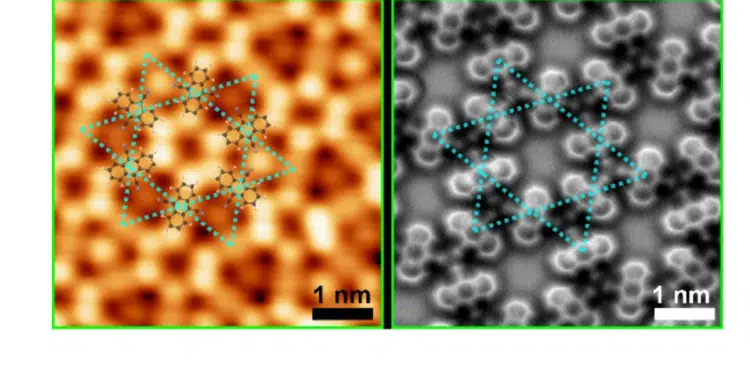
A 2D nanomaterial consisting of organic molecules linked to metal atoms in a specific atomic-scale geometry shows non-trivial electronic and magnetic properties due to strong interactions between its electrons.
A new study, published today, shows the emergence of magnetism in a 2D organic material due to strong electron-electron interactions; these interactions are the direct consequence of the material’s unique, star-like atomic-scale structure.
This is the first observation of local magnetic moments emerging from interactions between electrons in an atomically thin 2D organic material.
The findings have potential for applications in next-generation electronics based on organic nanomaterials, where tuning of interactions between electrons can lead to a vast range of electronic and magnetic phases and properties.
STRONG ELECTRON-ELECTRON INTERACTIONS IN A 2D ORGANIC KAGOME MATERIAL
The Monash University study investigated a 2D metal-organic nanomaterial composed of organic molecules arranged in a kagome geometry, that is, following a ‘star-like’ pattern.
The 2D metal-organic nanomaterial consists of dicyanoanthracene (DCA) molecules coordinated with copper atoms on a weakly-interacting metal surface (silver).
By means of careful and atomically precise scanning probe microscopy (SPM) measurements, the researchers found that the 2D metal-organic structure – whose molecular and atomic building blocks are by themselves non-magnetic – hosts magnetic moments confined at specific locations.
Theoretical calculations showed that this emergent magnetism is due to strong electron-electron Coulomb repulsion given by the specific 2D kagome geometry.
“We think that this can be important for the development of future electronics and spintronics technologies based on organic materials, where tuning of interactions between electrons can lead to control over a wide range of electronic and magnetic properties”, says FLEET CI A/Prof Agustin Schiffrin.
DIRECT PROBING OF MAGNETISM VIA THE KONDO EFFECT
The electrons of 2D materials with a kagome crystal structure can be subject to strong Coulomb interactions due to destructive wavefunction interference and quantum localisation, leading to a wide range of topological and strongly correlated electronic phases.
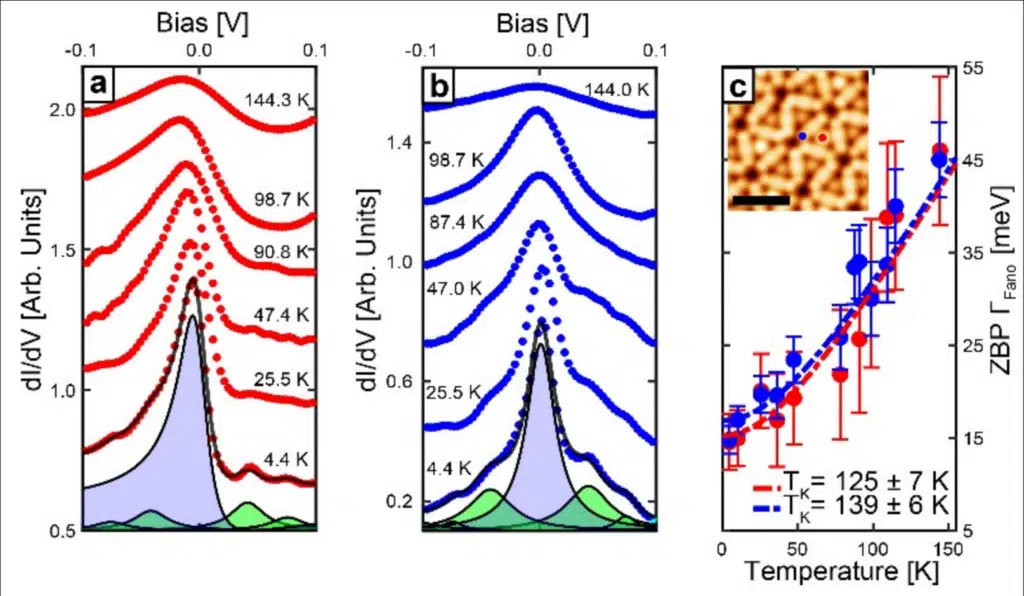
Such strong electronic correlations can manifest themselves via the emergence of magnetism, and, until now, have not been observed in atomically-thin 2D organic materials. The latter can be beneficial for solid-state technologies owing to their tunability and self-assembly capability.
In this study, magnetism resulting from strong electron-electron Coulomb interactions in a 2D kagome organic material was revealed via the observation of the Kondo effect.
“The Kondo effect is a many-body phenomenon that occurs when magnetic moments are screened by a sea of conduction electrons. For example, from an underlying metal,” says lead author and FLEET member Dr Dhaneesh Kumar. “And this effect can be detected by SPM techniques”.
“We observed the Kondo effect, and from there concluded that the 2D organic material must host magnetic moments. The question then became ‘where does this magnetism come from?’”
Theoretical modelling by Bernard Field and colleagues unambiguously showed that this magnetism is the direct consequence of strong Coulomb interactions between electrons. These interactions appear only when we bring the normally non-magnetic parts into a 2D kagome metal-organic framework. These interactions hinder electron pairing, with spins of unpaired electrons giving rise to local magnetic moments.
“Theoretical modelling in this study offers a unique insight into the richness of the interplay between quantum correlations, and the topological and magnetic phases. The study provides us with a few hints on how these non-trivial phases can be controlled in 2D kagome materials for potential applications in path-breaking electronics technologies,” says FLEET CI A/Prof Nikhil Medhekar.
THE STUDY
“Manifestation of Strongly Correlated Electrons in a 2D Kagome Metal-Organic Framework” was published in Advanced Functional Materials in September 2021. (DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202106474)
The research team consisted of FLEET experimentalists and theoreticians from Monash University’s School of Physics & Astronomy and Department of Materials Science & Engineering.