The blog article written by Robert Lu, KYOCERA-AVX Corporation explains impact of several factors such as temperature, applied DC/AC bias voltage, and age to capacitance stability of MLCC ceramic capacitors.
The multi-layer ceramic capacitor (MLCC) is one of the most common capacitor varieties found in electronic design. It offers a wide range of bulk capacitance and voltage tolerance in numerous form factors at relatively low cost. While these devices have become commonplace in the designers’ tool chest, they exhibit some often overlooked peculiarities.
Of primary concern is the sensitivity of effective capacitance to several environmental factors, including temperature, applied bias voltage, and age. If these factors are unaccounted for, the risk of product failure becomes very real, especially in manufacturing variability and overall tolerance stack-up.
MLCC Temperature Considerations
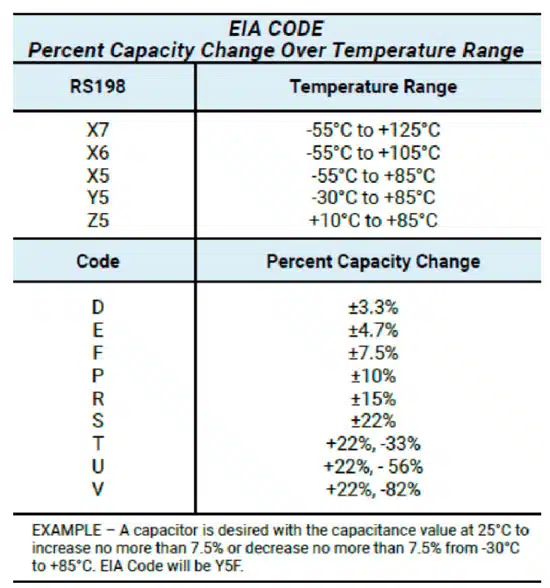
MLCC’s are typically divided into two classes based on the type of ceramic material used for the dielectric. Class I capacitors are the most robust with the fewest sensitivities and are usually built from TiO2. A three-letter EIA code is used to classify the temperature coefficient (TC) in ppm per degree Celsius, a multiplier, and a tolerance. Class I capacitors are often listed as C0G, which is the lowest of all temperature sensitivities, implying a -55°C to +125°C temperature range with a capacitance change of ±30ppm/°C and total capacitance varying less than ±0.3%.
Class II capacitors are typically constructed from BaTiO3 dielectrics and provide a much wider range of bulk capacitance at the expense of higher temperature sensitivity. The commonly used Class II devices are X7R, Y5V, Z5U. Table 1 presents the EIA codes and corresponding values for temperature coefficient and capacity range.
Using Table 1, a few examples are shown below:
- -55 to +125 degrees with a capacitance change of ±15% EIA code is X7R
- -55 to +85 degrees with a capacitance change of ±15% EIA code is X5R
- -30 to +85 degrees with a capacitance change of +22%, -82% EIA code is Y5V
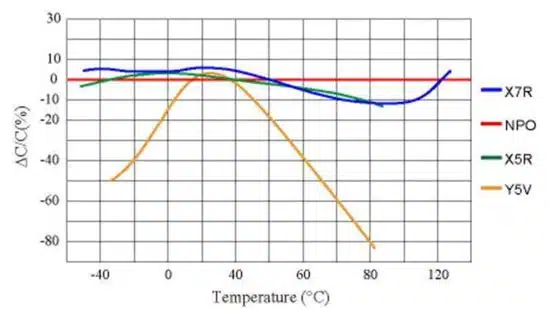
Figure 1 depicts the change in capacitance across the entire temperature range for several different EIA coded MLCC’s. Knowing the environmental conditions in which a capacitor operates and understanding the design’s tolerable variation can be critical to proper functionality. For example, in a high-temperature application, picking a low-cost Y5V device instead of a more appropriate X7R device would all but guarantee its failure.
DC BIAS Voltage Impact to MLCC Capacitors
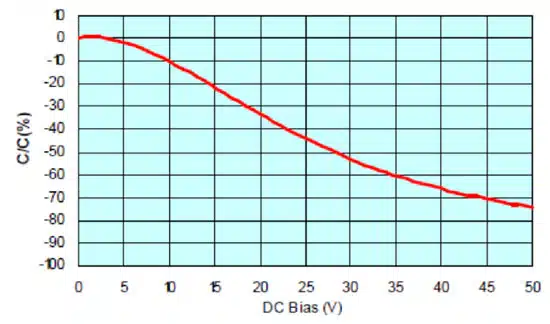
Another inherent sensitivity of MLCC capacitors is the change in bulk capacitance with applied DC bias voltage. For example, as shown in Figure 2, the larger the applied DC voltage, the smaller effective capacitance. The capacitance in this example drops by approximately 45% at 25V, which is only half of the device’s 50V rating.
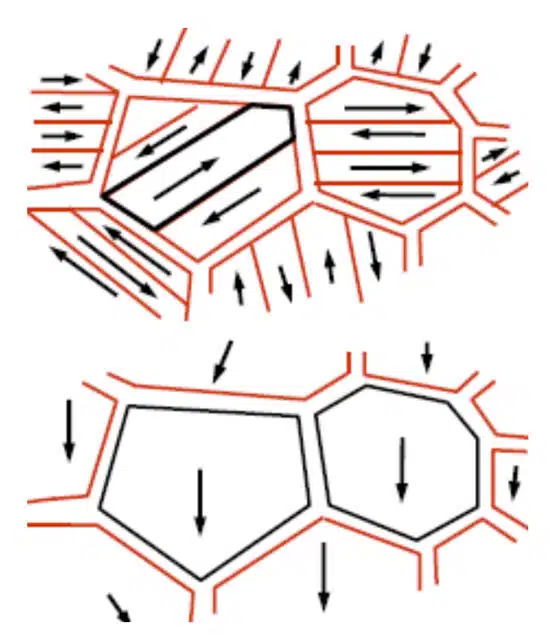
The origin of this phenomenon is the crystal structure of the ceramic dielectric. With no DC voltage applied, no electric field is present, and the crystal dipoles will arrange themselves randomly throughout the device. This scenario is referred to as spontaneous polarization and results in a high dielectric constant and, in turn, yields high capacitance.
As a low DC voltage is applied, the electric field causes some of the dipoles to align in parallel, as shown in Figure 3. This alignment of dipoles with the electric field decreases capacitance. As more DC voltage is applied, more dipoles will begin to align, and the capacitance continually degrades. Once the rated voltage is reached, capacitance levels can drop by as much as 70% from their nominal value. Class II devices, in particular, suffer from this due to their BaTiO3 construction.
Just as in the case of temperature sensitivity, being aware of the dependence on DC bias voltage can greatly influence a design. If an MLCC is being used to filter a small AC signal with minimal DC component, various MLCC options may be suitable. If, instead, the design is filtering the ripple from a high voltage DC regulator, the MLCC may not be the best choice.
The key factor of DC bias dependence is the thickness of the dielectric. As the dielectric gets thicker, the electric field intensity is weakened, and the capacitance reduction is minimal. Therefore, to minimize the DC bias effect, a designer can apply the following techniques:
- Choose a larger case size
- Choose higher rated voltage
- Choose a better dielectric
- Put multiple devices in parallel
MLCC Ageing
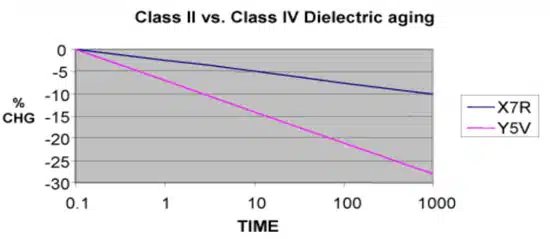
The dielectric materials used in higher class MLCC’s to achieve high capacitance suffer from an inherent aging process. The crystal lattice of these materials has built-in strain energy that gives rise to a permanent electric dipole. Over time, this strain relaxes, and the capacitance slowly degrades.
Figure 4 shows an example of an X7R and Y5V device over 1000 hours of aging. While this aging process can be reversed by raising the device’s temperature above 120C, the designer must simply include the aging effect into the lifetime calculations of the product.
Conclusion
While MLCC’s are invaluable devices in modern electronic design, their limitations must be understood. Unlike other capacitor technologies, the designer needs to be intimately familiar with the intended application’s temperature, DC bias, and aging requirements. Only then can the proper dielectric material, case size, and circuit topology be decided.
Further read: