Indian IISc researchers from Department of Instrumentation and Applied Physics (IAP) Bengaluru and their collaborators have designed a new supercapacitor that can be charged by shining light on it.
Such supercapacitors can be used in various devices, including streetlights and self-powered electronic devices such as sensors.
Supercapacitors are upgraded versions of capacitors – they exploit electrochemical phenomena to store more energy,” Abha Misra, professor, IAP and corresponding author of the study published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A, said.
The electrodes of the new supercapacitor were made of Zinc Oxide (ZnO) nanorods grown directly on Fluorine-doped Tin Oxide (FTO), which is transparent. It was synthesised by Pankaj Singh Chauhan, first author and CV Raman postdoctoral fellow in Misra’s group at IISc.
“Both ZnO and FTO are semiconductors with appropriately aligned energy levels, enabling superior performance of the photo-rechargeable supercapacitor. FTO, being transparent, allows light to fall on the optically active ZnO nanorods, which charge the supercapacitor,” IISc said.
Chauhan explained that two electrolytes — a liquid and a semi-solid gel — were used as the conducting medium between the electrodes. The capacity for storing charges (capacitance) is inversely proportional to the distance between the electrodes, IISc said.
“As the distance becomes very small, the capacitance shoots up,” Misra said. In electrostatic capacitors, maintaining a small distance between electrodes is difficult. However, in a supercapacitor, the electrodes’ charges attract the electrolyte’s oppositely charged ions, resulting in the formation of a charge layer just atoms away from each other — called an electric double layer or EDL. This results in the high capacitance of supercapacitors.
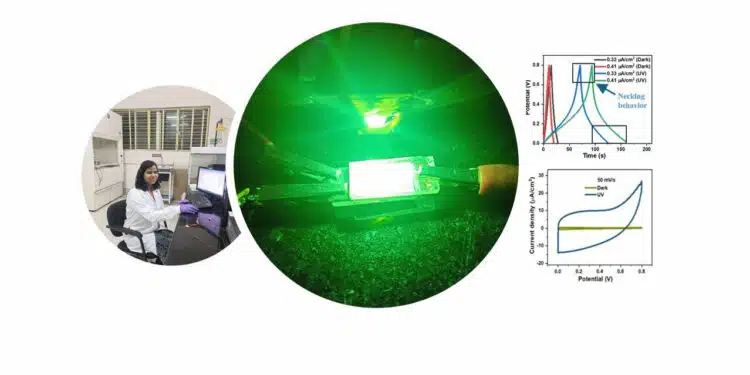
“When researchers shined ultraviolet (UV) light on their supercapacitor, they noticed a huge increase in the capacitance, several times higher than previously reported supercapacitors. They also noticed two unusual properties,” IISc said.
It added that first, while capacitance generally decreases as the voltage increases, they found the reverse — their supercapacitor’s capacitance under light illumination actually increased with increasing voltage.
“We call it the necking behaviour. This may be due to the high porosity of the electrodes. Second, the energy stored within the supercapacitor typically decreases when it is charged faster, because the ions in the electrolyte do not move fast enough to respond to the increased charging rate. However, with the liquid electrolyte, the team found that the energy stored in the supercapacitor surprisingly increased upon fast charging under UV light,” said AM Rao, Professor at Clemson University, USA, and co-author.
Mihir Parekh, a postdoctoral researcher in Rao’s group, developed theoretical models to explain these novel observations. The findings open the doors to developing simultaneously fast-charging and energy-dense supercapacitors, he suggests.
To design their present supercapacitor, the team explored two key ideas. “First, the surface area of the electrodes was increased by combining two optically active semiconductor interfaces in a way that maximises interaction with light, leading to higher charge generation. Second, a liquid electrolyte was used to ensure an effective EDL. Together, these resulted in superior performance,” IISc said.
Misra said that the ideas were simple. “…but when combined together, they worked very well.” She added that tweaking the design of the supercapacitor can enable its charging with visible and infrared light as well. The IISc-Clemson team aims to further explore and better understand the novel phenomena observed to design better supercapacitors.
Supercapacitors have lots of applications, Misra said. For example, they can potentially replace solar cells used in streetlights. They have high power density, so they can release charge more quickly than batteries. They can also be used to power chips in electronic devices like cell phones. “We have miniaturised supercapacitors to the micron scale so that they can be integrated along with these microelectronic chips,” Misra adds.
Reference Journal
Influence of electrolyte on the photo-charging capability of a ZnO–FTO supercapacitor; Journal of Materials Chemistry