Source: All3DP article
3D printed electronic components and circuits are becoming a reality. Find out how the process is being used to produce basic electronic components, circuitry, and printed circuit boards and the most advanced companies.
1. Nano Dimension and Harris Corp: 3D Printed Circuit Boards
Using a specialized 3D printer, Harris Corporation, a leading communications company, has successfully created 3D printed radio frequency (RF) electronics in-house. Their printer, a Dragonfly Pro 2020, comes from Nano Dimension, a leading additive electronics provider.
Initial testing indicated that the performance of 3D printed RF printed circuit boards (PCB) is comparable to that of conventionally manufactured circuits. The results will be presented by Harris at the upcoming IEEE Radio and Wireless Symposium.
The Present
One of the printed items is a circuit board that will be used to make RF amplifiers. This PCB also features an integrated 3D printed antenna. Amit Dror, CEO of Nano Dimension, explains that this breakthrough facilitates faster prototyping while lowering research and development costs. This allows for creating more proofs-of-concept for testing.
There are also product-specific advantages. 3D printing the PCBs makes it possible to develop smaller and lighter antennas and circuitry. Packaging is also made simpler thanks to flexible circuits and fewer cables and connectors.
The Future
Nano Dimension has already received funding to further develop 3D printed electronics, or so-called 3DPE. In collaboration with Harris Corp, they will be working to demonstrate the 3D printing of double-sided circuit boards and multi-layer circuits. The intention is to reduce size, weight, power, and costs of circuits that distribute digital, power, and RF signals for Harris’ communications systems used in space.
Dr. Arthur C. Paolella, of Harris Corp., said, “The ability to manufacture RF systems in-house offers an exciting new means for rapid and affordable prototyping and volume manufacturing.” He went on to explain that the results of the study provided substantial motivation for further development of 3D printed electronics.
3D Printed Electronics – Most Advanced Companies 2. Optomec: Aerosol Jet Technology

New-Mexico-based Optomec is a leading manufacturer and distributor of electronics 3D printers. They’ve developed an Aerosol-Jet-based 3D printing technology that’s capable of printing interconnects, traces, and even passive and active components on 2D and 3D substrates. They claim to have successfully printed resistors, capacitors, antennas, sensors, and thin film transistors.
The Aerosol Jet 3D printing process allows Optomec’s electronics printers to print on a wide variety of substrates, including plastics, ceramics, and metallic structures. They’re also capable of printing onto complex geometries. Using this process, they’ve 3D printed conformal antennas directly onto mobile device enclosures, reducing the complexity, parts count, and cost of these devices.
Optomec also has plans to become very involved in the Internet of Things (IoT). For such “smart connected devices”, there is an inherent need for sensors and antennas. Optomec’s process allows for rapid design and prototyping of IoT devices meeting these requirements, providing a solution for a wide variety of IoT applications. The company says their process can reduce manufacturing steps, associated costs, and provide a wider range of material possibilities.
3D Printed Electronics – Most Advanced Companies 3. UC Berkley: Microelectronics and Wireless Sensors
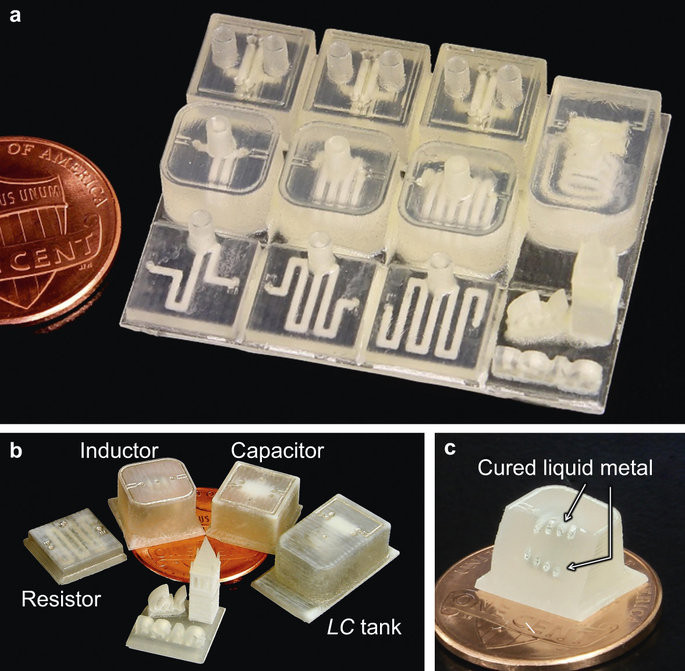
UC Berkley engineers and colleagues have been working on systems to 3D print microelectronics circuitry. In their paper “3D-printed microelectronics for integrated circuitry and passive wireless sensors“, they discuss how this is possible.
The team has reported successfully 3D printing passive microelectronics components including resistors, capacitors, and inductors, as well as circuits and passive wireless sensors. They even produced a miniaturized .53-GHz transmitter, which also acts as a wireless sensor. These specialized wireless sensors have been shown to be effective as quality control components in the liquid foods industry (e.g. milk and juice).
The structures are created using FDM technology, a multiple-nozzle system, and a printing resolution of 30 μm. After removing the support structures from the printed objects, a silver-based suspension is injected and solidified to form components and interconnects.
One possible consumer application is what the team is calling the “Smart Cap“, as in the cap on your milk or juice carton. Their liquid food carton cap, with integrated wireless sensor, can report content freshness.

3D printed smart cap. Source: Berkeley news
3D Printed Electronics – Most Advanced Companies 4. Duke University: Conductive Thermoplastic Materials
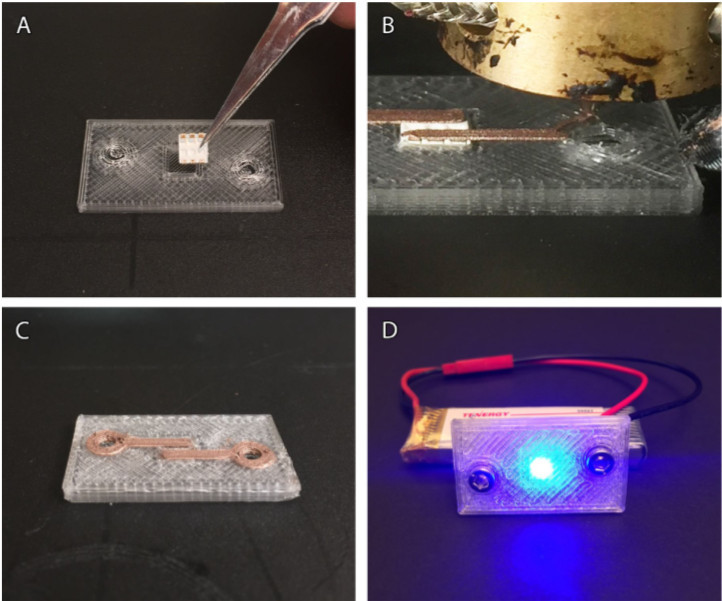
Engineers at Duke University are working on 3D printed electronic components using dual-material FDM technology. Their focus is on conductive thermoplastic 3D printing filaments infused with graphene, carbon-black, and copper.
According to their paper “3D printing electronic components and circuits with conductive thermoplastic filament“, they have achieved some very positive results. The team has produced 3D printed resistors with values spanning three orders of magnitude.
While the graphene and carbon-black materials have proven to be somewhat brittle, the copper-infused filament is much more resilient. 3D printed copper components and printed circuit board traces can be bent over 500 times with no breakage or change in resistance values. This makes the 3D printing of resilient flexible circuits and components a definite possibility.
They also showed that copper-infused thermoplastic filaments could produce impedances similar to standard copper printed circuit board traces at frequencies greater than 1 MHz, a prerequisite for RF applications.
Their capacitors and inductors are predictably tunable through modification of device geometry and selection of print material. The components are used to create a functional high-pass filter with characteristics comparable to conventional counterparts.
3D Printed Electronics – Most Advanced Companies 5. Adham Rabah: DIY PCBs
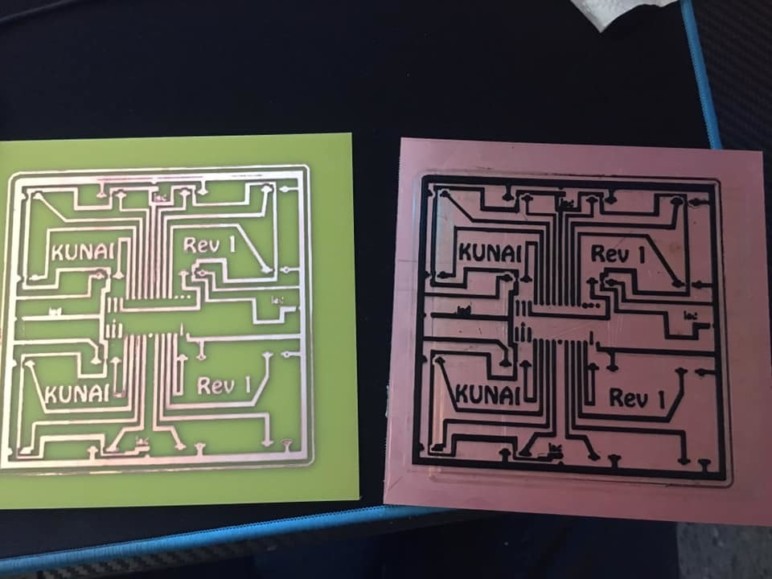
This project falls outside the realms of industry and research but says a lot about the future of 3D printed electronics. It seems that 3D printed electronics is already leaking into hobbyist and maker spaces. One example is Adham Rabah’s 3D printed PCBs, which he produced using a DIY 3D printer.
Adham explains that it took him many attempts over a year-long period to come up with a reliable method. He tried many different printing materials, build surface adhesion agents, and slicer configurations in order to find a combination that worked.
Using a hybrid method that incorporates new and old processes, Adham creates PCBs from standard copper-clad phenolic board. In the meantime, he makes copper-clad boards for PCB etching using standard PLA filament. Normally this would require several additional steps, but in this case, they’re replaced by a 3D printer.
The first step is to create an acetate mask of the circuit. Simply creating the mask requires several steps as well. Then you must project the acetate image, using UV light, onto a special photo-sensitive copper-clad board. This has to be done in an otherwise UV-free environment. Additionally, the photo-sensitive board can be significantly more expensive than the standard board used in Adham’s method. This makes his method less time-consuming and less expensive. A great combination for more economic rapid electronics prototyping at the maker level. Maker innovation for the win!