This Würth Elektronik webinar explains some basic PCB design via selection and considerations including via clearance in the solder mask, different possibilities of via treatments and fitting selection for your application.
PCB Via Design Selection – Plugging, Filling, and Tenting
This presentation explores the principles, methodologies, and design considerations associated with PCB via structures, including plugging, filling, and tenting techniques. It provides an in-depth analysis of the via design selection process, the impact of solder mask clearances, and the implications of different via treatments per IPC-4761 standards.
1. Introduction
Printed Circuit Board (PCB) technology has evolved significantly to meet the demands for high-speed, high-density electronic applications. Vias, derived from the Latin term for “path,” play an integral role in connecting different PCB layers. This paper provides insights into via design with a focus on plugging, filling, and tenting methods, vital for enhancing mechanical reliability and electrical performance.
2. Via Design Considerations
2.1. Importance of Via Structures
Vias facilitate the electrical connection between PCB layers. Improper via management can lead to solder wicking, unreliable joints, and functional failures. Thus, the correct sealing and insulation techniques are paramount.
2.2. Via Opening and Solder Mask Clearance
Clearance design around vias in the solder mask is critical. Recommendations include maintaining a clearance of at least 250 microns around the via to account for process tolerances. This ensures reliable solder mask application, reducing risks of electrical shorts and solder leakage.
3. Methods for Via Protection
3.1. Tented Vias
Tented vias involve applying a dry film solder mask over the via. Although they prevent solder flow, they are less common in advanced German facilities due to limited mechanical reliability.
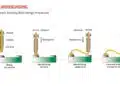
3.2. Plugged Vias (Type III and IV per IPC-4761)
- Type III: Partial via filling using thermal curing ink via screen printing. Provides good vacuum seals but limited fine-line design applicability.
- Type IV: Similar to Type III but covered with solder mask, providing extra isolation.
3.3. Filled Vias (Type V, VI, and VII)
- Type V and VI: Fully filled with non-conductive epoxy, offering excellent vacuum seals and flat surfaces post-sanding.
- Type VII: Filled and capped vias allow soldering directly on the via, supporting via-in-pad designs for high-density applications.
4. Manufacturing Processes
4.1. Drilling and Metallization
Vias are drilled and metallized through galvanic processes, applying copper layers within holes and on the PCB surface.
4.2. Filling Techniques
Vias are filled under vacuum to ensure void-free encapsulation. The filling materials are cured thermally, followed by surface grinding to achieve planar finishes.
4.3. Cap Plating for Type VII Vias
An additional metallization step creates a cap on filled vias, enhancing mechanical strength and thermal conductivity.
5. Design Rules and Material Considerations
5.1. Aspect Ratio
Maintaining optimal aspect ratios (drill diameter to PCB thickness) ensures process reliability.
5.2. Copper Thickness and Thermal Management
Copper wrap requirements and thermal expansion coefficients are critical in high-reliability applications. Material selection must align with these mechanical demands to prevent fatigue failures over thermal cycling.
6. Applications
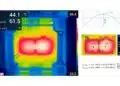
- Thermal Vias: For heat dissipation in high-power components.
- HDI Designs: Stacked microvias for compact, high-speed layouts.
- Vacuum Testing: Ensuring airtight seals in testing environments.
7. Conclusion
Selecting the appropriate via design—whether plugged, filled, or tented—depends on the specific PCB application requirements. Early collaboration with PCB manufacturers is recommended to optimize design for manufacturability and performance.
References
- IPC-4761: Design Guide for Protection of Printed Board Via Structures
- IPC-6012: Qualification and Performance Specification for Rigid Printed Boards