Source: 3D print.com article
by Bridget O’Neal.
While the substantial benefits of 3D printing are discussed often in the progressive industrial and technological sectors today, the advantages they can have for just one business and their innovative endeavors are enormous. For a company like GH Induction Group, being able to 3D print with copper allows the Valencia, Spain-headquartered induction heating company to offer improved solutions for over 4,000 customers around the globe—many of whom may benefit from electromagnetic induction heating based on new production processes in electron beam melting (EBM).
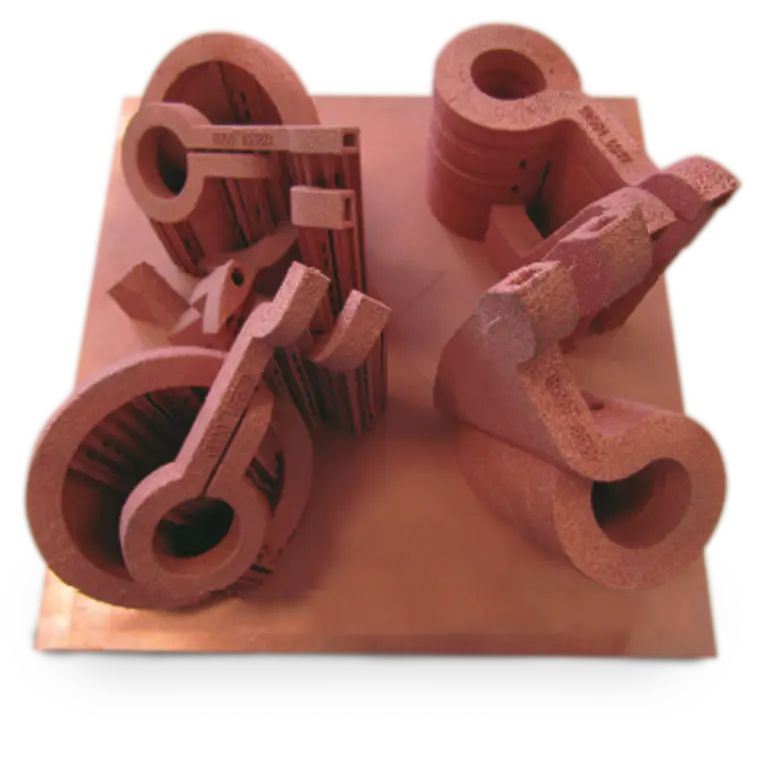
Now, GH Induction Group is launching 3Dinductors, their new website (http://www.3dinductors.com) completely dedicated to their 3D printed coils and inductors, made of pure copper. While copper is a metal that offers a list of almost magical benefits due to its malleable texture and excellent ductility, accompanied by 3D printing technology, GH can produce inductors with a significantly increased service life (up to four times higher in some cases), higher density, and stronger mechanical properties. Coil spares are manufactured to be identical geometrically, and all parts are optimized for the high performance.
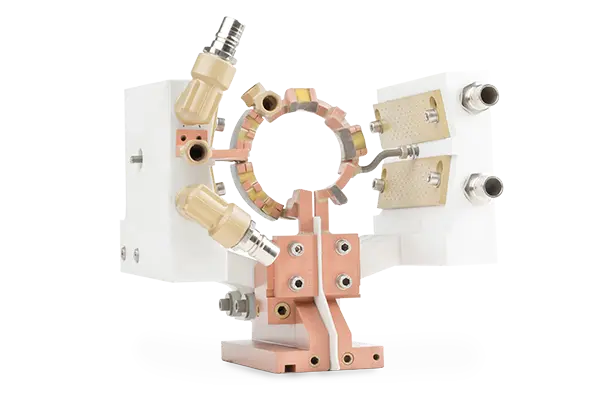
“This means reduced production costs per part and an improvement in treatment that cannot be achieved with current technology,” states the GH team.
Critical attention to research and design, and ongoing development—as well as experimenting with other 3D printing processes that could not deliver like EBM does—has allowed GH to make serious breakthroughs for industrial companies engaged in manufacturing processes that require industrial induction heating technology. Applications such as automotive are a perfect example of industries that will benefit further from such techniques as part production cost is significantly reduced, production is much more efficient overall, and less inventory is required.
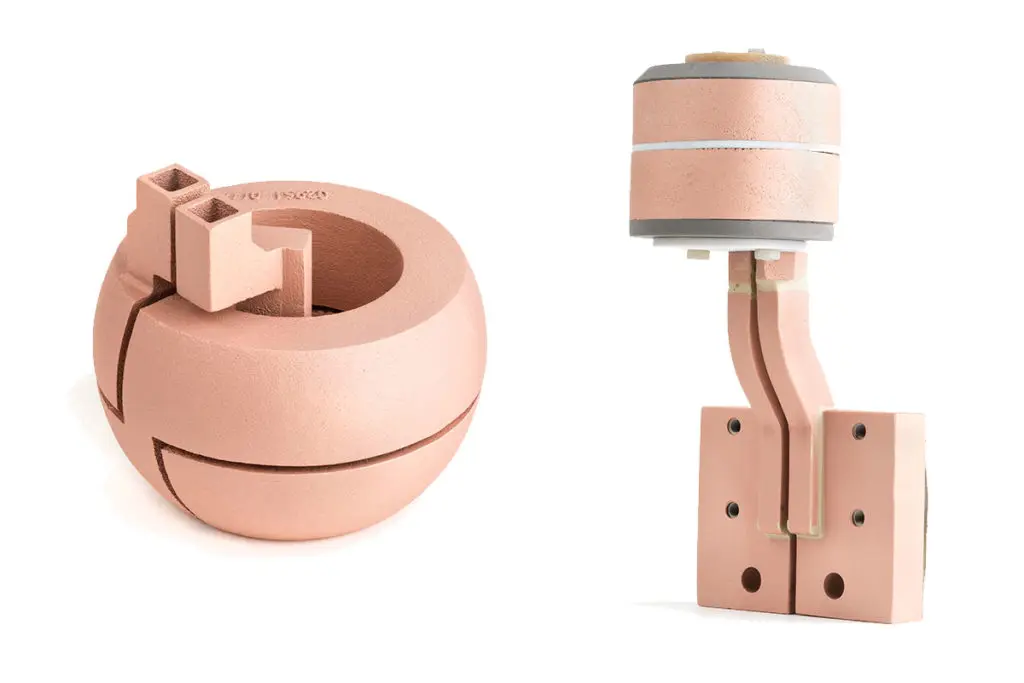
Although there are many different production methods for 3D printing and additive manufacturing methods today using metal, electron beam melting is the only method allowing GH to print pure copper alloy. To begin, the GH team can engineer their own 3D CAD designs, making changes as needed, and quickly. They are also able to control production and quality, preventing the number of hot spots, improving coil cooling as they transform inductor characteristics when necessary, and manufacture in a vacuum atmosphere to prevent porosity issues and rusting. 3D printed inductors can also be fixed just like conventionally-manufactured designs.

The EBM Printing process
- The coils are built up, layer-by-layer of metal powder, melted by a powerful electron beam. Each layer is melted to the exact geometry as defined by a 3D CAD model.
- First a thin layer of metal powder particles is deposited in the working plate and then flattened. Powder is preheated to very high temperatures.
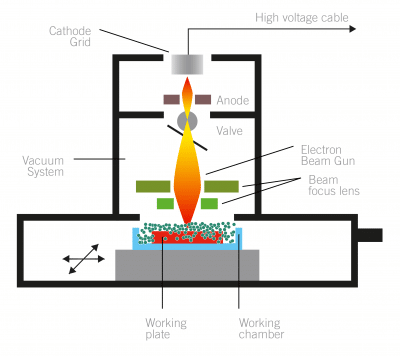
- In the next step the electron beam is focused and controlled in the X-Y dimension by means of an electromagnetic coil in order to selectively melt the powder particles on top of the working plate.
- The result is the creation of the desired section and simultaneously it is fused to the previous layer. A new layer is then created, and the steps are repeated up to the completion of coil .
Optionally the coil surface could be improved with sand shot blasting, classical manual finishing or through mechanical post-processes.
Conclusion
3D printing with metal has become popular for a wide range of industries because it offers the ability to manufacture extremely strong but lightweight parts with complex geometries. We have seen numerous other forays into 3D printing with copper too, as researchers create pure copper powder, construction engineers design 3D printed copper roofs, and others are dedicated to improving processes using this metal and others.
Image source: GH Induction Group































