Researchers from University of Alicante, Spain and CNRS Orléans France published in Carbon Jurnal its research on Adjusting the electrode surface functionality to improve the cell voltage of aqueous electrolyte carbon/carbon supercapacitors.
This article focuses on improving the performance of supercapacitors with aqueous electrolytes by modifying the surface of carbon electrodes.
The key points of the research:
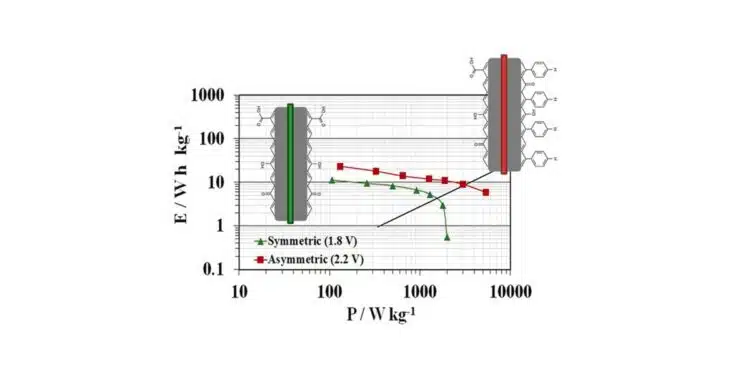
- Increasing Cell Voltage: Supercapacitors with carbon electrodes and Li₂SO₄ electrolyte can achieve a cell voltage of 1.8 V. Surface modifications can increase this voltage to 2.2 V.
- Positive Electrode Protection: Modifying the surface of carbon electrodes reduces oxidation and enhances stability.
- Surface Modification Methods: Techniques include chemical oxidation, hydrogen reduction, and chemical grafting.
- Electrochemical Characterization: Tests such as cyclic voltammetry, galvanostatic charge/discharge, and impedance were conducted.
- Results and Discussion: Surface modifications of carbon electrodes improve the performance and stability of supercapacitors.
Abstract
Improving the performance of supercapacitors in terms of energy density is a major technical challenge, especially in aqueous media where the operating voltage is limited by the electrochemical stability window of water and by undesirable reactions at the electrode/electrolyte interface. Carbon/carbon supercapacitors using 1.0 mol L−1 Li2SO4 as electrolyte can achieve cell voltages of 1.8 V.
Beyond this value, long-term supercapacitor operation is limited by positive electrode degradation due to irreversible oxidation reactions at the carbon/electrolyte interface. Such degradation processes can be minimized by selectively modifying the surface functionality of the porous carbon active electrode material. An in-depth study of the effect of different surface functionalities on the ageing of the supercapacitor, combining quantitative analysis of the gas generated during operation with electrochemical techniques and physical characterization of the carbon electrode, showed that among the different processes, the chemical grafting of low amounts of phenyl functionalities is the most effective in preventing the oxidation of the carbon. The origin of the resistance to oxidation was a combined effect of the blocking of active sites and the reduction of the local pH at the interface.
The cell voltage can be increased to 2.2 V and the energy density more than doubled by using an asymmetric system with the modified carbon as the positive electrode and an unmodified carbon as the negative electrode.
Conclusions
The effect of the surface functionality of carbon-based electrodes in aqueous electrolytes has been investigated from the point of view of decreasing the carbon reactivity at the positive electrode to avoid electrode degradation and to increase the cell voltage. A detailed analysis was conducted by examining gas levels and compositions during ageing, alongside the evolution of the physicochemical properties of carbon electrodes and electrochemical performance.
The results show that the numerous active oxidation sites initially present on the carbon surface cannot be fully removed by thermal hydrogen treatment, which only saturates high-energy sites with unpaired electrons. Similarly, chemical oxidation offers limited protection to the positive electrode. In contrast, after a chemical grafting, the carbon show significantly higher oxidation resistance, as grafted groups block active sites at graphene layer edges. This protection is more effective when the phenyl group bonded to active sites lacks electron-withdrawing groups, like carboxylic acid. The combination of this active site blocking effect with a reduction in the pHPZC to increase the oxidation potential is an effective strategy for protecting the positive electrode from oxidation, thereby increasing cell voltage and stored energy. An asymmetric system using the best-performing material (AC-Ph-H) as the positive electrode and unmodified carbon as the negative electrode enables long-term operation at a cell voltage up to 2.2V.
Therefore, protecting the surface of the positive electrode by grafting moieties that simultaneously lower the pHPZC and block active sites for oxidation proves to be a valuable strategy. This approach increases the energy density by 2.1 times and the power density by 4.5 times in supercapacitors operating with aqueous electrolytes.
Read the full article:
Alicia Gomis Berenguer, Martin Weissmann, Rachelle Omnee, Encarnación Raymundo-Piñero,
Adjusting the electrode surface functionality to improve the cell voltage of aqueous electrolyte carbon/carbon supercapacitors,
Carbon Journaů,
Volume 234, 2025, 119927, ISSN 0008-6223,
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbon.2024.119927