source: Schurter application note
A thermal runaway is an increasing threat to electronic devices where more and more power is packed in ever smaller spaces; it is a threat that is poorly dealt with using traditional means. SMD thermal fuses offer a solution that can be reflow-soldered at 260°C and still open at 210°C.
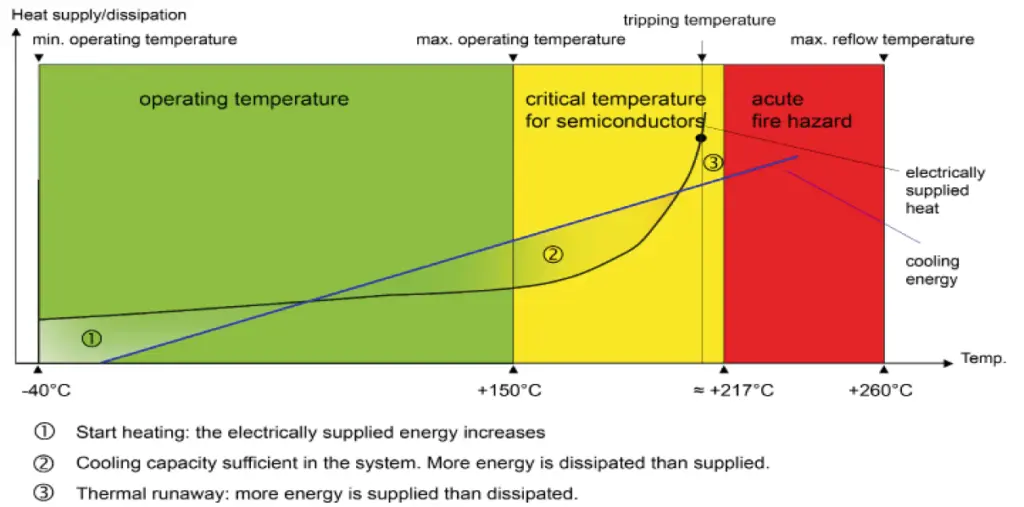
What is meant by a thermal runaway or the thermal damage of power semiconductors: A thermal runaway refers to the overheating of a technical apparatus due to a self-reinforcing process that
generates heat. This damage usually causes the destruction of the apparatus and often leads to a fire or explosion.
Causes
The causes of a thermal runaway are varied and often random in nature. However, the ever-higher power density in electronic wiring and the trend towards miniaturization are without a doubt of
particular importance. More and more functions are packed in compact modules, which then also have a correspondingly high power consumption. Even slightly excessive currents in power electronics with only a little power loss lead to elevated temperatures of approximately 200°C.
The possible consequences: damage or disconnection of surrounding components, damage to the printed circuit board structure or, in the worst case, the triggering of a fire.
Build up
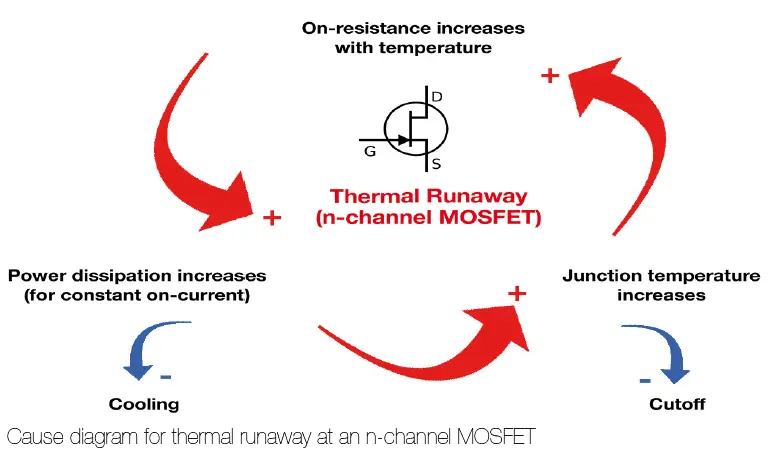
With a power semiconductor (e.g. MOSFET) the drain-source transmission resistance increases with rising temperatures, when connected, which results in an increasing loss of power
in the barrier layer. If the elements are not sufficiently cooled – the high power density permits cooling – the power loss output in the form of heat can no longer be sufficiently dissipated, which also increases the transmission resistance. This process escalates and ultimately leads to destruction of the component.