source: ECN article
Tue, 12/22/2015 – 12:07pm by American Institute of Physics
Carbon nanotubes are legendary in their strength—at least 30 times stronger than bullet-stopping Kevlar by some estimates. When mixed with lightweight polymers such as plastics and epoxy resins, the tiny tubes reinforce the material, like the rebar in a block of concrete, promising lightweight and strong materials for airplanes, spaceships, cars and even sports equipment.
While such carbon nanotube-polymer nanocomposites have attracted enormous interest from the materials research community, a group of scientists now has evidence that a different nanotube—made from boron nitride—could offer even more strength per unit of weight. They publish their results in the journal Applied Physics Letters.
Boron nitride, like carbon, can form single-atom-thick sheets that are rolled into cylinders to create nanotubes. By themselves boron nitride nanotubes are almost as strong as carbon nanotubes, but their real advantage in a composite material comes from the way they stick strongly to the polymer.
“The weakest link in these nanocomposites is the interface between the polymer and the nanotubes,” said Changhong Ke, an associate professor in the mechanical engineering department at the State University of New York at Binghamton. If you break a composite, the nanotubes left sticking out have clean surfaces, as opposed to having chunks of polymer still stuck to them. The clean break indicates that the connection between the tubes and the polymer fails, Ke noted.
Plucking Nanotubes
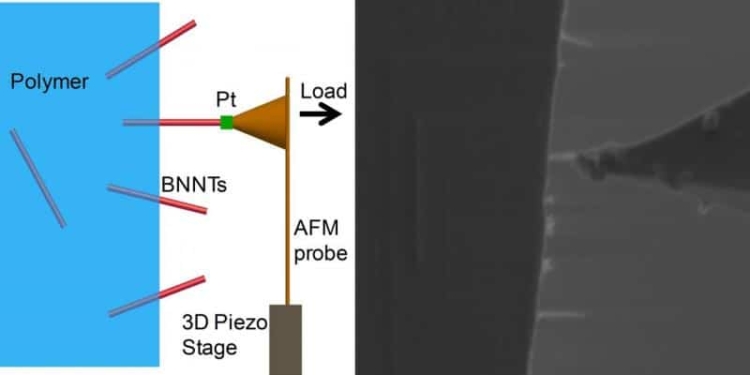
Ke and his colleagues devised a novel way to test the strength of the nanotube-polymer link. They sandwiched boron nitride nanotubes between two thin layers of polymer, with some of the nanotubes left sticking out. They selected only the tubes that were sticking straight out of the polymer, and then welded the nanotube to the tip of a tiny cantilever beam. The team applied a force on the beam and tugged increasingly harder on the nanotube until it was ripped free of the polymer.
The researchers found that the force required to pluck out a nanotube at first increased with the nanotube length, but then plateaued. The behavior is a sign that the connection between the nanotube and the polymer is failing through a crack that forms and then spreads, Ke said.
The researchers tested two forms of polymer: epoxy and poly(methyl methacrylate), or PMMA, which is the same material used for Plexiglas. They found that the epoxy-boron nitride nanotube interface was stronger than the PMMA-nanotube interface. They also found that both polymer-boron nitride nanotube binding strengths were higher than those reported for carbon nanotubes—35 percent higher for the PMMA interface and approximately 20 percent higher for the epoxy interface.
The Advantages of Boron Nitride Nanotubes
Boron nitride nanotubes likely bind more strongly to polymers because of the way the electrons are arranged in the molecules, Ke explained. In carbon nanotubes, all carbon atoms have equal charges in their nucleus, so the atoms share electrons equally. In boron nitride, the nitrogen atom has more protons than the boron atom, so it hogs more of the electrons in the bond. The unequal charge distribution leads to a stronger attraction between the boron nitride and the polymer molecules, as verified by molecular dynamics simulations performed by Ke’s colleagues in Dr. Xianqiao Wang’s group at the University of Georgia.
Boron nitride nanotubes also have additional advantages over carbon nanotubes, Ke said. They are more stable at high temperatures and they can better absorb neutron radiation, both advantageous properties in the extreme environment of outer space. In addition, boron nitride nanotubes are piezoelectric, which means they can generate an electric charge when stretched. This property means the material offers energy harvesting as well as sensing and actuation capabilities.
The main drawback to boron nitride nanotubes is the cost. Currently they sell for about $1,000 per gram, compared to the $10-20 per gram for carbon nanotubes, Ke said. He is optimistic that the price will come down, though, noting that carbon nanotubes were similarly expensive when they were first developed.
“I think boron nitride nanotubes are the future for making polymer composites for the aerospace industry,” he said.
featured picture: Researchers tested the force required to pluck a boron nitride nanotube (BNNT) from a polymer by welding a cantilever to the nanotube and pulling. The experimental set-up is shown in a schematic on the left and an actual image on the right. Credit: Changhong Ke/State University of New York at Binghamton