Source: Kyocera news
Kyocera’s ultra-high frequency (UHF) RFID transponders are applicable on metal and – due to their ceramic packages – suitable for sterilization processes of surgical instruments in hospitals involving high temperatures, humidity and chemical exposure.
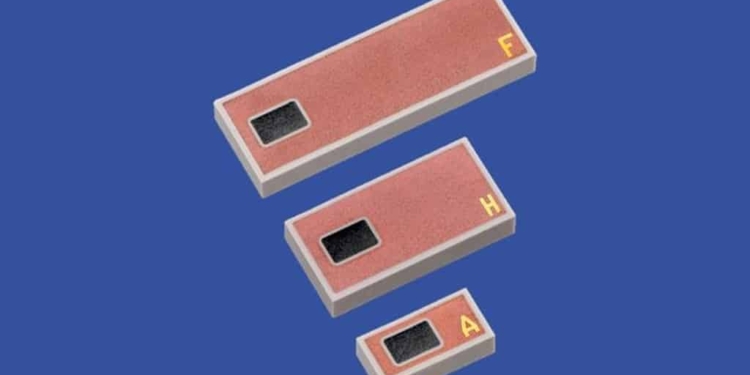
Kyoto/London – Kyocera offers small and robust UHF RFID tags consisting of ceramic packages with a proprietary multilayer structure including a built-in RFID antenna that can increase the read range up to 2X as compared with conventional tags of the same size. In addition, Kyocera has successfully developed a new ultra-small tag with a size of 5 x 2 x 1.5 mm, meaning a further reduction in the tag volume of almost 50 % when compared to the tag with a size of 3 x 6 x 1.7 mm.
The new product offers a robust package made of Low Temperature Co-fired Ceramic (LTCC) with embedded antenna that withstands high temperatures up to 300°C (depending on RFID tag structure) and humidity levels up to 85 %. Additionally, the ceramic package is designed with a special cavity structure to protect the IC chip against mechanical stress and chemical exposure.
Additionally, Kyocera’s UHF RFID tag has a unique antenna design which differentiates itself from conventional tags. The proprietary multilayer structure of the antenna results in an increased read range in combination with a miniaturized ultra-small tag size. The RFID tags offer a superior reading distance in regard to their small size, so that a reading distance of 0.4 m can be achieved with a tag of the size of 5 x 2 x 1.5 mm (when applied on metal).
![]()
![]()
ceramic RFID tag construction, image credit: Kyocera
Kyocera offers four different sizes of the robust UHF RFID tag; the smallest UHF RFID tag offering an ultra-small design of only 5 x 2 x 1.5 mm:
| Dimensions*1 | 5 x 2 x 1,5 mm | 6 x 3 x 1,7 mm | 10 x 5 x 1,7 mm | 15 x 5 x 1,7 mm | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Read Range |
250 mW | 10 cm | 10 cm | 25 cm | 35 cm |
| 1 W | 40 cm | 60 cm | 120 cm | 180 cm | |
| IC type | Monza R6-P | Monza 4QT | Monza 4QT | Monza 4QT | |
| Connection | Flip-Chip | Wire-Bonding | Wire-Bonding | Wire-Bonding | |
| EPC memory | 128 bits | 128 bits | 128 bits | 128 bits | |
| User memory | 32 bits | 512 bits | 512 bits | 512 bits | |
| Note | Possible to use on metal | ||||
RFID for the Medical Industry
With the new European Medical Device Regulation (MDR) coming into force, a new law regarding consistent traceability of surgical tools is currently introduced to Europe. The related worldwide system to assign a unique identifier to medical devices, called Unique Device Identification (UDI), will take effect from beginning of May 2021 for high risk products. In case of direct marking on the product, UDI will take effect from May 2023.
Besides the fact, that the new EU legislation fosters new ways of marking surgical instruments in the medical area, traceability of surgical instruments in general is gaining more and more importance. In an operation theatre, every surgical instrument has to be counted before and after an operation, in order to prevent those surgical instruments will be left behind in the body of a patient after treatment. According to a report from the UK National Reporting and Learning System, between the time period from 1st April 2007 to 31st March 2008, 496 patient incidents involving retained sponges and instruments, were reported.*2
In order to avoid retained instruments, Kyocera’s robust ceramic UHF RFID tags are suitable for identification and tracking of instruments. RFID tags will be attached to surgical instruments in order to stay on the instrument for the entire instrument lifetime. The attached tag will withstand operations and sterilization processes without negative impact on the reading performance due to the robust ceramic package of the RFID tag.
Additionally, RFID technology does not require line-of-sight scanning in contrast to barcode labels or direct marking technology. Through RFID tagging, multiple surgical instruments will be identified at a once through bulk reading, so that surgical instruments do not have to be counted manually by hospital staff anymore. The surgical instrument check in an operation theatre can be done faster and hospitals can save time and costs by automatically identify surgical instruments. Due to the fact that no line-of-sight scanning of RFID is required, it is also possible to read RFID tags regardless of an instrument’s condition (e.g. in case that the instrument is contaminated during operation).
The new robust and ultra-small ceramic UHF RFID tags of Kyocera open up new fields of applications which involve on-metal placement, high temperatures and require a small tag size.
*1 Customized designs can be provided upon request for individual customer requirements.
*2 D. Hariharan. D. Lobo. “Retained surgical sponges, needles and instruments” Publication of The Royal College of Surgeons of England (2013): https://publishing.rcseng.ac.uk/doi/10.1308/003588413X13511609957218