Source: University of Cambridge news
Researchers have found that certain ultra-thin magnetic materials can switch from insulator to conductor under high pressure, a phenomenon that could be used in the development of next-generation electronics and memory storage devices.
The international team of researchers, led by the University of Cambridge, say that their results, reported in the journal Physical Review Letters, will aid in understanding the dynamic relationship between the electronic and structural properties of the material, sometimes referred to as ‘magnetic graphene’, and may represent a new way to produce two-dimensional materials.
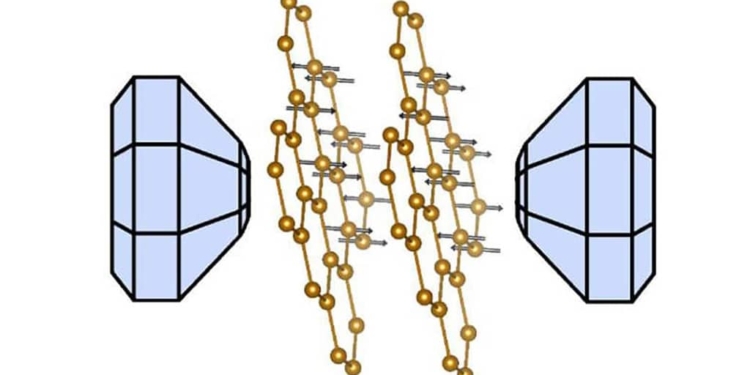
Magnetic graphene, or iron trithiohypophosphate (FePS3), is from a family of materials known as van der Waals materials, and was first synthesised in the 1960s. In the past decade however, researchers have started looking at FePS3 with fresh eyes. Similar to graphene – a two-dimensional form of carbon – FePS3 can be ‘exfoliated’ into ultra-thin layers. Unlike graphene however, FePS3 is magnetic.
“Magnetism in two dimensions is almost against the laws of physics, but in this material, it seems to be true” Seb Haines
The expression for electrons’ intrinsic source of magnetism is known as ‘spin’. Spin makes electrons behave a bit like tiny bar magnets and point a certain way. Magnetism from the arrangement of electron spins is used in most memory devices, and is important for developing new technologies such as spintronics, which could transform the way in which computers process information.
Despite graphene’s extraordinary strength and conductivity, the fact that it is not magnetic limits its application in areas such as magnetic storage and spintronics, and so researchers have been searching for magnetic materials which could be incorporated with graphene-based devices.
For their study, the Cambridge researchers squashed layers of FePS3 together under high pressure (about 10 Gigapascals), they found that it switched between an insulator and conductor, a phenomenon known as a Mott transition. The conductivity could also be tuned by changing the pressure.
These materials are characterised by weak mechanical forces between the planes of their crystal structure. Under pressure, the planes are pressed together, gradually and controllable pushing the system from three to two dimensions, and from insulator to metal.
The researchers also found that even in two dimensions, the material retained its magnetism. “Magnetism in two dimensions is almost against the laws of physics due to the destabilising effect of fluctuations, but in this material, it seems to be true,” said Dr Sebastian Haines from Cambridge’s Department of Earth Sciences and Department of Physics, and the paper’s first author.
The materials are inexpensive, non-toxic and easy to synthesise, and with further research, could be incorporated into graphene-based devices.
“We are continuing to study these materials in order to build a solid theoretical understanding of their properties,” said Haines. “This understanding will eventually underpin the engineering of devices, but we need good experimental clues in order to give the theory a good starting point. Our work points to an exciting direction for producing two-dimensional materials with tuneable and conjoined electrical, magnetic and electronic properties.”
The research was funded by the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council (EPSRC).
Reference:
C.R.S. Haines et al. ‘Pressure-Induced Electronic and Structural Phase Evolution in the van der Waals Compound FePS3.’ Physical Review Letters (2018). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.121.266801