Not graphene: researchers in Germany and Finland discover new type of atomically thin carbon material with metallic properties that is different to semiconductor-like behaviour of graphene. This discovery may lead to development of new electronic components or enhancement in battery technologies.
Carbon exists in various forms. In addition to diamond and graphite, there are recently discovered forms with astonishing properties. For example graphene, with a thickness of just one atomic layer, is the thinnest known material, and its unusual properties make it an extremely exciting candidate for applications like future electronics and high-tech engineering. In graphene, each carbon atom is linked to three neighbours, forming hexagons arranged in a honeycomb network. Theoretical studies have shown that carbon atoms can also arrange in other flat network patterns, while still binding to three neighbours, but none of these predicted networks had been realized until now.
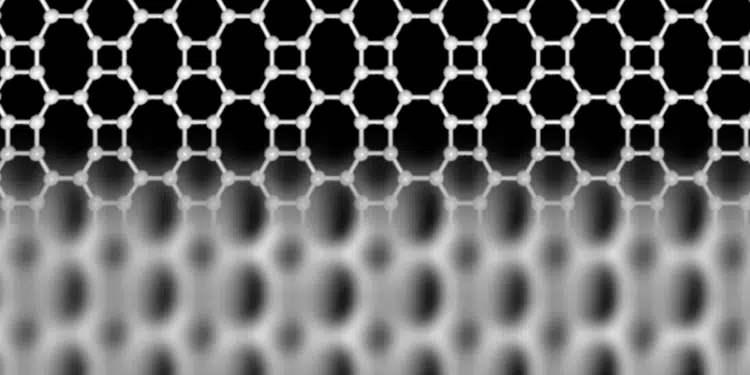
Researchers at the University of Marburg in Germany and Aalto University in Finland have now discovered a new carbon network, which is atomically thin like graphene, but is made up of squares, hexagons, and octagons forming an ordered lattice. They confirmed the unique structure of the network using high-resolution scanning probe microscopy and interestingly found that its electronic properties are very different from those of graphene.
In contrast to graphene and other forms of carbon, the new Biphenylene network — as the new material is named —has metallic properties. Narrow stripes of the network, only 21 atoms wide, already behave like a metal, while graphene is a semiconductor at this size. “These stripes could be used as conducting wires in future carbon-based electronic devices.” said professor Michael Gottfried, at University of Marburg, who leads the team that developed the idea. The lead author of the study, Qitang Fan from Marburg continues, “This novel carbon network may also serve as a superior anode material in lithium-ion batteries, with a larger lithium storage capacity compared to that of the current graphene-based materials.”
The team at Aalto University helped image the material and decipher its properties. The group of Professor Peter Liljeroth carried out the high-resolution microscopy that showed the structure of the material, while researchers led by Professor Adam Foster used computer simulations and analysis to understand the exciting electrical properties of the material.
The new material is made by assembling carbon-containing molecules on an extremely smooth gold surface. These molecules first form chains, which consist of linked hexagons, and a subsequent reaction connects these chains together to form the squares and octagons. An important feature of the chains is that they are chiral, which means that they exist in two mirroring types, like left and right hands. Only chains of the same type aggregate on the gold surface, forming well-ordered assemblies, before they connect. This is critical for the formation of the new carbon material, because the reaction between two different types of chains leads only to graphene. “The new idea is to use molecular precursors that are tweaked to yield biphenylene instead of graphene” explains Linghao Yan, who carried out the high-resolution microscopy experiments at Aalto University.
For now, the teams work to produce larger sheets of the material, so that its application potential can be further explored. However, “We are confident that this new synthesis method will lead to the discovery of other novel carbon networks.” said Professor Liljeroth.
Original publication: Q.T. Fan, L.H. Yan, M.W. Tripp, O. Krejči, S. Dimosthenous, S.R. Kachel, M.Y. Chen, A.S. Foster, U. Koert, P. Liljeroth, J.M. Gottfried, Biphenylene Network: A Nonbenzenoid Carbon Allotrope, Science 372, (2021). https://science.sciencemag.org/content/372/6544/852