Researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo demonstrated ultrathin ferroelectric capacitor stack with a total thickness of only 30 nm according to their published scientific paper in Advanced Electronic Materials.
Introduction
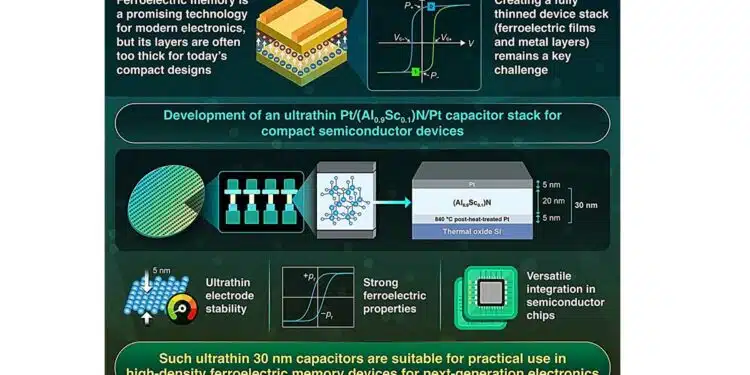
The article reports on the realization of an ultrathin ferroelectric capacitor stack with a total thickness of only 30 nm, including both top and bottom electrodes, while maintaining strong and stable electric polarization suitable for non-volatile memory applications. This work addresses the key challenge of scaling not only the ferroelectric film but the complete device structure for high-density embedded memory in advanced logic processes.
Ferroelectric capacitors are attractive for next-generation low-power memories because they store information in switchable polarization states that remain even when power is removed. However, conventional ferroelectric devices often lose performance as thickness is reduced, and previous research largely concentrated on thinning the ferroelectric layer alone rather than the integrated capacitor stack.
In this study, researchers from the Institute of Science Tokyo and Canon ANELVA Corporation demonstrate a Pt/(Al,Sc)N/Pt capacitor stack using a scandium-substituted aluminum nitride film as the ferroelectric layer, optimized down to a 20 nm active layer with 5 nm electrodes on both sides. Their results highlight that careful control of stack design and electrode processing can preserve high remanent polarization and robust switching even under aggressive thickness scaling.
Key points
- Demonstration of an integrated Pt/(Al0.9Sc0.1)N/Pt ferroelectric capacitor stack with a total thickness of 30 nm, including 5 nm top and 5 nm bottom platinum electrodes.
- Use of scandium-substituted aluminum nitride ((Al,Sc)N) as the ferroelectric layer, leveraging its inherently high remanent polarization at nanometer-scale thicknesses.
- Focus on thickness scaling of the entire capacitor stack, not only the ferroelectric film, to better match real device integration requirements.
- Preservation of high ferroelectric performance and strong electric polarization despite the drastic reduction in total stack thickness.
- Post-deposition heat treatment of the bottom Pt electrode at 840 °C improves crystal orientation and enhances polarization switching behavior in the thin stacks.
- Fabricated capacitors exhibit characteristics compatible with direct embedding in semiconductor logic circuits for on-chip non-volatile memory.
- The results form a basis for scaling other ferroelectric device types, such as FeRAM and ferroelectric tunnel junctions (FTJs), which also depend on stable polarization switching and retention.
- Future directions include exploring alternative electrode materials with more favorable crystal orientations and reduced thermal budgets to improve device durability and manufacturability.
Extended summary
The central problem addressed in the article is the challenge of achieving ultrathin ferroelectric capacitors that are not only functional at the material level but also realistic as integrated device stacks for embedded non-volatile memory in advanced electronics. As electronic systems continue to shrink, there is a strong demand for memory elements that occupy minimal area and thickness while maintaining reliable polarization switching and data retention without power. Prior work on ferroelectric memory scaling mainly pursued thinner ferroelectric layers, but frequently neglected the total stack thickness and the impact of electrodes and interfaces on device-level performance.
To bridge this gap, the team led by Professor Hiroshi Funakubo at the Institute of Science Tokyo, working with Canon ANELVA, developed a three-layer metal–ferroelectric–metal capacitor stack using a (Al0.9Sc0.1)N thin film sandwiched between platinum electrodes. The chosen composition of scandium-substituted aluminum nitride is known to exhibit robust ferroelectric behavior, with high remanent polarization that can persist even when the film is reduced to nanometer dimensions. In the reported structure, the total thickness is limited to 30 nm, consisting of a 20 nm (Al0.9Sc0.1)N layer, a 5 nm bottom Pt electrode, and a 5 nm top Pt electrode.
The fabrication strategy emphasizes not only ferroelectric layer deposition but also careful engineering of electrode properties and thermal processing. A critical step identified in the work is a post-heat treatment of the bottom Pt electrode at 840 °C, which enhances its crystal orientation. Improved electrode crystallinity in turn leads to better polarization switching in the ultrathin ferroelectric films, suggesting a strong coupling between electrode texture and ferroelectric domain behavior at these small dimensions.
From a performance standpoint, the capacitors demonstrate strong electric polarization and high remanent polarization even with the severely reduced stack thickness. Remanent polarization—the polarization that remains after the external electric field is removed—is crucial for non-volatile memory, as it encodes the stored bit states. The study shows that the inherent ferroelectricity of (Al,Sc)N can be retained in a fully scaled stack and that the device-level configuration does not necessarily require thick electrodes or ferroelectric layers to ensure robust switching.
The article emphasizes that scaling the full stack is essential for practical integration into logic circuits and semiconductor platforms. Ultra-thin, device-ready capacitors such as the reported Pt/(Al0.9Sc0.1)N/Pt stacks can be embedded alongside logic units, enabling compact on-chip memory with short interconnect distances and reduced parasitics. This integration pathway is especially relevant for Internet-of-Things (IoT) devices and mobile electronics, where space, power efficiency, and performance must be balanced carefully.
Beyond the specific device reported, the study lays conceptual groundwork for thickness scaling in other ferroelectric memory architectures. For example, FeRAM and ferroelectric tunnel junctions (FTJs) also rely on stable, switchable polarization and would benefit from design principles that maintain ferroelectric performance at minimal thicknesses. Lessons from this work—such as the importance of electrode orientation, proper thermal treatments, and integrated stack optimization—could guide future designs in those related technologies.
The authors also outline a path forward involving the exploration of alternative electrode materials with crystal orientations better matched to (Al,Sc)N and other ferroelectrics. Such materials might reduce the need for high-temperature processing, lowering the thermal budget and mitigating reliability concerns associated with aggressive annealing. Improved electrode–ferroelectric combinations could enhance durability and switching endurance, accelerating the adoption of ultrathin ferroelectric memories in industrial semiconductor lines.
Conclusion
The reported 30 nm Pt/(Al0.9Sc0.1)N/Pt capacitor stack demonstrates that high ferroelectric performance can be retained even under aggressive thickness scaling of the complete device, not just the ferroelectric layer. This represents a meaningful advance toward realistic, ultrathin ferroelectric memory elements suitable for direct integration with logic circuits in compact, high-density electronics.
At the same time, the work highlights limitations and open challenges, including the reliance on high-temperature treatments and the need to further optimize electrode materials and orientations for long-term device reliability. Future research aimed at lowering thermal requirements, improving endurance, and extending these design concepts to other ferroelectric architectures such as FeRAM and FTJs could further accelerate adoption in IoT and other miniaturized systems.
References
- Institute of Science Tokyo, “New ultrathin ferroelectric capacitors show promise for compact memory devices,” TechXplore (Advanced Electronic Materials coverage). Available at: https://techxplore.com/news/2025-12-ultrathin-ferroelectric-capacitors-compact-memory.html
- S. Doko et al., “Thickness Scaling of Integrated Pt/(Al0.9Sc0.1)N/Pt Capacitor Stacks to 30 nm,” Advanced Electronic Materials (2025). DOI: 10.1002/aelm.202500451