NICHICON CORPORATION has developed the SLB Series of small lithium-titanate rechargeable batteries for use in the Internet of Things (IoT) market. The SLB Series has an increased temperature range, as well as a much larger lifespan than other rechargeable batteries, with over 25,000 charge/discharge cycles.
The Internet of Things (IoT) is a term that describes the increasingly sophisticated ecosystems of online connected devices that we share our world with. IoT devices are used in all types of industrial and consumer markets with currently millions of devices, this will double in the next few years according to the current trend.
IoT is a trend that is driving the ongoing digitization and datafication of the whole industry and society. Remote medical devices that let doctors diagnose patients and carry out surgery, self-driving cars and autonomous manufacturing robots are all possible due to these networks of connected things. One of the challenges that IoT devices face is the need for reliable and sustainable power sources.
Many IoT devices are small, portable, or embedded in hard-to-reach places, which makes it difficult to replace or recharge their batteries frequently. Therefore, there is a growing demand for rechargeable batteries that are capable of low rate charging, increased cycle life as well as useable at very low temperatures. Low rate charging allows power being sourced via renewable energy such as sunlight, wind, or any means of kinetic energy – typically known as energy harvesting.
Energy Harvesting
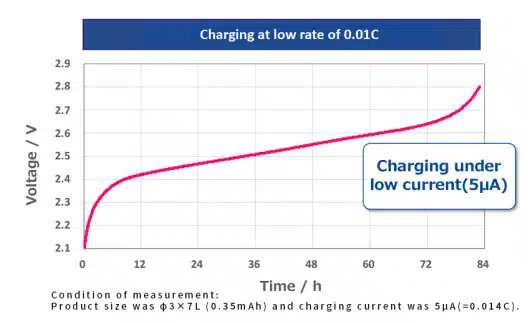
Energy harvesting is a technology that allows IoT devices to be powered from ambient sources such as indoor/outdoor light, RF, heat or vibration. Nichicon has developed its new radial Li-Ion SLB battery, achieving maintenance-free operation of IoT devices to reduce battery disposals and aim to improve life cycle assessment (LCA). One key feature is the very low internal resistance which enables a very low rate of charging (i.e. 5µA = 0.014C / 0.35mAh, 3x7L mm]). See Figure 1.
Indoor light harvesting requires low rate charging, for which Nichicon has been partnering with solar cell manufacturers such as Exeger to optimise clean and environmental friendly harvesting and energy harvesting under low levels of light. Typical harvesting solutions include wearables, maintenance-free electronic shelf-labels (ESL), CO2 and ambient sensors as well as Industrial IoT (I-IoT) devices.
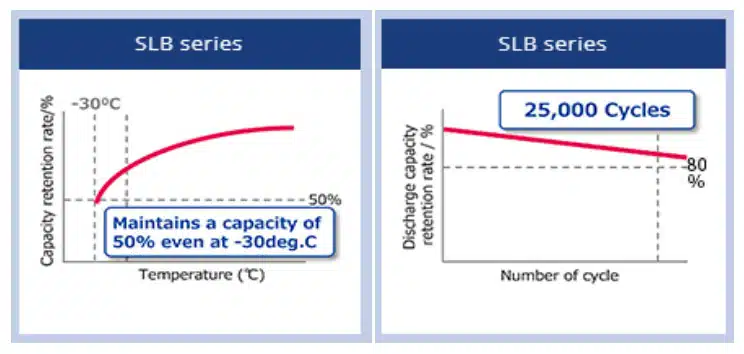
Due to the increased demand for environmental sensing and independent real-time localization devices (RTLS), Nichicon ensures continuous charging and discharging even under harsh conditions. Another key feature is the capability to operate at minus temperatures as low as -30°C. At this temperature, Nichicon SLB batteries can still maintain 50% of its original capacity – see Figure 2.
Safety
The safety of the battery is crucial for many industrial applications and depends on several factors, such as the chemistry, design, manufacturing, and usage of the battery.
Some of the common hazards associated with batteries are overheating, short-circuiting, fire, and explosion.
The SLB batteries are designed to prevent leakage, explosion and fire hazards under severe environmental conditions, crushing and nail penetration.
The SLB batteries also comply to UN38.3 requirements for safe transportation.
Maintenance-free Energy harvesting Demo Board with E-Peas PMIC and Nichicon SLB battery:
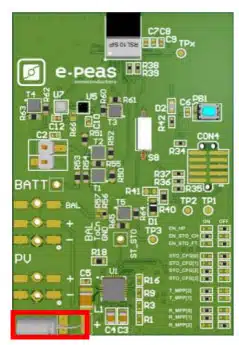
The E-peas evaluation board 4AAEM00190010 using the smallest SLB battery storage from Nichicon is one example of how a Nichicon SLB and an efficient PMIC works perfectly together. It can achieve unparalleled performance of continuous operation (up to 3 months under dark conditions and remains operating through harvesting energy) while sending temperature, pressure and tri-axis accelerometer data via BLE transmission. This is achieved with the smallest available Nichicon SLB03070LR35 (0.35mAh, D3x7L mm, inside the red rectangle on the picture in Figure 4.).
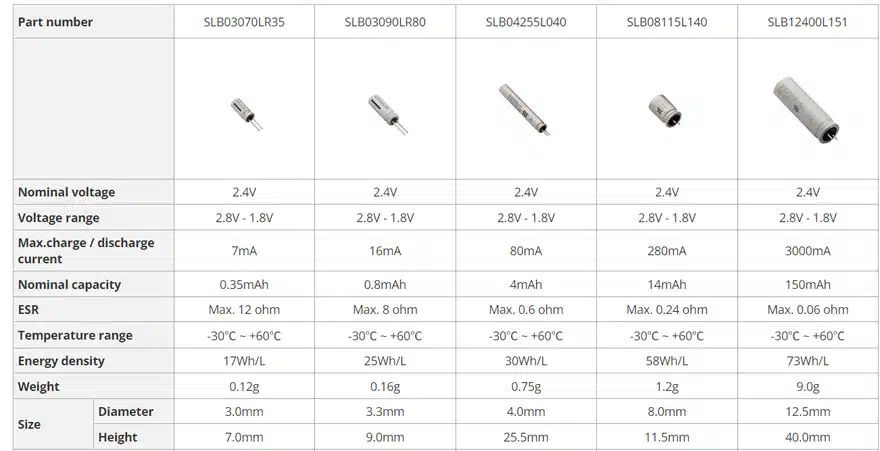
Main Specifications
- Rated Voltage : 2.4V
- Maximum charging voltage : 2.8V
- Discharge cut-off voltage : 1.8V
- Rated Capacity : 0.35mAh to 150mAh
- Category Temperature range : -30°C to +60°C
- Maximum current : 20C (Continuous)
- Product dimensions : φ3 × 7L (mm) to φ12.5 × 40L (mm)
- Life : 25,000 charge/discharge cycles
- Terminal shape : Lead typ