Pablo Blázquez, Power Εlectronics Εngineer of Frenetic in this blog discuss how to balance a Magnetic design by adjusting certain parameters in the core and windings.
One of the key challenges in Magnetic design is to achieve a balance between different performance parameters such as power efficiency, magnetic flux density, and operating frequency. This is particularly important in those applications where the device is expected to operate under different load conditions or in a range of environments.
In this edition, we will explore some of the techniques and principles involved in the balancing of a Magnetic design. We will focus on the role of both the core and the windings in achieving optimal performance, and we will discuss how modifications to these parameters can affect the overall magnetic properties of the device.
Whether you are an engineer, a researcher, or someone with an interest in Electronics, I hope that this post will provide you with valuable insights and ideas for improving the performance of your Magnetic designs.
Balance, Why?
Let’s start with a simple question: why do we want the losses to be perfectly distributed between core and windings in our Magnetic? In a magnetic component, such as a Transformer or an Inductor, energy losses can occur in both the core and the windings. The losses in the core are primarily due to hysteresis and eddy currents, while those in the windings are due to the resistance of the wire.
Ideally, we want the losses to be evenly distributed between the core and the windings, because this can improve the overall efficiency and reliability of the magnetic itself. If the losses are concentrated primarily in one area, for example in the core, it can lead to increased heating and temperature rise, which can therefore degrade the performance of the component and reduce its lifespan.
By distributing the losses evenly between the core and the windings, we can ensure that the heat generated is dissipated in a more uniform way, reducing the risk of hot spots and thermal stress. Additionally, a more balanced distribution of losses can also help to reduce the overall size and weight of the component, making it more cost-effective and easier to integrate into a wide range of applications.
In summary, distributing the losses evenly between the core and the windings is key to the optimization of the efficiency, reliability, and performance of our magnetic components.
How you can do that?
There are several ways to balance losses between the core and the windings in our Magnetic. Let’s analyze them starting from a design that you can access here:
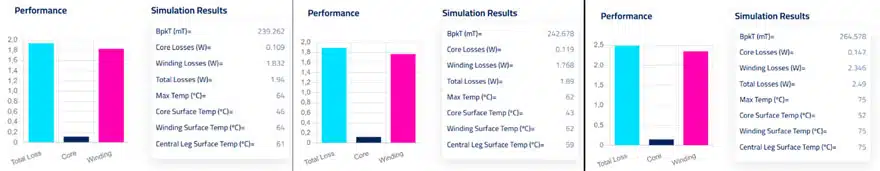
1. Choose the right core material
The choice of core material can have a significant impact on the distribution of losses. For example, using a core material with lower hysteresis losses can help you to reduce losses in the core. In Figure 1 you can see a comparison between the original design and two slightly different versions:
The first on the left is the original design. In the second version we have changed the original core material (Ferrite 3C97) to 3C90, while in the third one we have switched to powder material KoolMu 60. It is clearly visible that the core losses increase in both cases and, although the powder material provides more balance, it results in considerably higher losses.
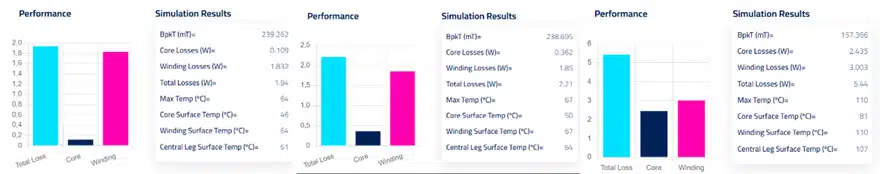
2. Adjust the core size
The size of the core can also affect the distribution of losses: by Increasing the core size, you can reduce the magnetic flux density and decrease core losses. Figure 2 shows the result of increasing the core size compared to the original design.
You can see how, in both examples, we have slightly increased the core losses. However, reducing the core temperature in the PQ 40 seems to have affected the overall temperature and this can be one of the reasons why the overall losses have decreased.
In the second example, the E41, we get the opposite result. The less efficient E core has raised the core losses and temperature, causing an increase in the winding losses and therefore a growth in the overall losses.
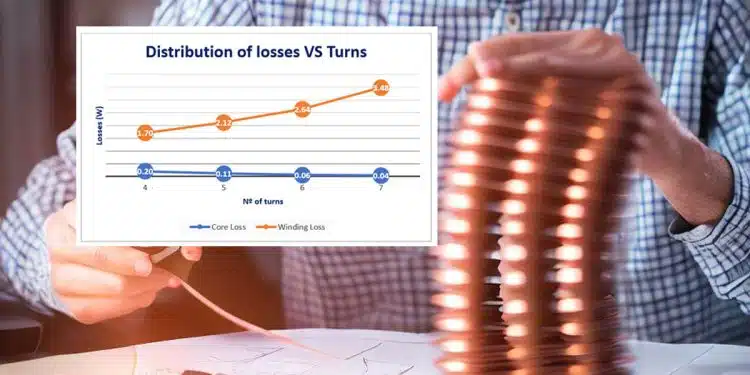
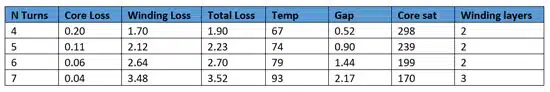
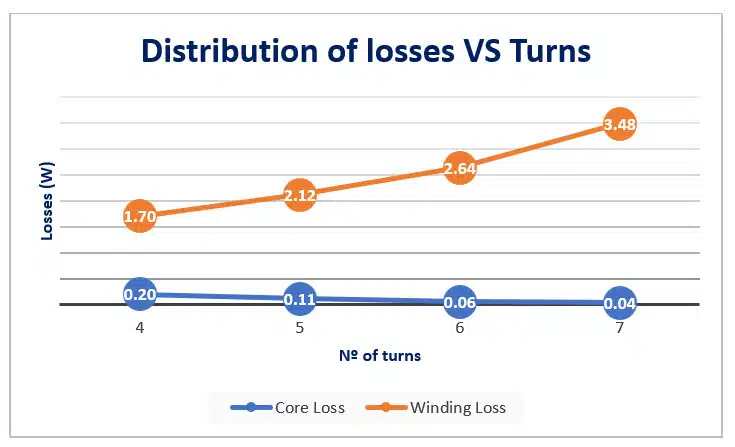
3. Change the number of turns
The number of turns in a magnetic component also affects the distribution of losses. Decreasing the number of turns can help you shift the winding losses to the core. In Figure 3 you can see the effect of changing the number of turns in the overall design:
4. Optimize the wire size
Using the right wire size can reduce the overall losses in the windings.
In Figure 4 you can see a comparison between several wires with different sizes and types. We have the litz wires on the top, and the round wires in the bottom. In terms of losses, you can clearly see that litz wire has much lower losses than the round ones. Moreover, in both examples the size incrementation of the wire reduces the overall losses.
5. Adjust the operating frequency
The operating frequency of a magnetic component can also impact the losses distribution. Operating at a lower frequency can help you reduce core losses, while operating at a higher frequency can help you reduce winding losses. You can read more on this topic in post here: Optimal Frequency for a PSFB.
Conclusions
In practice, achieving a perfectly balanced distribution of losses may not always be possible. However, by using a combination of the techniques explained today, it is possible to optimize the design of a magnetic component for a given application and therefore achieve a more balanced losses distribution.
It is completely up to you which options to choose, if not all of them work for you. Just bear in mind that you’re not always going to be able to have a balanced design that meets your requirements, and you might have to make the decision whether to have fewer losses or a balanced design