This blog article from Knowles Precision Devices explains what S-parameters can tell you about a filter’s performance and show an example of how to plot a filter’s S-parameters using a free open-source tool.
In general, we like to think of scattering parameters, commonly known as S-parameters, as the Swiss Army knife of RF data since this data can tell you quite a bit about the performance of a filter.
This is because an S-parameter file refers to the scattering matrix of a microwave network, which is a mathematical construct that quantifies how RF energy propagates through a linear multi-port network.
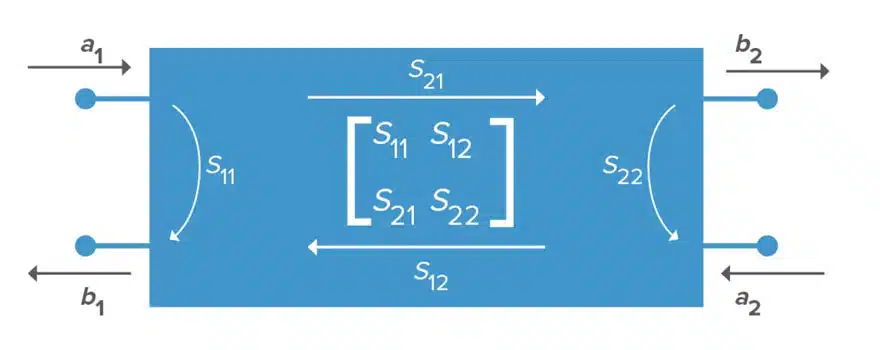
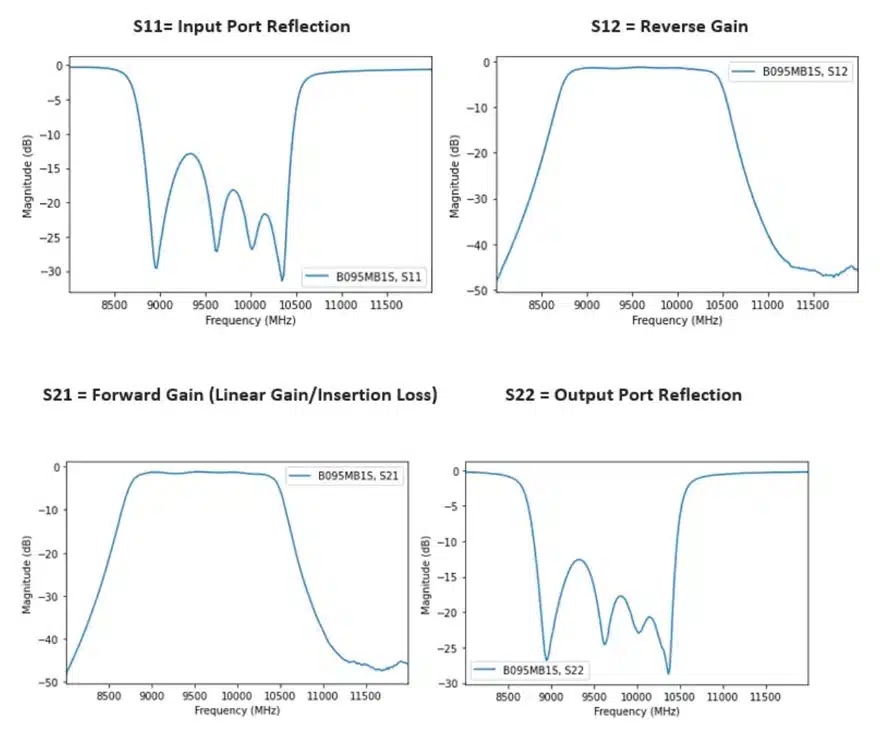
For a two-port network, the S-parameter matrix consists of four S-parameters – S11, S12, S21, and S22 –that define the relationships between the two ports in the RF system.
More specifically, these four S-parameters define the following elements in the bidirectional network:
- S11 – The reflection coefficient at the input, related to return loss
- S12 – A transmission coefficient that defines reverse gain
- S21 – Also a transmission coefficient that measures forward gain – in the case that the measurement ports have the same impedance, this is a measure of insertion loss
- S22 – Also a reflection coefficient, defines output port reflection
A Real-World Example of Plotting a Filter’s S-Parameters
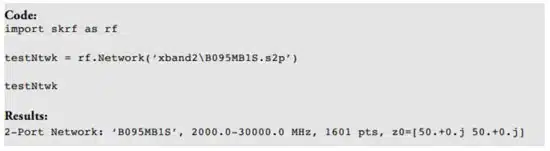
Let’s now look at an example of how to measure a filter’s performance using the S-parameter file for Knowles Catalog Filters, the B095MB1S, which is a 9.5 GHz surface mount bandpass filter. For the analysis in this example, we will use a free open-source tool, scikit-rf, which is based on the Python programming language, to plot the S-parameters.
To access the S-parameter file for this filter (or any of our filters), just search for the filter on our website. Once you have the file, store it on your computer in a location where it is easy to access from within your Jupyter setup (which is a tool that makes it easier to write Python code interactively in a local web browser). We recommend renaming the file with a name that is easy to recognize. For our example, we put the file in a folder called ‘xband2’ and named the file ‘B095MB1S.s2p.’ Since Jupyter can see this folder, we can make a Network and review the Network properties. Below is the Python code we input in Jupyter to call this S-parameter file and create this example Network as well as the results.
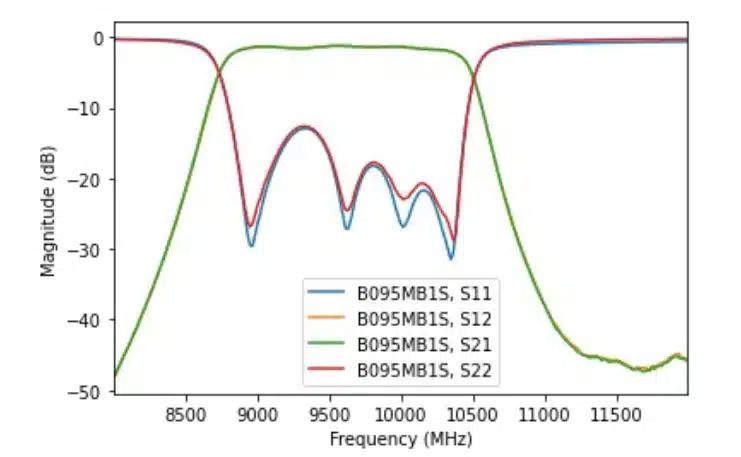
Note that in this example, the testNtwk is a Network object representing a two-port Network. The summary information in the results tells us the frequency range of this data set, the number of data points, and the impedance of the Network. The Network class also comes with convenient built-in methods for plotting and manipulating data. In this example, we can quickly plot the log-magnitude in decibels for the filter’s frequency range for four standard S-parameters by calling the plot s_db method, or we can plot each s-parameter individually (Figures 2 and 3).