inter-connect knowledge blog
Contact Finish Lubricants
Connector contact lubricants are used to provide two different performance benefits; reduction in friction and corrosion protection. Reducing friction will...
Read moreDetailsSilver Degradation Mechanisms
Silver surfaces react with sulfur and chlorine. Silver sulfide films, tarnish, are readily displaced on connector mating, but have been...
Read moreDetailsNickel Degradation Mechanisms
As noted previously, nickel surfaces always consist of a self limiting and very thin layer of nickel oxide, 0.01 µm...
Read moreDetailsFretting Degradation Mechanisms
For completeness it should be noted that there are several fretting degradation mechanisms: Fretting WearAll fretting motions will cause some...
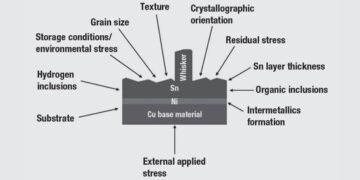
Read moreDetailsNon-Noble Finish Degradation Mechanisms
Because tin is the most commonly used non-noble contact finish, it will be the focus of this chapter. Silver and...
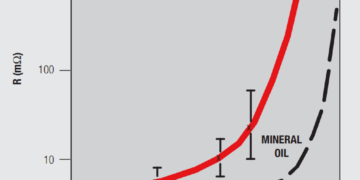
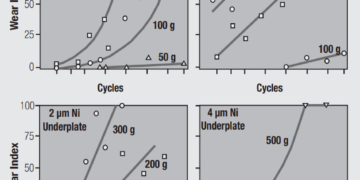
Read moreDetailsNickel Underplates and Noble Metal Finish Wear
Nickel underplates in noble metal finishes provide another very important performance benefit that is not related to corrosion. The durability...
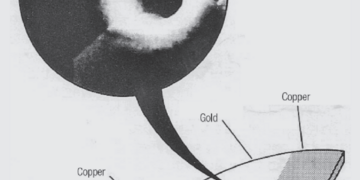
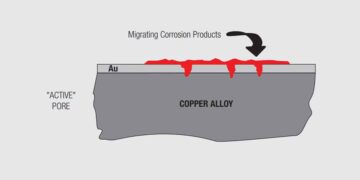
Read moreDetailsNoble Metal Finish Degradation Mechanisms
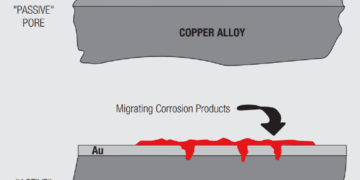
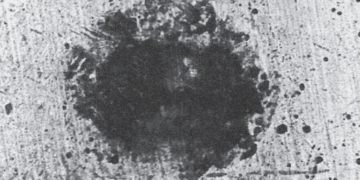
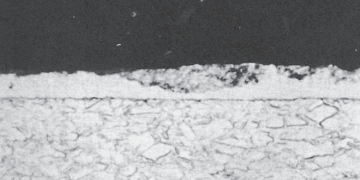
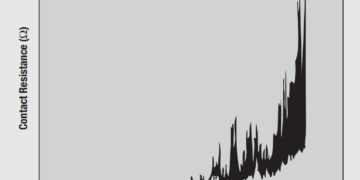
Noble metal finish degradation mechanisms include both corrosion and wear, with wear through of the noble metal leading to increased...
Read moreDetailsContact Finish Degradation Mechanisms
The two most significant contact finish degradation mechanisms are corrosion and wear. While wear is a degradation mechanism, its main...
Read moreDetailsNoble and Non-Noble Metal Finishes
Tin is the dominant non-noble contact finish due to its widespread use in connectors for commercial and industrial applications. Connectors...
Read moreDetailsConnector Design/Selection/Assembly
This chapter will provide an overview of design and material requirements for contact finishes, contact springs and connector housings as...
Read moreDetails