source: nanotechweb news
Could the inductor be redesigned in a fundamentally new way? Yes, according to new work by researchers in the US, Japan and China who have made the first high-performance inductors from intercalated graphene that work in the 10-50 GHz range thanks to the mechanism of kinetic inductance – rather than magnetic inductance as in conventional devices.
The new inductors, which have both small form-factors and high inductance values, of around 1-2 nanoHenry (a combination that has been difficult to obtain so far), are a third smaller in terms of surface area than conventional devices but with the same performance. They might thus be used in ultra-compact wireless communication systems for applications in the Internet of Things (IoT), sensing and energy storage/transfer.
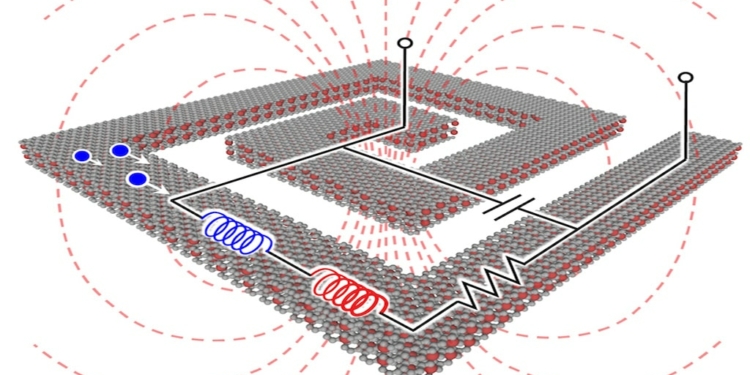
featured image: A spiral inductor and its simplified equivalent circuit
“The inductor was invented nearly 200 years ago, but this is the first time since then that a completely new mechanism (kinetic inductance) is being exploited (using intercalated graphene) to re-invent this fundamental passive device,” team leader Kaustav Banerjee of the University of California, Santa Barbara, tells nanotechweb.org. “This could have significant implications for wireless communications, sensing and energy storage/transfer applications for the IoT era. It also highlights a practical application for graphene beyond circuit interconnects.”
The IoT promises to connect us with as many as 50 billion objects by 2020, with a potential impact of $2.7 to 6.2 trillion per year by 2025. This revolution will require an enormous number of miniaturized, high-performance and scalable wireless connections that are driven by radio-frequency (RF) integrated circuits (RF-ICs). Another important area, that of radio-frequency identification (RF-ID), which relies on electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects, is predicted to increase to nearly $19 billion by 2026.
Planar on-chip metal inductors are the main types of device employed in RF-ICs and can take up as much as half of the chip area space. They are also responsible for the major part of the form factor of RF-IDs.
Scaling down difficult for on-chip inductors
However, the problem is that, unlike transistors and interconnects in IC technology that have been successfully scaled down, the same cannot be said for on-chip inductors. This is because inductors have been traditionally designed to work using magnetic fields alone, so a certain amount of inductor area is needed to capture these fields. What is more, conventional metals only have a small kinetic inductance because of their low momentum relaxation time (which is the average time for a carrier – an electron or hole – to lose its original momentum because of a scattering event).
To scale down inductors, we need to improve their inductance density. This is defined by the inductance per unit area = total inductance (Ltotal)/inductor area, where Ltotal is the sum of the magnetic inductance (LM) and the kinetic inductance (LK).
Kinetic inductance is a purely material property
Magnetic inductance is the property of an electrical conductor by which a change in current through it induces an electromotive force in both the conductor itself (self-inductance) and in any nearby conductors (mutual inductance) that opposes the change. Kinetic inductance, for its part, is the inertial mass of mobile charge carriers in alternating electric fields and so does not rely on the magnetic field.
All this means that the magnetic inductance depends on the geometrical design of the inductor itself, while the kinetic inductance is a purely material property, says Banerjee. Improving both the LM and LK should thus improve the overall inductance density, which is our goal.
Carbon nanomaterials to the rescue
Banerjee and colleagues recently found that carbon materials, including carbon nanotube bundles and multilayer graphene, are attractive materials for on-chip inductors thanks to their high magnetic inductance and high LK, which can be equal or even greater than the magnetic inductance. “We can thus use these materials to now scale down the on-chip inductor size without compromising their inductance values.”
In this work, the researchers started out with millimeter-sized multi-layer graphene sample transferred to isolating substrates that they intercalation doped with bromine.
Layer separation increases the kinetic inductance
“Intercalation involves inserting ‘guest’ molecules between the two other ‘host’ molecules in multilayered structures, which in this case are bromine and MLG respectively,” explains Banerjee. “This intercalation introduces two important properties in the MLG. First, and perhaps most crucially, it increases the separation between the adjacent graphene layers. This increase has the effect of ‘decoupling’ these layers and thereby increases the kinetic inductance by increasing the momentum relaxation time.”
Thanks to its linear electronic band structure, monolayer graphene typically has a significantly larger momentum relaxation time compared to its multi-layer counterpart. In fact, interlayer coupling in MLG transforms the linear band structure of the monolayers to hyperbolic, which leads to lower momentum relaxation times and thus lower kinetic inductance.
A new working mechanism for inductors
“Secondly, intercalation dopes the MLG and increases its electrical conductivity, which helps in improving its performance (or Q-factor).”
The work could revolutionize the way we make on chip inductors employed in analogue/RF ICs for wireless communications, and highlights a new working mechanism for these devices, he says. “Such inductors are set to become crucial in the near future where billions of connected IoT devices will send and receive huge quantities of information to each other in applications such as continuous monitoring of vital health signs and security, and also provide unprecedented connectivity for living a smarter life.”
The team, which includes researchers from the Shibaura Institute of Technology in Tokyo and Shanghai Jiao Tong University, is now busy looking into ways to further improve the efficiency of the intercalation process so that the kinetic inductance can be further increased. “This would in turn increase the inductance density and could help further downscale on-chip inductors and thus improve the area-efficiency of the chip as well as its Q-factor,” explains Banerjee. “We are also trying to make the entire inductor fabrication process compatible with back-end-of-line CMOS technology.”
Full details of the research are reported in Nature Electronics doi:10.1038/s41928-017-0010-z.
About the author
Belle Dumé is contributing editor at nanotechweb.org