source: Graphene-info news
May 15, 2017 Boron Nitride Graphite Technical / Research MIT
MIT researchers have found that a flake of graphene, when brought in close proximity with two superconducting materials, can “borrow” some of those materials’ superconducting qualities. When graphene is sandwiched between superconductors, its electronic state changes dramatically, even at its center.
The researchers showed that graphene’s electrons, formerly behaving as individual particles, instead pair up in “Andreev states”—a fundamental electronic configuration that allows a conventional, non-superconducting material to carry a “supercurrent,” an electric current that flows without dissipating energy.
The researchers’ graphene platform may, in the future, be used to explore exotic particles, such as Majorana fermions, which are thought to arise from Andreev states and may be key particles for building powerful, error-proof quantum computers.
In 1962, the British physicist Brian David Josephson predicted that two superconductors sandwiching a nonsuperconducting layer between them could sustain a supercurrent of electron pairs, without any external voltage. As a whole, the supercurrent associated with the Josephson effect has been measured in numerous experiments. But Andreev states—considered the microscopic building blocks of a supercurrent—have been observed only in a handful of systems, such as silver wires, and never in a 2D material.
The MIT team tackled this issue by using graphene, as an extremely “clean” system, exhibiting very little scattering of electrons. Graphene’s extended, atomic configuration also enables scientists to measure graphene’s electronic Andreev states as the material comes in contact with superconductors. Scientists can also control the density of electrons in graphene and investigate how it affects the superconducting proximity effect.
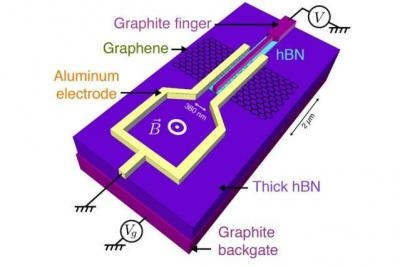
The researchers exfoliated a very thin flake of graphene, just a few hundred nanometers wide, from a piece of graphite, and placed the flake on a small substrate made from a crystal of boron nitride overlaying a sheet of graphite. On either end of the graphene flake, they placed an electrode made from aluminum, which behaves as a superconductor at low temperatures. They then placed the entire structure in a dilution refrigerator and lowered the temperature to 20 millikelvin—well within aluminum’s superconducting range.
In their experiments, the researchers varied the magnitude of the supercurrent flowing between the superconductors by applying a changing magnetic field to the entire structure. They also applied an external voltage directly to graphene, to vary the number of electrons in the material.
Under these changing conditions, the team measured the graphene’s density of electronic states while the flake was in contact with both aluminum superconductors. Using tunneling spectroscopy, the researchers were able to probe the graphene’s central region to see whether the superconductors had any effect, even in areas where they weren’t physically touching the graphene.
The measurements indicated that graphene’s electrons, which normally act as individual particles, were pairing up, though in “frustrated” configurations, with energies dependent on magnetic field. “Pairs in the central graphene are frustrated… These frustrated pairs are what physicists know as Andreev states; they are carrying the supercurrent.”
The team found Andreev states vary their energy in response to a changing magnetic field. Andreev states are more pronounced when graphene has a higher density of electrons and there is a stronger supercurrent running between electrodes.
“[The superconductors] are actually giving graphene some superconducting qualities,” the researchers said. “We found these electrons can be dramatically affected by superconductors.”
While the researchers carried out their experiments under low magnetic fields, they say their platform may be a starting point for exploring the more exotic Majorana fermions that should appear under high magnetic fields.