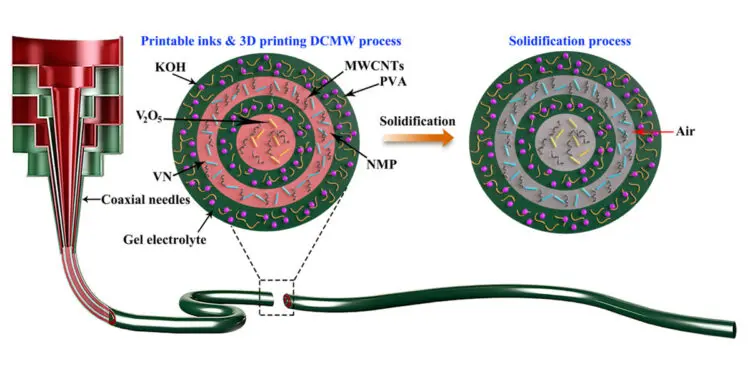
Coaxial fiber-shaped supercapacitors with short charge carrier diffusion paths are highly desirable as high-performance energy storage devices for wearable electronics. However, the traditional approaches based on the multistep fabrication processes for constructing the fiber-shaped energy device still encounter persistent restrictions in fabrication procedure, scalability, and mechanical durability. To overcome this critical challenge, a team of scientists based in China, the U.S. and Singapore realized an all-in-one coaxial fiber-shaped asymmetric supercapacitor (FASC) device by a direct coherent multi-ink writing three-dimensional printing technology via designing the internal structure of the coaxial needles and regulating the rheological property and the feed rates of the multi-ink.
Benefitting from the compact coaxial structure, the FASC device delivers a superior areal energy/power density at a high mass loading, and outstanding mechanical stability. As a conceptual exhibition for system integration, the FASC device is integrated with mechanical units and pressure sensor to realize high-performance self-powered mechanical devices and monitoring systems, respectively.
Advanced fibrous energy storage devices with excellent knittability, flexibility and high mechanical stability allow the development of advanced textile-based wearable electronics. For this, Fibre-shaped Asymmetric Supercapacitors (FASCs) have been widely used in wearable electronics, which have high-power density, long cycling stability, good reversibility and energy density features.
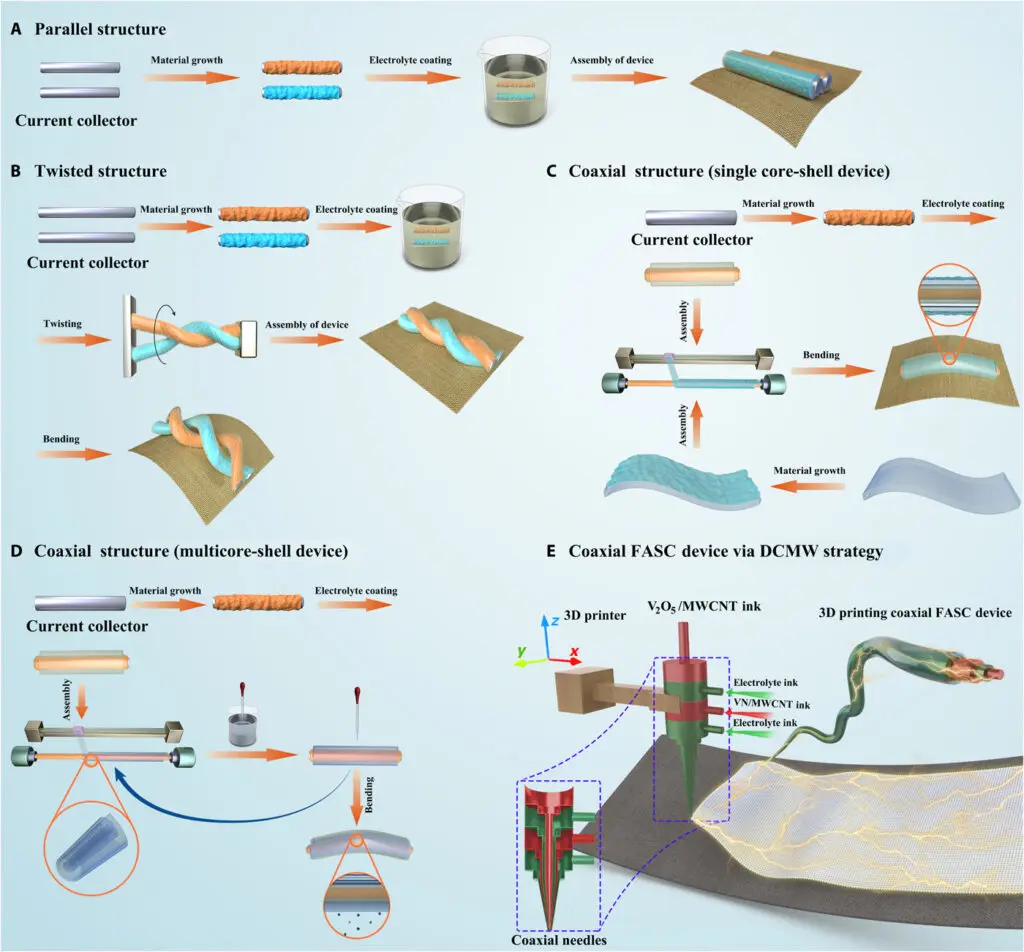
However, they are not ideal for electron transfer and ion diffusion because of their larger spacing between two electrodes. Additionally, they have a massive volume structure, posing a serious challenge for the large-scale integration process. Although FASC with shorter charge carrier paths can improve device performance, they suffer from the separation of negative/positive electrodes when a device is bent.
To overcome the above challenges, a team of scientists based in China, the U.S. and Singapore has developed an all-in-one coaxial FASC device with compact internal structures using 3D printing direct ink writing technology. The asymmetric supercapacitors were obtained using different electrode inks/electrolytes since the traditional direct ink writing technology is based on single-ink printing, which can only write one electrode at one time.
Impressively, the device exhibited great flexibility with capacitance retention of 95.5 per cent after 5000 cycles of repetitive bending, which is better than traditional coaxial (87.1 per cent) or twisted (78.2 per cent) asymmetric supercapacitors.
To demonstrate the feasibility of powering electronic devices, a fully charged 3D printed coaxial FASC device in the shape of a dragon was used for illuminating a 1.5-V red LED. Moreover, two 3D printed coaxial FASC devices in series can illuminate a 3.0-V blue LED.
Self-powered systems with energy storage
To obtain a device with high energy density that can drive a mechanical unit, a chip-based FASC device was constructed by realising the 3D printed coaxial FASC device in series. The chip-based FASC devices charged by a solar cell were able to drive an electric motor for continuous rotation.
To test the endurance of a self-powered system, an electric car was actuated with and without the chip-based FASC devices. t resulted in the electric car with solar cell run a short distance because of the lack of external energy supply. In contrast, the electric car with the solar cell and the chip-based FASC devices ran a longer distance, demonstrating enhanced durability for future application in self-powered electric vehicles. Similarly, sightseeing cable cars with a self-powered system demonstrate faster running speed than that with solar cell only.
People usually monitor their health status using sensors, which need to be charged or replaced frequently. Therefore, the self-energy monitoring system can solve the aforementioned problem. To investigate the sensing capability of the pressure sensor, the pressure sensor was attached to the wrist and fingertip of an adult tester and the response signals were detected before and after exercise. The results depicted that both the big and small signals can be monitored, indicating excellent pressure-sensing performance. Thus, an all-in-one coaxial solid-state FASC device with high energy density will become a prospective candidate to be used in more new fields such as artificial intelligence, robotics and sensing.