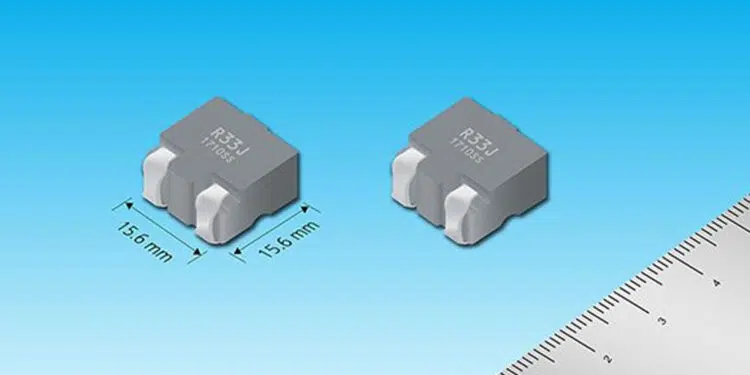
Panasonic commercializes a surface mounted automotive power inductor capable of passing large currents.
Panasonic Corporation announced today that its Industry Company has commercialized a low-loss and high vibration-resistant surface mounted automotive power inductor [1] (PCC-M15A0MF series). This 15.6 mm square inductor meets the market needs for larger working currents and smaller ECU (Electronic Control Unit) board sizes, which are called for with the increasing performance of automotive device functions. The product will be mass-produced starting in January 2022.
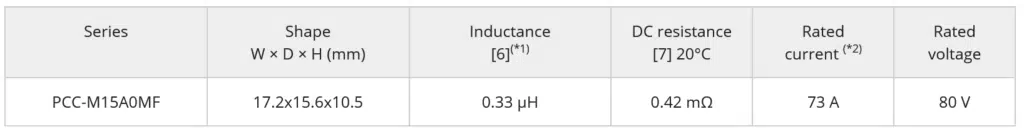
As the performance of automotive device functions gets higher, the amount of electric current flowing through electric circuits and the number of ECUs mounted on a vehicle will increase. Therefore, in order to save space inside a vehicle, ECU boards must be downsized. For that purpose, it is essential for electronic components mounted on such boards to be able to pass large currents as well as being small. However, large current type inductors are usually the through hole mounting type and large in size, which means they are unsuitable for miniaturization of the ECU board. Moreover, many passive components such as resistors and capacitors are surface-mounted. As surface mounting cannot be simultaneously performed with through hole mounting, two board processes are required to mount them on the board. Accordingly, Panasonic has commercialized a 15.6 mm square power inductor that can be surface mounted and is capable of passing a large current of 70 A for automotive use (PCC-M15A0MF series), which is an upsized version of the PCC-M1280MF series.
With this highly reliable PCC-M15A0MF series power inductors, the company will improve the reliability of power circuits while contributing to the reduction of environmental impact by saving space in power circuit mounting areas. In the future, the product lineup will also be enhanced by expanding the inductance range of products to respond to market needs.
Features:
1. Industry’s smallest class (15.6 mm square) of surface-mounted inductor capable of passing large currents*1
- – Rated current*2: 30 to 70A
- – Size: Width 15.6 mm x Depth 17.2 mm x Height 10.5 mm
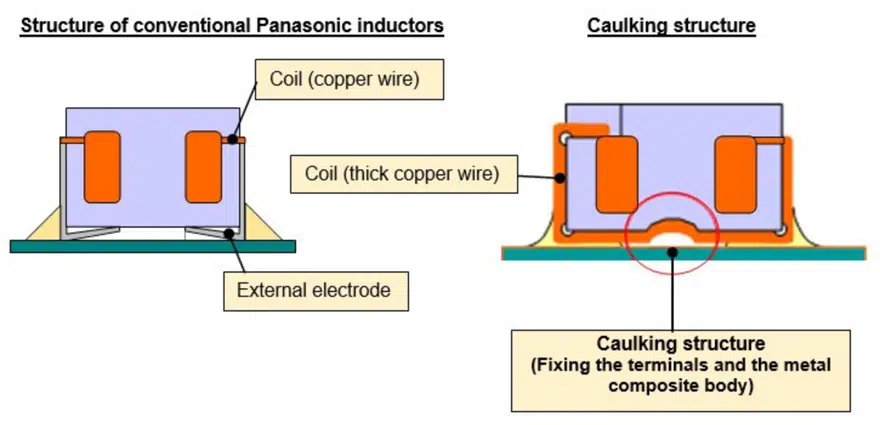
With the rapid electronization of vehicles, the number of ECUs installed inside the engine compartment and directly mounted on engines increases, therefore requiring the downsizing of ECUs. Panasonic adopted metal composite materials [4] using its original metallic magnetic materials and a wound coil using a thick copper wire and further developed a gapless integral structure where the materials and coil are integrally molded without gaps. The new inductor uses a copper wire that is 1.4 times thicker than that of the 12.6 mm square PCC-M1280MF series inductor, reducing the heat generation and loss of the coil. This enabled the new product to pass large currents ranging from 30 A to 70 A despite its small size of 15.6 mm square, which is the industry’s smallest class of surface mounted inductors. These features enabled the direct mounting of ECUs on engines and the space saving of power circuits.
2. The inductor enables ECUs to be directly mounted on engines by achieving excellent heat and vibration resistance.
- – Heat resistance: 160°C/2000 hours
- – Vibration resistance: 5 Hz to 2 kHz/30 G
For applications when ECUs are directly mounted on engines, they are required to be able to be installed under severe thermal and vibration conditions. Similarly, coils mounted on ECUs are also required to have excellent heat and vibration resistance. Accordingly, Panasonic achieved high heat resistance up to 160°C by devising the composition of metal composite materials. Moreover, the company adopted its original inductor structure, where both ends of the thick copper wire that makes up the coil are pulled out and used as terminals, and at the same time, a caulking structure is provided on the bottom surface to fix the terminals and the body made of the metal composite materials. This improves vibration resistance after mounting on boards. This structure enables the inductor to be mounted around engines, directly on engines, or near motors.
3. The environmental impact can be reduced through installation space saving.
- *1: As surface-mounted inductors as of January 14, 2022 (Panasonic data)
- *2: Rated current: Current value at which the product temperature increases by 40°C due to self-heating
Currently, approximately 60% of automotive power inductors use ferrite [5] as magnetic materials, whereas approximately 40% of those use metal composite materials (Panasonic data as of 2021). By adopting metal composite materials that are suitable for downsizing, the company achieved a smaller inductor size of 15.6 mm square compared to the standard size of 20 mm square for ferrite type inductors with a similar performance. This enables space saving by reducing the installation area by 30 to 50% by replacing ferrite type inductors with a similar performance with the company’s product, thereby enabling the downsizing of devices and the reduction of environmental impact by reducing of the number of components and materials to be used.
Applications:
- Step-up or step-down DC/DC convertors for gasoline, diesel, and hybrid vehicles [2]
- High-performance automotive ECU power circuits, automotive ECU circuits with integrated mechanical and electronic components [3]
Basic specifications:
- *1): Measured at 100 kHz
- (*2): Current value at which the product temperature increases by 40°C due to self-heating
Term descriptions:
- [1] Power inductor
Among inductors, this type is used for electrical circuits in power supply systems and plays a role of a filter to store energy and remove noise in DC/DC converter circuits, etc. - [2] DC/DC converter circuit
This is a circuit that converts direct current from one voltage to another. - [3] Integration of mechanical and electronic in-vehicle components
This refers to a design in which mechanical drive components and automotive ECUs are integrated. Mechanical drive components and automotive ECUs used to be installed separately, but were interconnected via cables. However, the demand for high-precision control, higher degree of freedom in component layout, reduction in the number of cables, etc. has led to the adoption of an integrated configuration of mechanical and electrical components. - [4] Metal composite material
This refers to a magnetic material made by the compression molding of metallic magnetic material-based (iron group) powder insulated with resin. - [5] Ferrite
Magnetic material obtained by mixing and Sintering cobalt, nickel, manganese, etc. with iron oxide as a main component - [6] Inductance
This is an indicator of coil performance. Passing a changing current through a coil will generate a voltage that passes current in a direction that hinders the current change. The rate of the generated voltage is referred to as inductance. - [7] DC resistance
DC resistance is the resistance component of a winding (copper wire). The lower the DC resistance, the smaller the power loss, thereby improving the power supply efficiency.