Advantages and disadvantages of MLCC downsizing is discussed in AVX technical papers written by Frank Hodgkinson and Maureen Strawhorne.
Abstract:
As integrated circuits (ICs) continue to pack more functionality into smaller packages, the need for bulk off-chip capacitance remains. In resonant circuits, such as phase-lock-loops (PLLs) and switching regulators, precision class one ceramic capacitor may be required.
Such capacitors must maintain a tight capacitance range over process, voltage, and temperature variation (PVT) for the host IC to meet its performance specifications. In contrast, class two ceramic capacitors are required for nearly every IC in the form of decoupling and bypass capacitance. They may also be found in amplifier circuits, simple filters, and linear regulators where their function is less dependent on tightly specified impedance requirements.
Such requirements for class two capacitors often create a trap for the unwitting designer, who might naturally focus on voltage rating, size, and cost when choosing these devices. This is especially true when the top-level application is overly constrained by form factor. One can imagine the selection filtering process: start with an approximate capacitor value (i.e., 100 nF), choose a voltage rating with some reasonable headroom (i.e., 6.3 V), and finally, find the smallest surface mount (SMT) package (i.e., 0402) and cost combination to create room for other components and PCB routing.
Considering voltage rating and capacitance separately from package size may seem reasonable, but therein lies the potential trap. As capacitor sizes have grown smaller and smaller, manufacturers have developed new technologies to increase capacitance density to achieve standard value-package combinations. In doing so, dependencies have also been introduced that may create unexpected surprises during testing.
Tradeoffs in Capacitance Density
High permittivity is mainly a function of dielectric choice. Typical ceramic materials, titanium dioxide, for example, exhibit relative permittivity values in the tens. Ferroelectric materials, on the other hand, can achieve relative permittivities in the thousands. Most modern MLCCs are constructed using Barium Titanate (BaTiO3), which can yield relative permittivity values up to 7,000. In fact, much of the capacitor manufacturing expertise lies in the milling, casting, and sintering of this insulator.
Materials research and optimization will undoubtedly continue to provide enhanced dielectric properties in the future. Still, the primary knobs for maximizing capacitance density are the number of layers and the layer spacing. In the mid-1990s, minimum layer thicknesses were in the 5-micron range, and common capacitor values were built from several hundred layers. Nearly two decades later, the thickness of the minimum layer was reduced by a factor of ten, and capacitors with more than one thousand layers were not unusual. This miniaturization trend comes with significant tradeoffs that must be considered when selecting MLCCs during the design cycle.
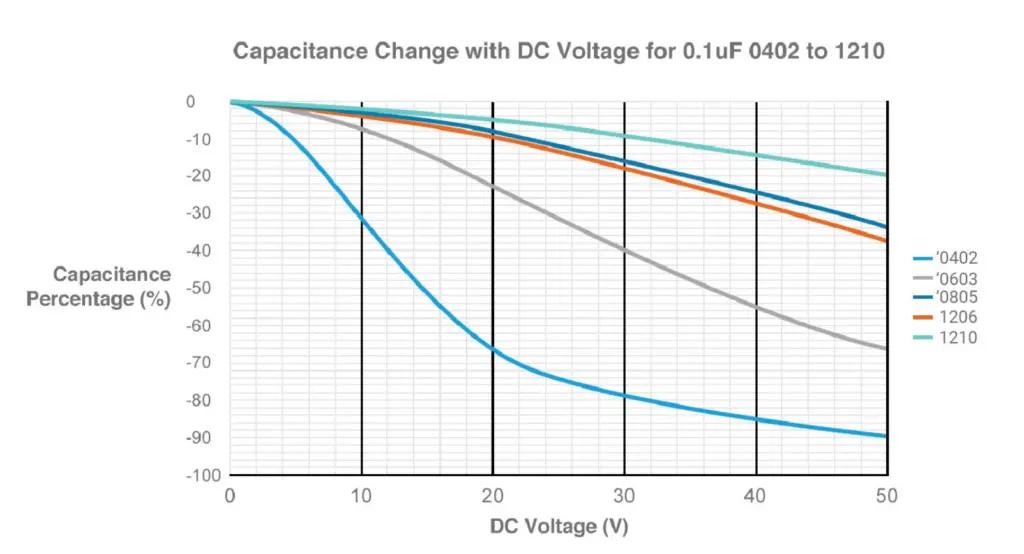
As layer thicknesses are reduced, the electric field strength through the dielectric is increased for the same applied voltage. Since the dielectric materials are typically ferroelectric, their permittivity reduces as electric field strength increases. Therefore, the same capacitor in a 0402 package will have poorer voltage dependence characteristics compared to a 0805 package. At high voltages, this can be particularly problematic. An example is shown below, where a 0402 capacitor has lost 90% of its capacitance capability at an applied voltage of 50V.
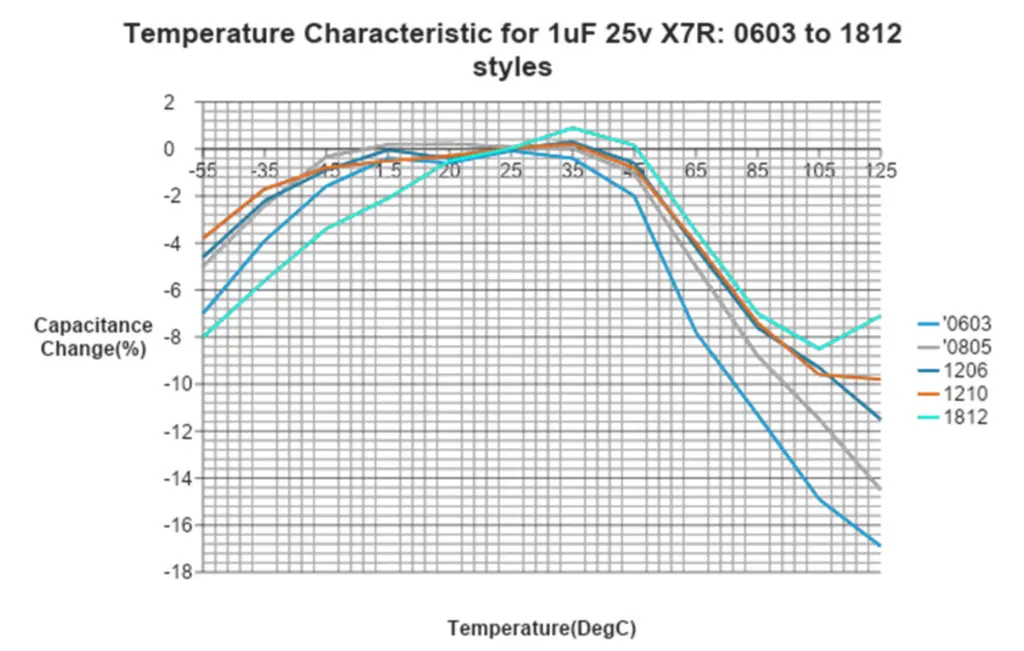
Similar trends are seen when looking at the temperature performance of size reduced MLCC’s. The figure below demonstrates how for the same capacitance, a 0603 package loses nearly double the effective capacitance compared to an 1812 package at high temperatures.
The story doesn’t end there. Miniaturization of capacitors has a deleterious effect on numerous other performance parameters, including ripple current handling capability, ESD protection, and electrical strength. Many of these weaknesses are particularly noticeable in high voltage and high power applications. Of greater concern than the performance tradeoffs is the potential for failure over time, especially in safety-critical systems.
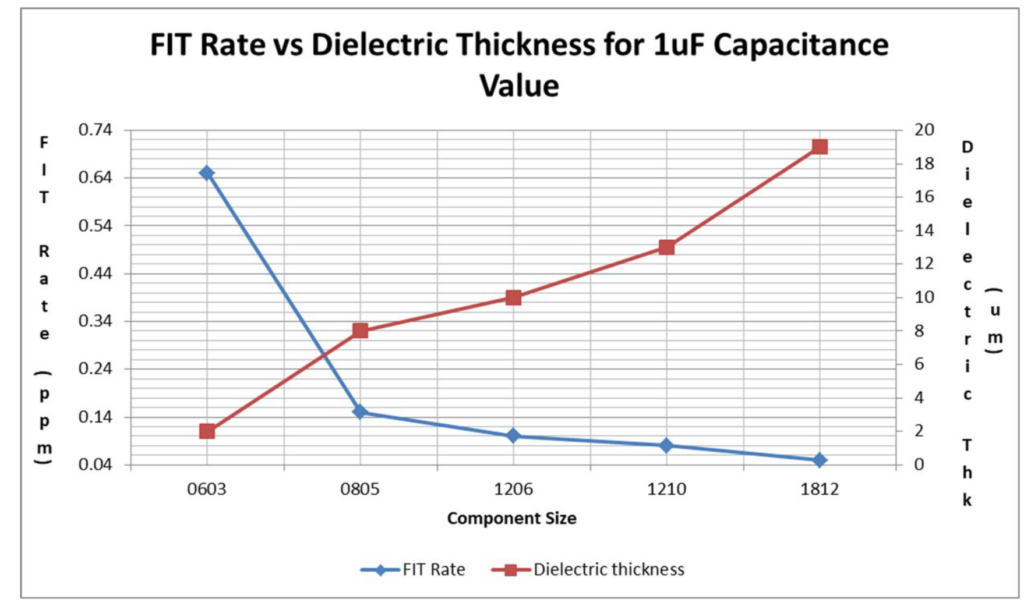
The following figure depicts the failure rate of a typical one microfarad capacitor compared to its dielectric thickness, which is directly correlated to package size. As the size moves from 1812 to 0603, the failure rate increases by more than an order of magnitude.
Miniaturization Tradeoffs
Manufacturing techniques and material technologies have pushed the envelope of achievable capacitance density further, yielding incredibly compact circuits at very attractive price points. This trend will undoubtedly continue, and in most cases, with little overhead to the design cycle. However, in specific applications, aggressive miniaturization is accompanied by nuanced performance tradeoffs that can greatly hinder a product’s success. Increased voltage dependence, temperature sensitivity, and electrical strength are a few discussed above. If the designer is not at least aware of what these tradeoffs are and when they matter, the downstream effects of poor manufacturing yield, field failures, and warranty returns can quickly overtake the potential success of any product.
pdf version of the paper is available from AVX website link below