Source: Nasa nepp article
Dr. Alexander Teverovsky of ASRC Federal Space and Defense has concluded design review of the
T22 wet tantalum capacitor robustness for space applications. His “Evaluation of Series T22 Wet
Tantalum Capacitors” was recently published and is available at the following link.
The work was performed at the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center and includes both a design review
and electrical and mechanical evaluations.
Series T22 of hermetically sealed wet tantalum capacitors (see featured image, credit: Vishay) is designed for avionics and aerospace applications and features a relatively small case size (LxWxH = 0.35×0.28×0.29) and compatibility with surface mount assembly technology.
Considering that heat release in vacuum occurs mostly by thermal conduction through the leads, this design allows using higher ripple currents in space systems. The manufacturer specifies that the part can
operate in a typical for tantalum capacitors temperature range from -55 °C to +85 °C, and to +125 °C with voltage derating.
All parts are screened by 48 hr burning-in at 85°C and rated voltage, can endure 300 thermal shock cycles, 3 V of reverse bias, 100 g mechanical shock, and 27.8 g rms of random vibration testing (RVT) per MIL-PRF-39006. Capacitors are capable of withstanding 2000 hr life testing at +85 °C and
rated voltage (VR) or at +125 °C and 2/3VR.
Key features of the T22 SMD wet tantalum capacitor:
- Capacitance range: 10uF to 68uF
- Voltage range: 50 V to 125V
- Tolerance: 10 % and 20%
- Life: 2000 hours
- Reliability: tested to M39006 requirements
- SMD: 9 mm x 7.1mm
Design of the parts allows using these wet electrolytic capacitors similar to regular chip tantalum capacitors, so in the following evaluations characteristics of the parts were measured similar to chip tantalum capacitors. In particular, alternative current (AC) characteristics included capacitance (C) and dissipation factor (DF) measured at 120 Hz and equivalent series resistance (ESR) measured at 100 kHz.
The parts are designed without internal Teflon sealing that is used for CLR style capacitors typically used
for space systems. This raises concerns about their hermeticity and the capability of withstanding high internal gas pressure. To address these issues, in addition to highly accelerated life testing (HALT)
at 125 °C and rated voltage, and step stress random vibration testing (RVT), the parts were evaluated by high temperature storage (2500 hr) testing at 150°C (HTS150) with measurements of electrical characteristics through the testing and the hermeticity leak rate before and after the testing. Also, the parts soldered onto printed wired boards (PWB) were stressed by 1000 temperature cycles between
-55 °C and +125 °C and their quality was assessed by additional HALT at different temperatures.
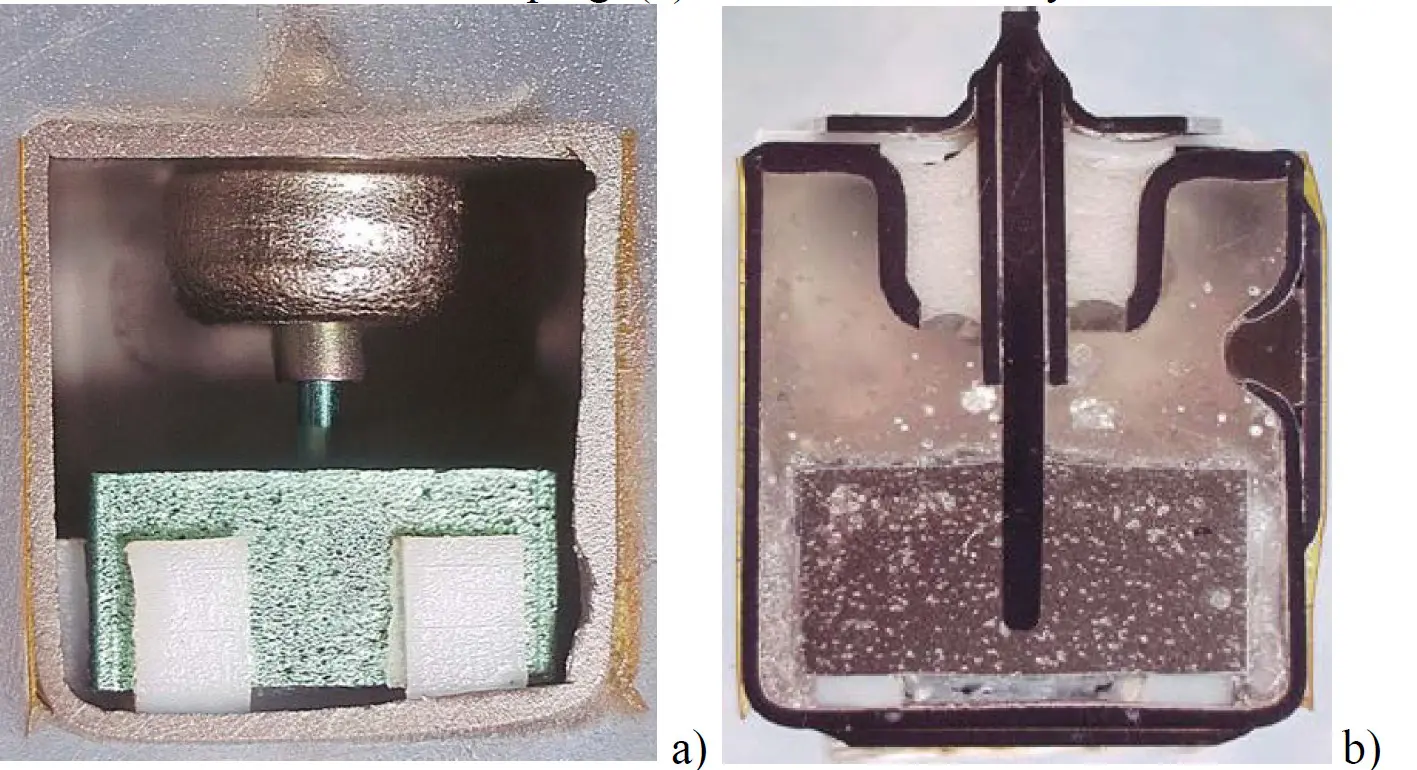
An internal (a) and cross-sectional (b) views of a 50 V capacitor. Image credit: NASA NEPP
Conclusions
Evaluation of T22 series of capacitors that included high temperature storage at 150 ºC for 2500 hours
, hermeticity leak testing, random vibration testing at different stress levels, accelerated life test
at 125 ºC, rated voltage for 770 hours, and extensive temperature cycling between -55 ºC and +125 ºC
in mounted conditions showed that the design is robust enough for space applications.
Capacitors rated to 50 V exceed the specified requirements regarding random vibration testing, accelerated life testing at conditions outside the specified limits, and temperature cycling. This part
can be used at relaxed derating requirements.
Capacitors rated to 125 V showed some anomalies during random vibration testing at 34 g rms that exceeds the specified level of 27 g rms and failed accelerated life testing at 125 ºC and rated voltage
that above the specified voltage for this temperature. This indicates much less quality margin in the design of 125 V capacitors and requires a strict enforcement of the existing derating requirements.
see the complete NASA NEPP report here.































