Source: Murata news
Murata Manufacturing Co., Ltd. has introduced the wire-wound common mode choke coil (CMCC) DLW32SH101XF2, which is the world’s first*1 CMCC to support DCMR*2 Class 3*3, fulfilling the IEC62228-3*4 requirement for use in CAN FD*5 next-generation automotive networks.
In the automotive industry, technologies that control basic automobile behavior are advancing rapidly with the aim of providing safer and more comfortable driving. In keeping with this market demand, faster automotive networks are required for connecting ECUs*6, sensors, and motors, with the result that conventional CAN*7, which transmits data at a rate of up to 1Mbps (megabits per second) is being replaced with the faster CAN FD.
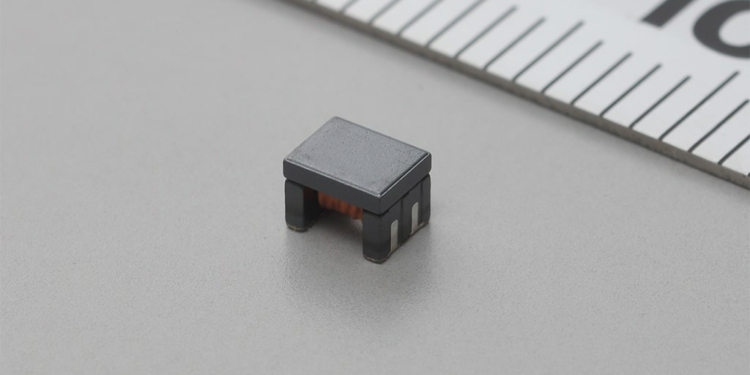
The new product draws on Murata’s CMCC design and manufacturing expertise to deliver the high performance and reliability required for CMCCs used in CAN FD networks while realizing a small size thanks to the company’s unique wire-wound structure.
Highlights
- Supports DCMR Class 3, fulfilling the IEC62228-3 requirement for CMCCs used in CAN FD
- Operating temperature range: -40 to +125ºC
- AEC-Q200*8 compliant
- The industry’s smallest size (3.2mm x 2.5mm)
Other technical information
In automotive networks, in order to ensure stable communication it is essential to implement ongoing measures to reduce noise from the several sources within the vehicle. In transitioning from CAN to the faster CAN FD, more stringent noise-reduction measures are required. Conventional CMCCs for CAN support DCMR Class 1 or, in the case of high-precision products, Class 2. By minimizing the difference in characteristics between the two coils comprising the CMCC and controlling DCMR degradation, this product successfully supports DCMR (Ssd21, Ssd12*9) Class 3, which is required for CMCCs used in CAN FD according to IEC62228-3, the CAN specification defined by the IEC. Particularly in the low frequency band in the range of several hundred kilo hertz and higher, the new product delivers the highest level of DCMR.
*1 Based on an internal study as of the end of July 2019.
*2 DCMR (Differential to Common Mode Rejection): The amount of mode conversion from differential components to common components
*3 DCMR Class 3: The DCMR characteristics required for CMCC used in CAN are classified into three classes. DCMR Class 3 means the most severe DCMR characteristics among them.
*4 IEC62228-3: One of electrical/electronics technology specifications defined by the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
*5 CAN FD (CAN with Flexible Data-Rate): A next-generation vehicle bus standard that enables transmission and reception of a larger amount of data (up to 64 bytes per frame) at a higher speed (1Mbps or faster) than the conventional CAN vehicle bus standard
*6 ECU (Electronic Control Unit): An automotive electronic control device
*7 CAN (Controller Area Network): A vehicle bus standard that enables transmission and reception of up to 8 bytes per frame at up to 1Mbps
*8 AEC-Q200:One of the specifications defined by the Automotive Electronics Council
*9 Ssd21, Ssd12: Parameters indicating the amount of mode conversion