Engineers at UC Berkeley have developed a new technique for making stretchable flexible electronics – wearable sensors and supercapacitors – that enables medical researchers to prototype test new designs much faster and at a far lower cost than existing methods.
The new technique replaces photolithography — a multistep process used to make computer chips in clean rooms — with a $200 vinyl cutter. The novel approach slashes the time to make small batches of sensors by nearly 90% while cutting costs by almost 75%, said Renxiao Xu (Ph.D.’20 ME), who developed the technique while pursuing his Ph.D. in mechanical engineering at Berkeley.
“Most researchers working on medical devices have no background in photolithography,” Xu said. “Our method makes it easy and inexpensive for them to change their sensor design on a computer and then send the file to the vinyl cutter to make.”
A description of the technique was published Jan. 25 in ACS Nano. Xu, who now works at Apple, and Liwei Lin, professor of mechanical engineering and co-director of the Berkeley Sensor and Actuator Center, were the lead researchers.
Wearable sensors are often used by researchers to gather medical data from patients over extended periods of time. They range from adhesive bandages on skin to stretchable implants on organs, and harness sophisticated sensors to monitor health or diagnose illnesses. These devices consist of flat wires, called interconnects, as well as sensors, power sources and antennas to communicate data to smartphone apps or other receivers. To maintain full functionality, they must stretch, flex and twist with the skin and organs they are mounted on — without generating strains that would compromise their circuitry.

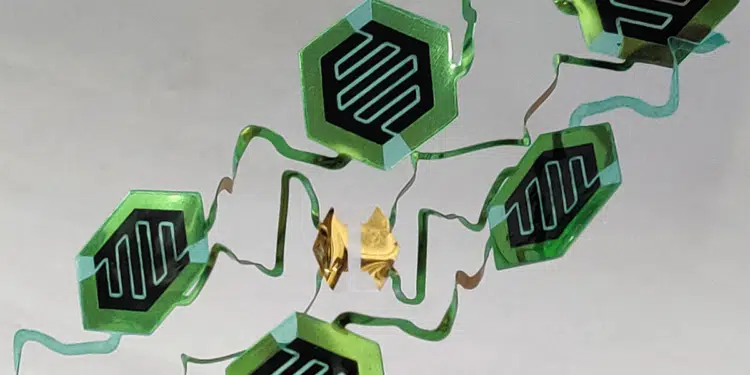
To achieve low-strain flexibility, engineers use an “island-bridge” structure, Xu said. The islands house rigid electronics and sensor components, such as commercial resistors, capacitors and lab-synthesized components like carbon nanotubes. The bridges link the islands to one another. Their spiral and zigzag shapes stretch like springs to accommodate large deformations. In the past, researchers have built these island-bridge systems using photolithography, a multistep process that uses light to create patterns on semiconductor wafers. Making wearable sensors this way requires a clean room and sophisticated equipment.
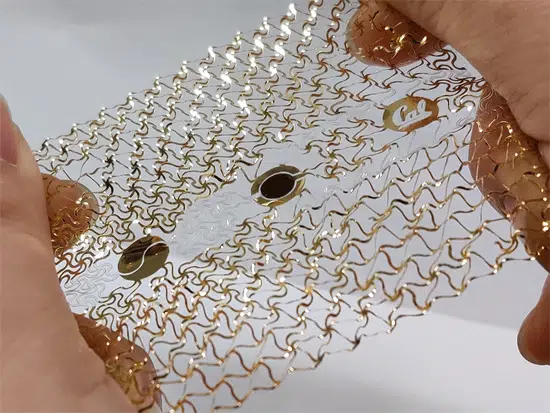
The new technique is simpler, faster and more economical, especially when making the one or two dozen samples that medical researchers typically need for testing. Making sensors starts by attaching an adhesive sheet of polyethylene terephthalate (PET) to a Mylar (biaxially oriented PET) substrate. Other plastics would also work, Xu said.
A vinyl cutter then shapes them using two types of cuts. The first, the tunnel cut, slices through only the top PET layer but leaves the Mylar substrate untouched. The second type, the through cut, carves through both layers. This is enough to produce island-bridge sensors. First, tunnel cuts are used in the upper adhesive PET layer to trace the path of the interconnects; then the cut PET segments are peeled off, leaving behind the pattern of interconnects on the exposed Mylar surface.
Next, the entire plastic sheet is coated with gold (another conductive metal could be used as well). The remaining top PET layer is peeled away, leaving a Mylar surface with well-defined interconnects, as well as exposed metal openings and contact pads on the islands. Sensor elements are then attached to the contact pads. For electronic devices, such as resistors, a conductive paste and a common heat plate are used to secure the bond. Some lab-synthesized components, such as carbon nanotubes, can be applied directly to the pads without any heating. Once this step is done, the vinyl cutter uses through cuts to carve the sensor’s contours, including spirals, zigzags and other features. To demonstrate the technique, Xu and Lin developed a variety of stretchable elements and sensors. One mounts under the nose and measures human breath based on the tiny changes in temperatures it creates between the front and back of the sensor.
“For a breath sensor, you don’t want to something bulky,” Lin said. “You want something thin and flexible, almost like a tape beneath your nose, so you can fall asleep while it records a signal over a long period of time.”
Another prototype consists of an array of water-resistant supercapacitors, which store electrical power like a battery but release it more rapidly. Supercapacitors could provide power for some types of sensors.
“We could also make more complex sensors by adding capacitors or electrodes to make electrocardiogram measurements, or chip-sized accelerometers and gyroscopes to measure motion,” Xu said.
Size is sensor cutting’s one key limitation. Its smallest features are 200 to 300 micrometers wide, while photolithography can produce features that are tens of micrometers wide. But most wearable sensors do not require such fine features, Xu noted. The researchers believe this technique could one day become a standard feature in every lab studying wearable sensors or new diseases. Prototypes could be designed using high-powered computer-aided design (CAD) software or simpler apps made especially for vinyl printers. Other study authors are Kamyar Behrouzi, Peisheng He, Tao Jiang, Guangchen Lan, Ashley Lee, Yu Long, Yande Peng and Dongkai Wang.