University of Porto researchers have created a simple self-charging battery which offers power solutions for various devices. To create the battery, the researchers used ferroelectric glass electrolyte inside of an electrochemical cell.
Collaborative team of researchers based in Porto, Portugal and Texas, United States hope to make this user-unfriendly requirement a thing of the past with the development of a new type of battery that can recharge itself without losing energy.
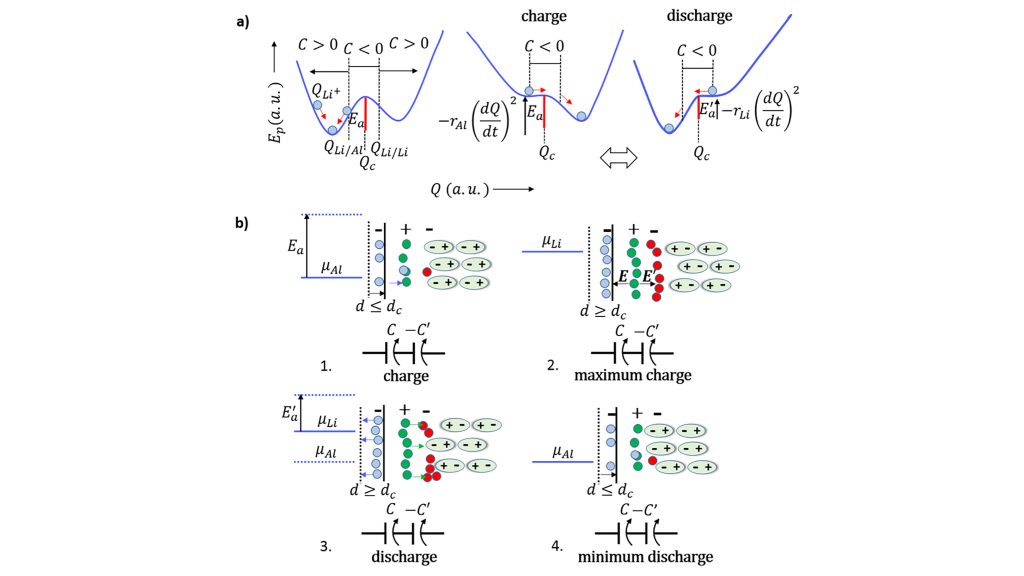
The team’s research, which was published by AIP Publishing in Applied Physics Reviews, propose a new type of battery that combines negative capacitance and negative resistance within the same cell, allowing the cell to self-charge without losing energy, which has important implications for long-term storage and improved output power for batteries.
These batteries can be used in extremely low-frequency communications and in devices such as blinking lights, electronic beepers, voltage-controlled oscillators, inverters, switching power supplies, digital converters and function generators, and eventually for technologies related to modern computers.
In Applied Physics Reviews, from AIP Publishing, Helena Braga and colleagues at the University of Porto in Portugal and the University of Texas at Austin, report making their very simple battery with two different metals, as electrodes and a lithium or sodium glass electrolyte between them.
“The glass electrolyte we developed was lithium-rich, and so I thought that we could make a battery in which the electrolyte would feed both electrodes with lithium ions, on charge and discharge with no need for lithium metal,” said Braga.
This work is significant, because it unifies the theory behind all solid-state devices — such as batteries, capacitors, photovoltaics and transistors – where the different materials in electrical contact exhibit the properties of the combined material instead of those of the individual materials.
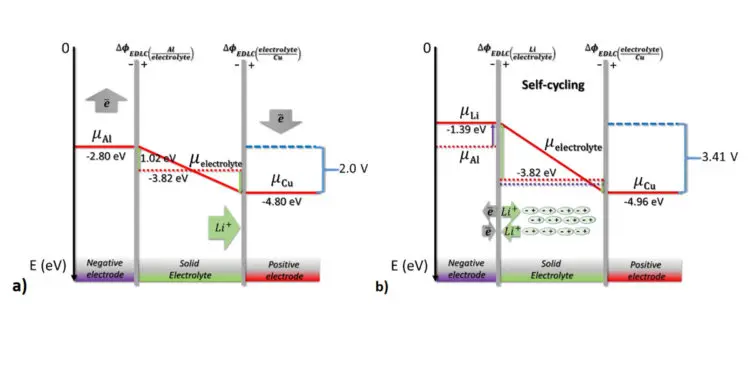
“When one of the materials is an insulator or dielectric, such as an electrolyte, it will locally change its composition to form capacitors that can store energy and align the Fermi levels within the device,” said Braga.
In a battery, the open circuit potential difference between electrodes is due to an electrical need to align the Fermi levels, a measure of the energy of the least tightly held electrons within a solid, which is also responsible for the polarity of the electrodes. The chemical reactions come later and are fed by this electrical potential energy stored in the capacitors.
“Our electrochemical cells, which in principle are simpler than batteries, are all about self-organization, which is the substance of life,” Braga said.
To contribute to a more sustainable world, self-cycling can be stopped or mitigated by not allowing a leap in the Fermi levels or by configuring a negative resistance to happen.
“This can be obtained by having the negative electrode of the same material as the positive ions of the electrolyte,” said Braga. “It gives rise to a device that self-charges without self-cycling — increasing the energy stored in it — as opposed to the natural degradation of the electrochemical process that makes the energy stored decrease by dissipation of heat. The latter has applications in all energy storage devices, such as batteries and capacitors, and can substantially improve their autonomy.”