Würth Elektronik has introduced a new partner program designed to formalize and scale collaboration with key players around its passive components and related technologies.
The multi‑tier structure and defined support pillars aim to give design houses, semiconductor vendors and system integrators a clearer framework for co‑developing solutions and bringing designs to market faster.
Key features and benefits
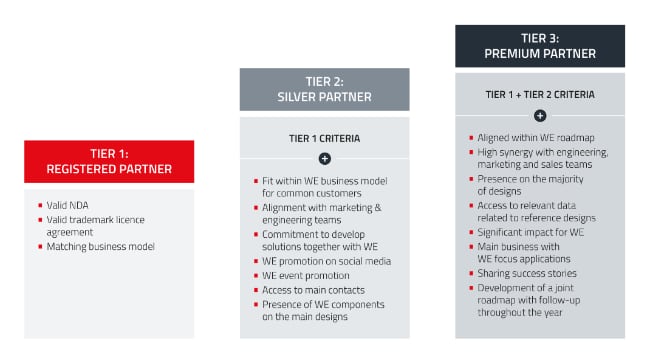
The Würth Elektronik partner program is built around a three‑tier model (Entry Level, Silver, Premium) that reflects the depth of cooperation between the partner and Würth Elektronik. The intent is to provide a transparent path from initial technical collaboration up to strategic, co‑branded platforms.
Key characteristics include:
- Entry based on low administrative overhead, typically requiring a non‑disclosure agreement, basic brand licensing, and a defined business model.
- Progression criteria that look beyond volume, focusing on brand commitment, shared growth objectives, and the extent to which Würth Elektronik components are integrated into the partner’s designs.
- Clear differentiation between Entry Level, Silver and Premium tiers, so engineering and purchasing teams understand what kind of support they can expect from the relationship.
- A focus on passive components and related technologies that directly affect EMC behavior, power integrity, signal integrity and robustness of end systems.
For engineering organizations, this means better access to reference designs, joint validation and support when choosing inductors, capacitors, filters and protection elements around complex ICs or modules. For purchasing and supply chain, a formalized partnership can translate into earlier visibility on roadmaps and more stable sourcing options.
Four support pillars
To make the tiers meaningful in practice, the partner program is structured around four main support pillars:
- Technical support: direct access to field application engineers and product specialists for design reviews, component selection, EMC optimization and troubleshooting in real projects.
- Products and tools: preferential access to samples, evaluation boards, design kits and software tools (for example, component selection and simulation tools) to accelerate design‑in of Würth Elektronik components.
- Marketing support: coordinated activities such as joint press releases, co‑branded reference platforms, whitepapers, webinars and trade‑fair presence to promote combined solutions.
- Knowledge transfer and training: targeted workshops, training sessions and documentation to keep engineering teams up to date on new passive component series, application notes, layout recommendations and standards.
For companies working on power supplies, automotive ECUs, RF front ends or industrial control, these pillars can significantly reduce the risk and effort of integrating new passive components or transitioning to new series.
Typical partners and use cases
The first public partner examples provide a good indication of the program’s target audience. Texas Instruments has been presented as a Premium Partner, reflecting deep cooperation between a major analog/mixed‑signal semiconductor supplier and a passive component specialist. This is particularly relevant for power management, signal conditioning, data conversion and RF designs where component interoperability and reference designs are critical.
Nexperia, a global semiconductor manufacturer, has joined as a Silver Partner, underlining the program’s fit for companies that provide discrete devices, logic, MOSFETs or power ICs and want to align their ecosystems with proven inductors, capacitors, ferrites and protection components. Typical use cases include:
- Power supply reference designs where semiconductor vendors recommend Würth Elektronik magnetics, capacitors and filters as baseline BOM options.
- Automotive and industrial platforms where partners coordinate qualification levels, derating recommendations and layout examples around safety‑relevant and high‑reliability applications.
- RF, wireless and IoT designs where antenna matching components, EMI suppression elements and DC/DC converter magnetics are co‑validated with specific chipsets.
Technical highlights of the program concept
There are several technical implications that are relevant for engineers:
- Early access to new series and technologies: partners can typically evaluate upcoming inductors, capacitors, EMI filters or surge protection components in pre‑release phases, allowing design‑in before public release, according to the respective manufacturer datasheets.
- Reference designs and simulation models: coordinated development between IC vendors and Würth Elektronik often results in reference designs with validated passive BOMs, complete with inductor and capacitor models, EMC test data and layout recommendations.
- System‑level optimization: instead of selecting passive components in isolation, partners can work on system‑level targets such as efficiency, conducted/radiated emissions, thermal behavior and long‑term reliability, and select component values and packages accordingly.
- Standards‑aligned design: training and joint work can help ensure that component choices support compliance with relevant EMC, safety and automotive standards, as specified in the underlying datasheets and reference designs.
For teams designing power stages, converters or high‑speed digital interfaces, these aspects can significantly shorten the iteration loop between simulations, prototypes and compliance testing.
For practicing design engineers, a structured partner program has several practical consequences when working with passive components:
- Better alignment between IC datasheets and passive component recommendations: when a semiconductor vendor is an official partner, its reference designs are more likely to feature up‑to‑date Würth Elektronik components with realistic derating, footprint and thermal guidance.
- Faster root cause analysis: with closer ties between the semiconductor and passive component suppliers, cross‑vendor debug of EMI issues, stability problems, saturation behavior or resonance effects can be more efficient.
- Reduced qualification effort: where partners coordinate on qualification and reliability aspects, engineers can sometimes benefit from pre‑qualified BOM combinations for specific sectors (for example, industrial or automotive) according to the latest datasheet information.
- More consistent lifecycle planning: a partner relationship can improve transparency on lifecycle status, second‑source options at series‑level and long‑term supply expectations, important for long‑lived industrial and automotive platforms.
Source
This article is based on information published by Würth Elektronik about the launch of its partner program.