by DOE/Argonne National Laboratory, original written by Jared Sagoff. Researchers have created a permanent static ‘negative capacitor,’ a device believed to have been in violation of physical laws until about a decade ago. Newly devised static negative capacitor could improve computing and yield more energy-efficient computers.
With a little physics ingenuity, scientists have designed a way to redistribute electricity on a small scale, potentially opening new avenues of research into more energy-efficient computing.
In a new study, researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory, together with collaborators in France and Russia, have created a permanent static “negative capacitor,” a device thought to have been in violation of physical laws until about a decade ago.
“The objective is to be able to get electricity where it is needed while using as little as possible in a controlled static regime.” — Argonne materials scientist Valerii Vinokur
While previously proposed designs for negative capacitors worked on a temporary, transient basis, the new Argonne-developed negative capacitor concept works as a steady-state, reversible device.
The researchers found that by pairing a negative capacitor in series with a positive capacitor, they could locally increase the voltage on the positive capacitor to a point higher than the total system voltage. In this way, they could distribute electricity to regions of a circuit requiring higher voltage while operating the entire circuit at lower voltage.
“The objective is to get electricity where it is needed while using as little as possible in a controlled, static regime,” said Argonne materials scientist Valerii Vinokur, the corresponding author of the study.
In traditional capacitors, the electric voltage of the capacitor is proportional to their stored electrical charge — increasing the amount of stored charge increases the voltage. In negative capacitors, the opposite happens — increasing the amount of charge decreases the voltage. Because the negative capacitor is a part of the larger circuit, this does not violate conservation of energy.
“One way you can think about it is like having a refrigerator,” said University of Picardie (France) scientist Igor Lukyanchuk, the first author of the paper. “Inside the refrigerator, of course, it is much colder than the outside environment, but that is because we are heating up the rest of the environment by expending energy to cool the refrigerator.”
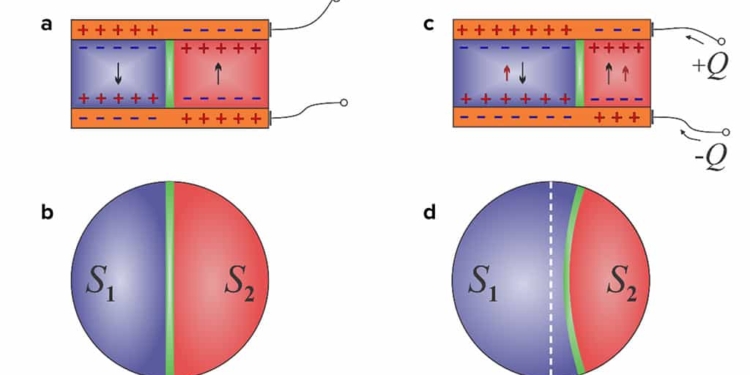
A prime component of the negative capacitor put forward by Vinokur and his colleagues involves a filling made of a ferroelectric material, which is similar to a magnet except that it has an internal electric polarization, rather than a magnetic orientation.
“In a ferroelectric nanoparticle, on one surface you will have a positive charge, and at the other surface you will have negative charges,” Vinokur said. “This creates electric fields that try to depolarize the material.”
By splitting a nanoparticle into two equal ferroelectric domains of opposite polarization, separated by a boundary called a domain wall, Vinokur and his colleagues were able to minimize the effect of the total depolarizing electric field. Then, by adding charge to one of the ferroelectric domains, the researchers shifted the position of the domain wall between them.
Because of the cylindrical nature of the nanoparticle, the domain wall began to shrink, causing it to displace beyond the new electric equilibrium point. “Essentially, you can think of the domain wall like a fully extended spring,” said Lukyanchuk. “When the domain wall displaces to one side because of the charge imbalance, the spring relaxes, and the released elastic energy propels it further than expected. This effect creates the static negative capacitance.”
An article based on the study, “Harnessing ferroelectric domains for negative capacitance,” appeared in the February 26 online edition of Communications Physics. Authors of the study also include Anaïs Sené of the University of Picardie, and Yuri Tikhonov and Anna Razumnaya of the Southern Federal University (Russia).
The research at Argonne was funded by the DOE’s Office of Science. Research at the collaborating institutions was funded by the European Commission’s HORIZON 2020 initiative.
Journal Reference:
I. Luk’yanchuk, Y. Tikhonov, A. Sené, A. Razumnaya, V. M. Vinokur. Harnessing ferroelectric domains for negative capacitance. Communications Physics, 2019; 2 (1) DOI: 10.1038/s42005-019-0121-0
featured image: shows the movement of the domain wall (a-c and b-d) in a capacitor when a charge is added to one side (c). The resulting redistribution of the domain wall causes a negative capacitive effect. Credit: Argonne National Laboratory