SLCs vs. MLCCs – when such ceramic capacitor construction type fits better to my application? Knowledge Precision Devices blog posted by Victor Lu highlights specific benefits of these individual types.
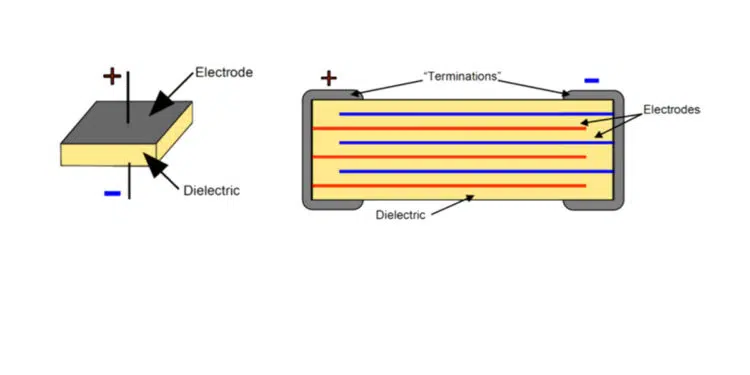
At a high-level, these capacitor types seem similar as both SLCs and MLCCs can be used for charging and storing, filtering, or bypass functions in a circuit. To determine which one is the best fit for your application, let’s first look at the basic structure of each capacitor type. SLCs are the most basic capacitor type available since these capacitors consist of a single layer of dielectric material, or insulating layer, sandwiched between a positive and a negative electrode.
An MLCC uses the basic principle of this capacitor design to build multiple layers in the same capacitor, resulting in a single capacitor that provides a capacitance level that is equivalent to using multiple SLCs connected in parallel. This multi-layer design in slightly thicker (taller) than an SLC but decreases the overall footprint needed for a capacitor to achieve higher capacitance – a critical concern for many RF and microwave applications today as size, weight, and power (SWaP) are driving many design decisions. Featured image illustrates the construction of an SLC versus an MLCC.
When an SLC May Be the Best Fit
SLC’s are specifically designed for use in microwave and RF applications. This is because the inherent self-resonant frequency (SRF), which is the point where the capacitor will exhibit the least amount of impedance, of an SLC is the highest of any discrete lumped constant capacitor. Capacitors with a high SRF have low equivalent series resistance (ESR), which is the internal resistance in the capacitor that appears in series with the capacitance of the device.
This is important because, in general, ESR increases as frequency increases, so using a capacitor that has inherently low ESR is necessary. Additionally, since SLCs are formed monolithically, the number of mechanical parts in the SLC is limited, which also contributes to a lower ESR value.
One potential drawback of SLCs is that since it is just a single layer of material, capacitance is heavily dependent on the dielectric constant of the dielectric used, which limits the capacitance that can be achieved. Therefore, SLCs are mainly ideal for high-frequency, low-capacitance applications.
When an MLCC May Be the Best Fit
In general, MLCC’s can be used in a variety of applications since these capacitors have a much higher capacitance range than that of SLCs. This is possible because MLCCs are made with multiple layers of dielectric and conductors. In addition to offering higher capacitance, this design means MLCCs can be used for much higher voltage applications, up to 12 kV for some of our designs. However, since multiple layers of electrodes and dielectric are used, the ESR of an MLCC is usually much higher than that of an SLC. As a result, MLCC’s, even those made with high Q (ultra-low loss) Class 1 dielectrics, can only handle frequencies up to 30 GHz because of the high ESR values relative to SLCs, while SLCs can handle frequencies up to 100 GHz.
When it comes to RF and microwave applications, MLCCs are ideal for applications that require higher capacitance levels and higher operating voltages. However, when looking at applications beyond the RF and microwave industry, MLCCs, especially those taking advantage of a variety of our MLCC innovations, can be used for some of the world’s most demanding applications, including medical implantables, electric vehicles, and high-reliability detonation devices.
As shown in this post, the uses cases for SLCs and MLCCs are not interchangeable since each capacitor type handles variables such as voltage, frequency, and capacitance differently. In general, SLCs are well-suited for high-frequency, low-voltage RF and microwave applications, while MLCCs can be used for all types of high-capacitance, high-voltage applications within a much more limited frequency range.