This article written by Wataru Muraoka, KYOCERA-AVX Corporation explains properties and characteristics of crystal units.
Numerous devices in people‘s lives today are becoming more sophisticated. As a result, the number of crystal devices installed is increasing.
For example, with the evolution of autonomous driving, we are using crystal devices for many functions such as sensor systems to detect distance, camera systems to capture images, image processing systems to process captured images, and communication systems to communicate many of those digital data in and out of the vehicle at high speed.
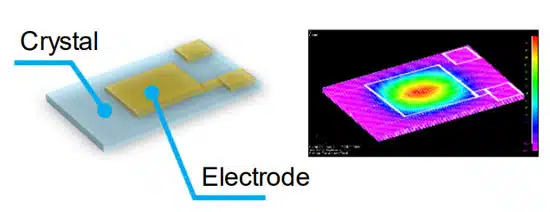
Crystal Units are a piezoelectric element which produces electricity on the surface when mechanical pressure is applied, and when electricity is applied it vibrates in a certain manner. A Crystal Unit is a product that utilizes this piezoelectric effect.
In addition, in the network market, the number of crystal devices is increasing along with the further increase in the speed of communication devices, as
well as the increase in the frequency and precision. This paper describes KYOCERA AVX’s technology for Crystal Units, one of its crystal device products.
What are Crystal Units?
Crystal Unit is a piezoelectric element which produces electricity on the surface when mechanical pressure is applied, and when electricity is applied
it vibrates in a certain manner. A Crystal Unit is a product that utilizes this piezoelectric effect.
Figure 1. shows the overall image, and Figure 2 shows the vibration mode.
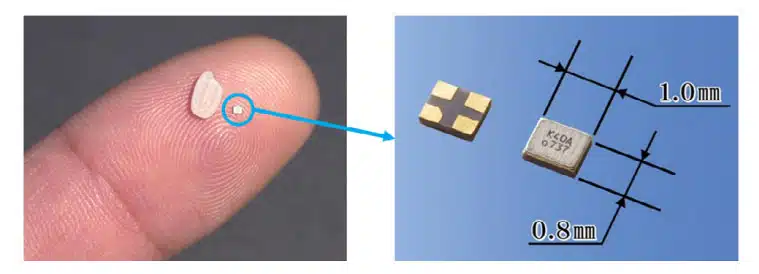
Frequency is dependent on Crystal thickness, the thinner it gets the higher the frequency. Our technology development is targeted for thinner and smaller products. Due to our own unique technology which are CVM technology and photolithography, we have realized the world’s smallest Crystal Unit in 1008 size shown in Figure 3.
From here we will explain regarding increased reliability in the junction.
Due to the difference ceramic package and customer’s board, when the component is mounted on a board residual stress remains in the junction, which may lead to solder cracks as shown in Figure 4.
In order to improve the above, the pitch between the terminations have been shortened and termination area has been enlarged as shown in Figure 5.
Ceramic package and the glass epoxy board are electrically connected with solder. The improved junction reliability is one of the main features of this product.
Miniaturization of Crystal Units
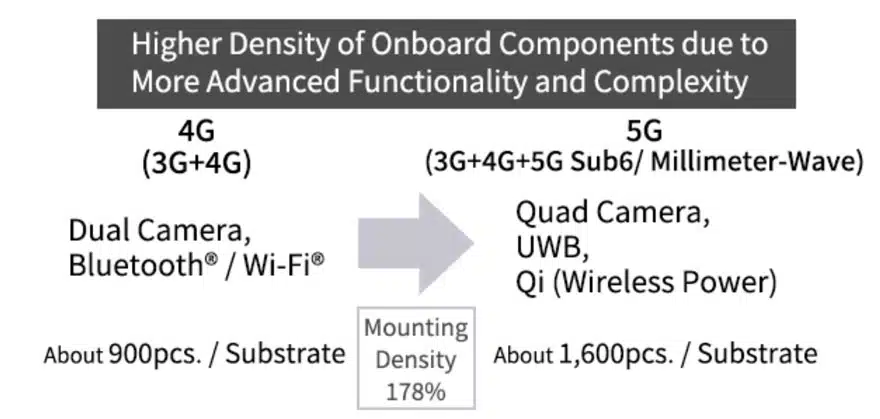
In recent years, the mounting density of electronic devices has increased due to the increasing number of functions of communication terminals for 5G communications, faster Wi-Fi®, and the electrification of onboard components.
In addition, due to the limited space available in the mounting area, the size of mounted components is becoming smaller. Among them, Kyocera developed excellent photolithography and ultra-high precision machining technology jointly with Osaka University, and we have succeeded in mass producing an ultra-small crystal unit, the CX1008SB Series.
If the size is reduced from the conventional size of 1.2 x 1.0mm to 1.0 x 0.8mm, the series resistance value (CI value) will increase by about 30%. To avoid
this, it was necessary to review the circuit design of the substrate on which the crystal is mounted.
Therefore, by optimizing the design of the crystal device using Kyocera’s proprietary piezoelectric analysis technology, Kyocera achieved a size as small as 1.0 x 0.8mm while also achieving electrical characteristics equivalent to 1.2 x 1.0 mm (Kyocera’s CX1210 Series). This made it possible to use the circuit on the board without making changes.
Plasma CVM Machining
With conventional machining accuracy, when a crystal device is miniaturized there is a problem that variations in electrical characteristics become large. Kyocera has resolved this problem with its ultra-high precision machining technology which Kyocera developed in collaboration with Osaka University.
This technology is a processing method that uses neutral radicals in plasma and chemical reactions on the surface of the workpiece, enabling precise control of crystal thickness and surface conditions. This has resulted in a successful reduction in frequency fluctuation.
Plasma is radiated to crystal wafers in atmospheric pressure, triggering a chemical reaction with neutral radicals to realize equal wafer thickness.