Researchers from Polytechnic of Turin, Italy and CEEC Jena, Germany studied aluminum dissolution processes in supercapacitors to increase its operating voltage. This study may also lead to new ways of aluminum thin film depositon techniques.
The present work addresses a new finding observed while performing aluminum dissolution experiments for supercapacitors (SCs) stability investigation.
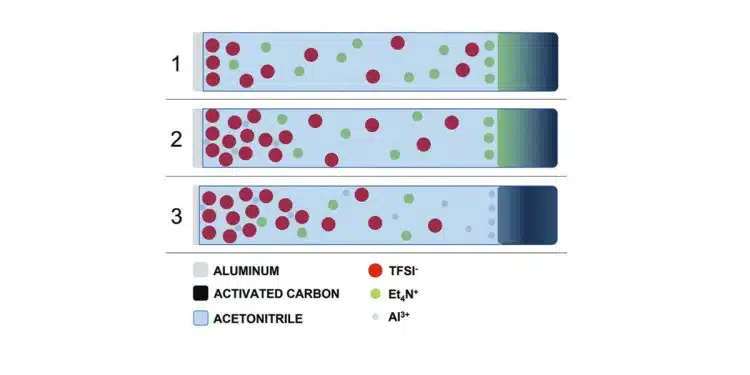
Supercapacitor (SC) electrodes based on carbon-coatedaluminum foils are electrochemically cycled in harsh conditions into bis-trifluoromethylsulfonyl imide (TFSI)-based electrolyte and using Acetonitrile (ACN) as solvent. Dissolution of aluminum is observed withsubsequent plating on the carbonaceous surface of counter electrodes.
Moreover, the same process can be reproduced also on standard SC activated carbon electrodes. This mechanism can open the way to an effective strategy to achieve Al film deposition by electroplating becoming competitive with the most common copper counterpart.
Introduction
Supercapacitors represent one of the most promising electro-chemical energy storage device complementary to rechargeable batteries. The state-of-the-art technology relies on largely available and relatively cheap active materials and electrolytes, i.e., activated carbons and inorganic salts such as tetraethylam-monium tetrafluoroborate (TEABF4), dissolved into organic sol-vents, typically acetonitrile (ACN).
These combinations warrantoperating power greater than 10 kW kg−1. However, the practical voltage window that can be exploited is limited to ≈3V, above which several degradation phenomenaon the electrode or in the electrolyte can occur. Several alternative electrolyte components have been proposed in the past years with the aim to increase the operating voltage, and thus the energy density of EDLCs. At this point, it is important to remark that the electrochemical performance of EDLC is also strongly affected by processes occurring at the current collectors used in such devices, which are made of aluminum. For this reason, while developing novel electrolytes, their interplay with the current collector needs to be carefully considered.
Among the proposed alternative salts, those based on the imide anions, i.e., bis-trifluoromethylsulfonyl imide (TFSI), are regarded with great interest due to their high chemical and ther-mal stability. However, the main drawback associated to the use of these salts in electrolyte formulations is the occurrence of anodic dissolution at the aluminum current collectors. As re-ported in several studies, the aluminum substrate dissolves as Al3+ions when subjected to high oxidation potentials. The dissolved aluminum ions react with the electrolyte mixture to form aluminum salts, the nature of which depends on the salt and solvents in the electrolyte system.
While electrolytes containing BF4−or PF6−display the ability to prevent this dissolution pro-cess, those containing TFSI−are forming complexes which are typically highly soluble in organic solvent. Therefore, a strong anodic dissolution of the Al current collector is taking place when they are used.
In the last years several studies have addressed this aspect, and it has been shown that the selection of solvents displaying low dielectric constant, i.e., 3-cyanopropionic acid methylester (CPAME), and the use of highly concentrated solution are interesting strategies to minimize the Al dissolution and guarantee the realization of high voltage EDLCs with high cycling stability. It is interesting to observe that the dissolution of Al, although deleterious for the stability of EDLCs, is a process of great interest because it could be used for the electrodeposition of this metal.
Currently,Al is plated using baths consisting of low melting point aluminum halides such as AlCl3or AlBr3, either mixed with some metal hydrates or in non-polar solvents. Aluminum halides are toxic and expensive, as well as highly poisonous if dispersed in the environment. Furthermore, they are flammable and corrosive. This makes them an appealing solution for technological purposes, however, from a sustainability point of view, bath solutions based on these salts are not environmentally friendly.
Aim of the Research
In this work, we consider for the first time the electrodeposition of Al on carbonaceous substrates from highly concentrated organic electrolytes containing TFSI anion. The proposed electrolytic solutions benefit from the absence of halogenated aluminum salts making them less moisture sensitive and less prone to develop harmful gases such as HCl fumes. The proposed electrolytes rely on acetonitrile that is still flammable as other solvents proposed in recent literature, but still, the bath does not produce harmful gases. The investigated electrolyte possesses the requirements for electrodeposition baths, and this electrodeposition process opens the possibility of exploration of novel, safe, and stable plating solutions for Al. It is shown how a one solvent and one salt electrolyte can be exploited to get Al plating, with the potential development of a low-cost bath solution.
Conclusions
The electrodeposition of aluminum on an amorphous carbon surface, stainless steel, and copper foil in an ACN based electrolyte was presented in this work. A thorough characterization of the deposition process results was carried out by means of elemental spectroscopies, morphological, and thermal characterizations.
The present discovery opens the opportunities to deepen the process knowledge, allowing for a more efficient bath solution and opening the possibility to deposit a uniform aluminum phase without any chloroaluminate salt. It is not excluded that this discovery could also open the possibility to the development of aluminum based electrochemical energy storage devices.
The development of chloroaluminate free electrolytes opens the possibilities to develop safer and cost effective processes for aluminum plating, which is still a good technological solution to develop coatings against corrosion, to improve the wear resistance and aesthetic appeal of surfaces. However, deeper insights must be given into the deposition mechanism on the carbon surface to better exploit the observed phenomena, especially the different effects on carbon blacks and activated carbons.
Read the full article here:
Zaccagnini, P., Heß, L.H., Baudino, L., Laurenti, M., Serrapede, M., Lamberti, A. and Balducci, A. (2023), From Aluminum Dissolution in Supercapacitors to Electroplating: A New Way for Al Thin Film Deposition?. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2202470. https://doi.org/10.1002/admi.202202470