from April 2022 through July of 2022 (to date) as much of the pressure that was on the supply chain to support the global increase in demand for computing devices began to drop off – post Christmas buying season. The parts are largely consumed only in circuits where other capacitors cannot be consumed because of the need for high capacitance, high voltage and small case size. Weakness in the computer markets is suspected.
Plastic Film Capacitors
Lead times for plastic film capacitors stabilized between May and July 2022 on a month-to-month basis but remain elevated. Because of its key use in renewable energy systems, PHEV and EVx propulsion, film capacitors got a boost in the March 2022 and June 2022 quarters and their respective markets remain elevated.
Resistors
In July of 2022 the resistor market showed clear signs of weakening in multiple categories, especially in thick film chip and thin film chip resistors. Resistor network markets and through-hole resistor markets also demonstrated clear month-to-month signs of weakness.
Thick Film Chip Resistors
Thick film chip resistor lead times have declined steadily between May 2022 and July 2022 (to date). The supply chain for ruthenium and alumina were impacted by conflict in Eastern Europe in the earlier par6t of the year, although now there clearly appears to be a recession in demand as lead times decline.
Thin Film Resistors
The thin film chip resistor markets reacted swiftly to the increased nickel price with lead times increasing 10 percent to 15 percent at the end of March 2022 and continuing their extension into April of 2022. However, from May through July 2022, a weakening in the market caused a slowdown impacting the lead times for the ultra-small chips in the 0402, 0603 and 0805 thin film chip case sizes. In July 2022, all thin film chip case sizes showed weakness except for the largest case size parts above 1210, which once again supports a wider shift bin July to support infrastructure spending in Europe.
Resistor Networks
After a significant increase in lead times driven by higher raw material prices for ruthenium and alumina substrates, the resistor network markets began to decline from May through July of 2022, with a steep drop in May and a levelling off in June 2022 as markets return to normal trading levels in July. This product line has been impacted by rising variable cost structure based upon alumina substrate, ruthenium content and large physical case sizes requiring large amounts of raw materials per unit.
Axial and Radial Leaded Resistors
In June and July of 2022, demand for axial and radial leaded resistors, especially those consumed in mission critical applications, stabilized but remained slightly elevated. This was after seeing increases in demand for the month of April as the war in Eastern Europe consumed defense related products that require replenishment and challenge an older type of legacy supply chain.
Inductors
Discrete Inductors
In July of 2022, discrete inductor lead times and demand remained at extremely elevated levels following market wide concerns over consolidation in the supply chain and variable raw materials costs associated with keystone metals that have become choke points due to EU conflict. The markets came back down in June and July following spikes in the markets in April and May 2022. The collective declines for capacitors, resistors and inductors point toward an active global economic recession.
Strong Dollar!
In July 2022 the currency exchange rates for the yen, won and NT dollar weakened as the U.S. dollar strengthened in value quite noticeably for the first time since 2016. The dollar is being viewed as a “safe haven” amidst a growing crisis in Eastern Europe. The spike in yen, won and NT dollar has been noticed in the global financial press and will impact revenue forecasts for fiscal year 2023.
Raw Materials
The raw material price index for passive electronic components relaxed down from May through July 2022 as all keystone metals tracked in the index did an about-face as the world gripped and accepted the reality of an ongoing conflict on the European continent. Metal prices are moving back down after profit taking at key mining operations in the December 2021 quarter, filtering up the supply chain. The China COVID 19 alert in April, May and June had a negative impact on the global recovery. Prices adjusted downward post profit taking.
Cornerstone Metal Trends
These four metals – copper, nickel, silver and palladium – are keystone metals for passive component production worldwide. The charts clearly show these rising costs are at levels that have not been experienced in the monthly histories of each chart and are therefore creating new levels of costs as they filter up the supply chain. In July, all of these metals experienced a severe decline in value, signalling the collective push-back of a wider economic event.
The aluminum price was clearly affected by the conflict in Eastern Europe, as Russia is a key smelter in the supply chain. The ruthenium price reacted upward as well, as ruthenium is a by-product of platinum mining, which will be impacted by a shortage of palladium. The zinc price also reacted upward. Tantalum, however, with limited ties to Eastern Europe, showed a slight uptick in price. All keystone materials consumed in passive electronic components reacted to the conflict in Europe by increasing, with aluminum directly affected and also showing increased lead times further up the chain.
Summary and Conclusions
The data suggests that the global market for passive components is in clear recession in July of 2022 but remains at elevated levels in terms of comparable dollar value to prior years and cycles due to hyper-inflation. Components and supporting materials markets are in the process of correcting in July 2022 as the global markets seek supply chain parity and harmony of past cycles as illustrated in Figures 1, 2 and 3 of this Special MarketEYE Report.