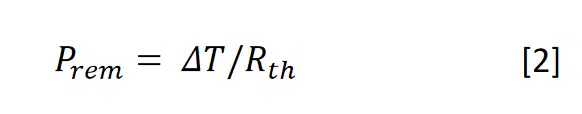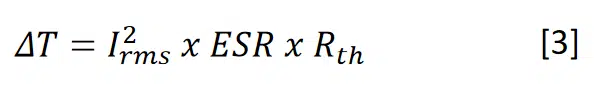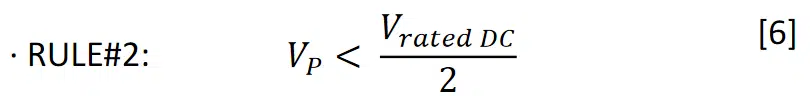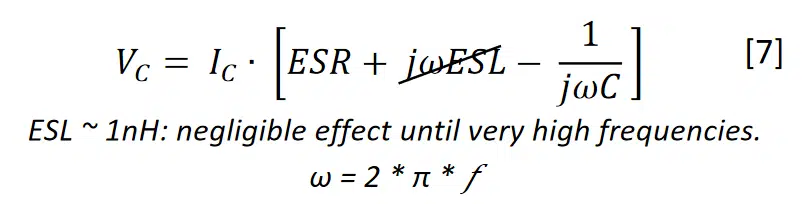When talking about ripple current in capacitors, terms like ESR, overheating, lifetime and reliability cannot be out of the conversation. Choosing the correct solution by considering the ripple current of the application could prevent shorter component lifetime. See Kemet Technical paper that explains the basic principles.
WHAT IS RIPPLE CURRENT?
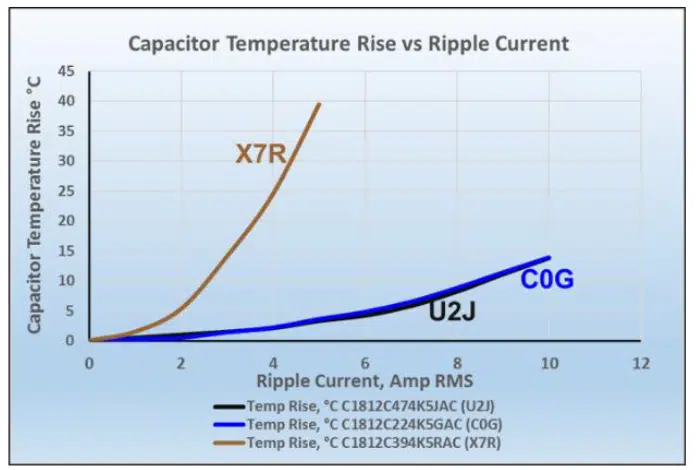
Ripple current is the AC current that enters and leaves the capacitor during its operation in a circuit.
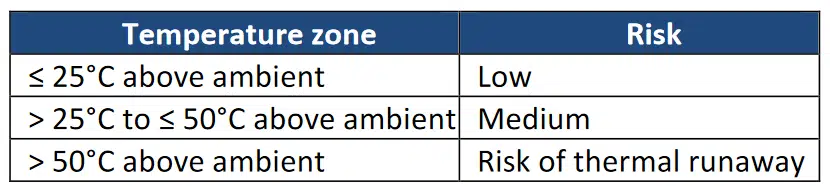
Ripple current generates heat and increase the temperature of the capacitor. This rate of heat generation in a capacitor can be described by using the common power formula:
HEAT AND RIPPLE CURRENT RELATION
As there is a heat generation, there is also a rate of heat removal (Prem) from the capacitor:
At steady state Pdis = Prem, so:
It is important to mention that is influenced by factors as MLCC design, ambient temperature, PCB characteristics, circuit design, pads, trace thickness, etc.
AC VOLTAGE CONSIDERATIONS
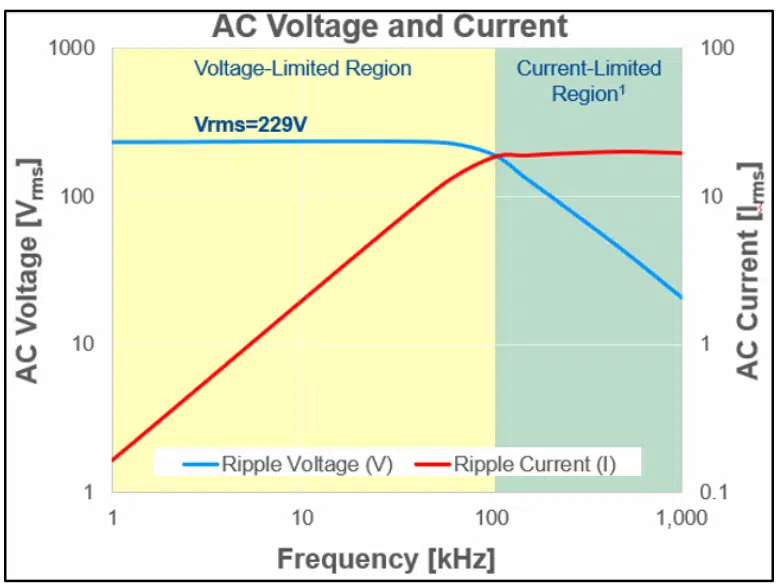
MLCCs normally rated at DC voltages still can be used in AC applications, but there are some considerations since DC ≠ AC (e.g. 100 VDC ≠ 100 VAC):
- Heating due to losses (Current limited region)
- High AC voltages (Voltage limited region)
Heating due to I2R losses (Current limited region)
If the voltage is known, this equation can be used to calculate the AC current by following the conventional RLC equivalent circuit and capacitor parameters:
If AC Voltage is held constant, higher frequencies, as well as higher capacitance, result in higher AC currents, even with low AC voltages.
Power can be calculated by using equation [3] with capacitor and application parameters, in order to determine if the chosen MLCC is suitable for it.
High AC Voltages (Voltage limited region)
Figure 2 shows that at lower frequencies no more voltage is allowed, and the reason is that the amount of power dissipated is not high enough to overcome the following two rules for max voltage allowed for an MLCC.
Even if ripple current does not cause excessive heating, peak AC voltage (vp) needs to be considered.
Vp from AC waveform plus the DC voltage must be less than the rated DC voltage of the MLCC.
Vp from AC waveform must be less than the rated DC voltage of the MLCC divided by two.
Then, if the current is known, the AC voltage can be calculated by the following formula:
If AC Current is held constant, lower frequencies, as well as lower capacitance, results in higher AC voltages.
EXTERNAL FACTORS AFFECTING CURRENT
AC Current not only depends on the losses, but also:
- Ambient temperature.
- Thermal characteristics of PCB.
- Active/passive cooling of the MLCC.
- Proximity of the part to other sources of heat.
FINAL RECOMMENDATIONS
When working with high ripple current, recommended MLCCs are Class I dielectrics which have a higher ripple current capability, compared against Class II. If more capability is needed, stacking capacitor solution as KEMET KC-LINK™ which is a Class I 150°C, could be an option.
This last technology is also available merged with KONNEKT™ Technology, that stacked in low loss orientation offers even a higher ripple current capability.