source: Energy Harvesting Journal article
Nearly a century after it was theorized, Harvard scientists report they have succeeded in creating the rarest material on the planet, which could eventually develop into one of its most valuable.
Thomas D. Cabot Professor of the Natural Sciences Isaac Silvera and postdoctoral fellow Ranga Dias have long sought the material, called atomic metallic hydrogen. In addition to helping scientists answer some fundamental questions about the nature of matter, the material is theorized to have a wide range of applications, including as a room-temperature superconductor. Their research is described in a paper published today in Science.
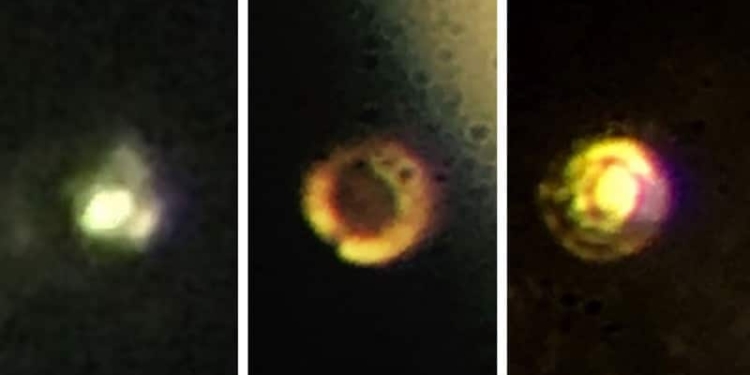
“This is the Holy Grail of high-pressure physics,” Silvera said of the quest to find the material. “It’s the first-ever sample of metallic hydrogen on Earth, so when you’re looking at it, you’re looking at something that’s never existed before.”
In their experiments, Silvera and Dias squeezed a tiny hydrogen sample at 495 gigapascal (GPa), or more than 71.7 million pounds per square inch, which is greater than the pressure at the center of the Earth. At such extreme pressures, Silvera explained, solid molecular hydrogen, which consists of molecules on the lattice sites of the solid, breaks down, and the tightly bound molecules dissociate to transforms into atomic hydrogen, which is a metal. While the work creates an important window into understanding the general properties of hydrogen, it also offers tantalizing hints at potentially revolutionary new materials.
“One prediction that’s very important is metallic hydrogen is predicted to be meta-stable,” Silvera said. “That means if you take the pressure off, it will stay metallic, similar to the way diamonds form from graphite under intense heat and pressure, but remain diamonds when that pressure and heat are removed.” Understanding whether the material is stable is important, Silvera said, because predictions suggest metallic hydrogen could act as a superconductor at room temperatures. “As much as 15 percent of energy is lost to dissipation during transmission,” he said, “so if you could make wires from this material and use them in the electrical grid, it could change that story.” A room temperature superconductor, Dias said, could change our transportation system, making magnetic levitation of high-speed trains possible, as well as making electric cars more efficient and improving the performance of many electronic devices. The material could also provide major improvements in energy production and storage. Because superconductors have zero resistance, superconducting coils could be used to store excess energy, which could then be used whenever it is needed.
Metallic hydrogen could also play a key role in helping humans explore the far reaches of space, as a more powerful rocket propellant. “It takes a tremendous amount of energy to make metallic hydrogen,” Silvera explained. “And if you convert it back to molecular hydrogen, all that energy is released, so that would make it the most powerful rocket propellant known to man, and could revolutionize rocketry.” The most powerful fuels in use today are characterized by a “specific impulse” (a measure, in seconds, of how fast a propellant is fired from the back of a rocket) of 450 seconds. The specific impulse for metallic hydrogen, by comparison, is theorized to be 1,700 seconds. “That would easily allow you to explore the outer planets,” Silvera said. “We would be able to put rockets into orbit with only one stage, versus two, and could send up larger payloads, so it could be very important.”
In their experiments, Silvera and Dias turned to one of the hardest materials on Earth, diamond. But rather than natural diamond, Silvera and Dias used two small pieces of carefully polished synthetic diamond and treated them to make them even tougher. Then they mounted them opposite each other in a device known as a diamond anvil cell.
“Diamonds are polished with diamond powder, and that can gouge out carbon from the surface,” Silvera said. “When we looked at the diamond using atomic force microscopy, we found defects, which could cause it to weaken and break.” The solution, he said, was to use a reactive ion etching process to shave a tiny layer — just five microns thick, or about a tenth the thickness of a human hair — from the diamond’s surface. The diamond was then coated with a thin layer of alumina to prevent the hydrogen from diffusing into the crystal structure and embrittling it. After more than four decades of work on metallic hydrogen, and nearly a century after it was first theorized, it was thrilling to see the results, Silvera said. “It was really exciting,” he said. “Ranga was running the experiment, and we thought we might get there, but when he called me and said, ‘The sample is shining,’ I went running down there, and it was metallic hydrogen.” “I immediately said we have to make the measurements to confirm it, so we rearranged the lab … and that’s what we did.”
Source and top image: Harvard University