Researchers from Osaka University developed a cellulose nanofiber coating that counters bending damage, retains electrode function underwater, and thus offers unparalled water resistance for flexible electronic devices.
Osaka, Japan – Most electronic devices aren’t waterproof, much to your irritation if a sprinkler suddenly sprays you while you’re talking outside on your cellphone. Some electronics can be made at least water-resistant by, for example, using special glues to fuse outer components together. Flexible electronics are another story. Their sealant materials must be able to bend, yet with current technology it’s inevitable that eventually such a sealant will crack or separate from the device–and there goes your water-resistant coating.
Researchers are determined to come up with a solution. Cellulose nanofibers are a proposed polymer coating for flexible electronics. These fibers are made from renewable resources and are environmentally friendly. However, they usually absorb water–commonly thought to be a fatal limitation for imparting water resistance.
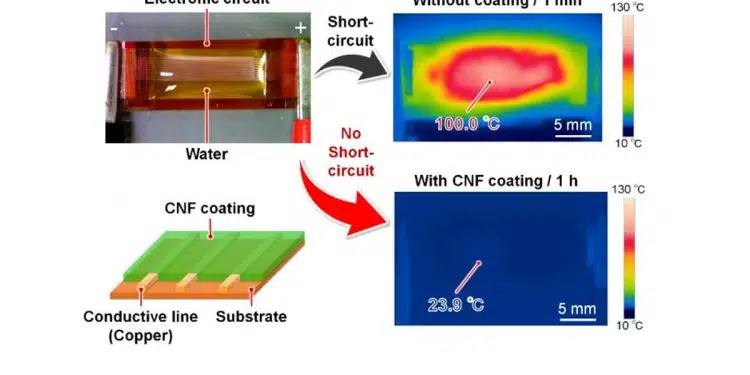
In a study recently published in ACS Applied Nano Materials, researchers from Osaka University developed self-healing cellulose nanofibers that slightly disperse in water and act to protect a copper electrode, enabling the electrode to function for an extended period. The researchers’ flexible circuit protection mechanism retains electrode function underwater and can undergo hundreds of bending cycles.
“In our initial work, an unprotected copper electrode failed after 5 minutes of dripping water onto it,” says Takaaki Kasuga, lead author. “Remarkably, a cellulose nanofiber coating prevented failure over at least a day of the same water challenge.”
Why is this? Remember that cellulose fibers don’t repel water. Instead, this polymer coating migrates in the electrode in such a way to prevent formation of conductive metal filaments that cause short-circuits. The electrodes even maintained their function after the celluose coating was scratched to simulate bending damage.
“Our results aren’t attributable to simple ion-exhange or nanofiber length,” explains Masaya Nogi, senior author. “The nanofibers aggregate in water into a protective layer made cohesive by locally acidic conditions and polymer cross-linking.”
A more rigorous test of the polymer coating was its performance after 300 cycles of bending underwater over the course of an hour. A conventional polymer coating usually failed, but the cellulose nanofibers continued to power LEDs.
“You’ll be able to stretch, bend, and fold electronics with our coating, and they’ll still retain their water resistance,” says Kasuga. “This is critical for use in applications under extreme conditions where device failure is unacceptable–for example, medical devices used in emergency disaster response.”
In preliminary work, even an ultrathin polymer coating thickness of only 1.5 micrometers, and some other polymers, performed similarly to the originally tested setup. They’ll become a staple of wearable electronics, and perhaps even medical devices, in the coming years.
###
The article, “Cellulose nanofiber coatings on Cu electrodes for cohesive protection against water-induced short-circuit failures,” was published in ACS Applied Nano Materials at DOI: https://doi.org/10.1021/acsanm.1c00267