Source: EDN article
Power Tips #87: How to design a high voltage DCM inverting charge pump converter. By John Betten
A low-current, negative high-voltage is required to bias sensors in advanced driver assistance systems, ultrasonic transducers for sonar applications and communications equipment. Flyback, Cuk and inverting buck-boost converters are all possible solutions, but are penalized by bulky transformers (flyback and Cuk) or limited in their maximum negative voltage by the controller’s input-voltage rating (inverting buck-boost). In this power tip, I’ll detail the operation of a converter that pairs a single inductor with an inverting charge pump operating in discontinuous conduction mode (DCM). Paired with a ground referenced boost controller, a large negative output voltage can be generated at a lower system cost.
Figure 1 shows a simplified power-stage schematic. Note that this schematic is different from a traditional inverting buck-boost converter, which “floats” the controller between VIN and -VOUT. In that converter, the maximum -VOUT achievable is the maximum VCC of the controller minus the maximum input voltage. This would make it nearly impossible to find a controller that can drive an N-channel field-effect transistor (FET) for an output voltage of -100 V or more.

Figure 1 Simplified power stage of an inductor-driven inverting charge pump.
The circuit’s operation can be split into three intervals, detailed in Figure 2. In the first interval, the FET is on during duty cycle (d), which applies VIN across the inductor, allowing current to ramp up from zero, storing energy. However, in the previous cycle, C1 (which maintains a voltage of approximately equal to VOUT) has depleted its excess stored energy, reverse-biasing D1 and D2. This is why D1, D2 and C1 are not shown in this interval. C2 supplies all load current.
In the next interval, d’, the FET turns off and the inductor current begins to discharge, causing its voltage polarity to reverse. This greatly increases the voltage present at node VFET, allowing C1 to recharge through D1. During this interval, current ramps downward until D1 turns off. However, due to the reverse-recovery characteristics of D1, current goes negative before it eventually turns off, at which point the inductor current slope changes and its voltage polarity reverses once again.
The third interval, d’’, is when the energy transfer from C1 to C2 takes place. When D1 stops conducting, the inductor voltage is clamped to VIN because the VFET node voltage is forced to ground by a current path through the FET’s body diode. Current flows through D2 until the voltages across C1 and C2 equalize, but current through the FET’s body diode continues until the inductor’s current reaches zero. At this point, the voltage across the inductor collapses and resonates with circuit parasitics until the FET turns on again.

Figure 2 The three phases of DCM operation.
Figure 3 details the key voltage and current waveforms. DCM operation allows for the smallest possible inductance, but with a higher peak current. Inductance for DCM operation is determined at the maximum duty cycle, minimum VIN and full load. Carefully check the maximum duty cycle against the controller data sheet, but you can typically choose 60%-90%, or otherwise pulse skipping can occur. Larger inductances will push operation into continuous conduction mode (CCM), since the current will not return to zero before the next switching cycle. This results in using an inductor that may be larger than necessary and requires extra care to prevent subharmonic oscillation.

Figure 3 Key circuit waveforms in DCM.
Design equations
For DCM operation, Equation 1 satisfies the relationship involving the inductor’s stored energy:

where ipk is the peak inductor current and η is the converter’s efficiency. The peak inductor current is then equal to Equation 2:

From the following two equations, Equation 3 expresses the duty cycle (d) in terms of :

Since VIN is the voltage across the inductor when the FET is on and ipk is the inductor current at the end of duty cycle d, substituting Equation 2 into Equation 3 yields Equations 4 and 5:

The average load current is determined by the geometric relationship in Equations 6 and 7 during interval d’:

Substituting Equation 2 into Equation 7 provides Equation 8:

The remainder of the period is defined as d’’, which is when the energy transfers into C2 and the remaining inductor current discharges to zero (Equation 9):

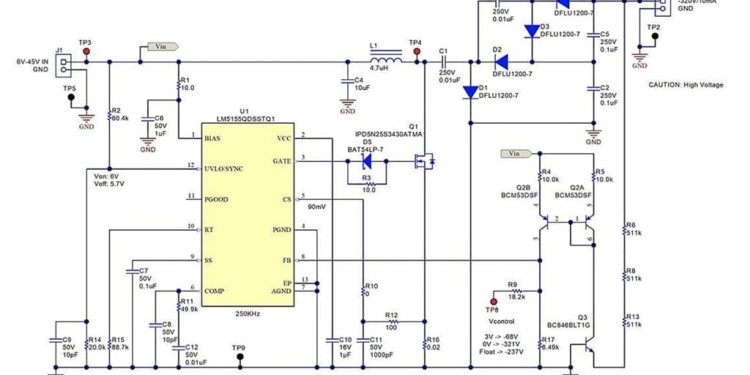
Figure 4 shows an example schematic implementing this converter with a voltage doubler, which allows the voltage stress of each power-stage component to be equal to one-half of the full output voltage. This provides a wider selection of components from which to choose. In this application, the inductance was calculated as if the output voltage was one-half, but at twice the load current.

featured image and Figure 4 Inductor-driven inverting charge pump with voltage doubler and level-shifting current mirror schematic
This converter provides a small, single-inductor solution for generating a large negative voltage. Additionally, it allows the use of an inexpensive ground-referenced boost controller to drive an N-channel FET.
For more Power Tips, check out TI’s Power Tips blog series on Power House.