This article based on Knowles Precision Devices blog digs into trends in solar power electronics and its impact on componets requirements.
The developmental trajectory of many modern power electronics systems is driven by evolving carbon dioxide (CO₂) regulations. By maintaining compliance, green energy production, like photovoltaics (PV) and wind, and high-efficiency distribution systems, like high-voltage direct current (HVDC) and battery energy storage systems (BESS), support our transition to a more sustainable future.
Here, we’ll focus on a few trends we’re watching in PV, one of the most available and economical energy sources in many parts of the world.
Trend 1: Increasing Voltage
PV cells generate direct current (DC) electricity as they convert sunlight into electrical energy. For this energy to be fed into the electrical grid and used for commercial and residential power, DC must be converted to AC. The conversion is achieved using inverters.
Today, inverter voltage has increased from 500V to 1500V. This is made possible by two main developments. Component costs are lower (and systems require fewer components overall), and more systems feature wide band gap (WBG) filters that are high-voltage capable.
Across power electronics systems, a wider variety of applications have these high-voltage, high-temperature requirements, and it’s sparking new circuit design trends. While the cost of silicon carbide (SiC) diodes and MOSFETs are still limiting their adoption in PV, the industry is starting to understand the advantages of SiC in high-power string inverters. Using these components, manufacturers are designing inverters in the 100kW power range that are much lighter than those designed with insulated-gate bipolar transistors (IGBTs).
Trend 2: Changing Inverter Types in Solar Plants
Large solar plants are shifting their systems to rely on smaller, multi-string configurations that leverage microinverters rather than one central inverter. There are several approaches to a shift like this:
Large Central Inverter Architectures
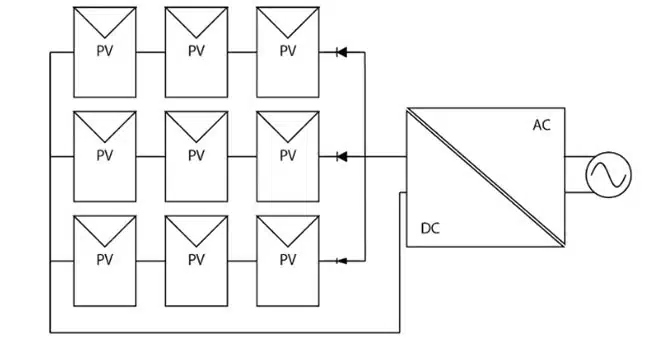
In traditional PV systems, solar panels are combined in parallel, so the inverter sees one large, combined DC voltage. This arrangement disregards several important real-world conditions. Each PV panel has a different optimal operating point based on its irradiance and temperature. Since the inverter assesses the string of PV panels as a single voltage source, power can’t be optimized on a panel-by-panel basis. While a centralized inverter (Figure 1) is an economical choice at scale, it’s susceptible to the drawbacks of non-optimal maximum power point tracking (MPPT), where the MPPT algorithm doesn’t perfectly align with the actual maximum power point (MPP) of the solar panel array.
String Inverter Architecture
By connecting smaller strings of panels and providing each string with an inverter, the MPP of each string can be optimized, preventing a scenario with a single point of failure; however, each panel can’t be optimized individually. If a string fails to create a high enough DC voltage for its inverter, there are additional inefficiencies to consider. With this string inverter configuration (Figure 2), it’s easier to expand the PV system by adding strings.
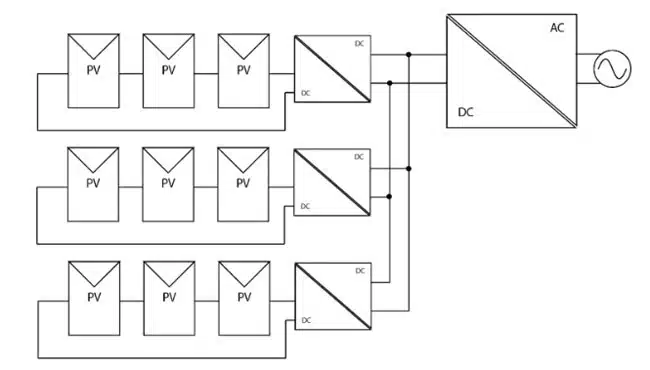
Multi-String Inverter Architectures
Multi-string inverters (Figure 3) are a variation of the two-stage string inverter. Here, several PV strings are connected to a common DC bus via DC/DC converters. A DC/AC converter exports the energy that was aggregated at the DC bus to the AC system. This configuration retains both the optimal MPP of each string (also achieved by a string inverter) and added flexibility in string design. As a result, this approach is becoming more popular in large-scale solar plants.
Microinverter Architectures
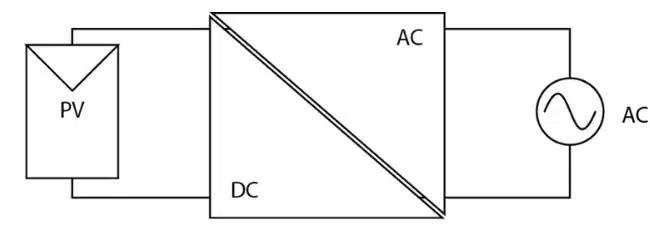
Embracing a modular system configuration, microinverters (Figure 4) accommodate an inverter-per-panel design, minimizing single-point failures. While microinverters are a poor choice for near-ideal conditions (e.g., shading-free solar farms), installations are becoming more complex. There are multi-angled roofs, installation costs to consider and lifetime restraints that limit the effectiveness of central inverter installations in residential and commercial settings. Under these conditions, microinverters are growing in popularity.
Trend 3: A Rising Tide for Solar Energy and Energy Storage Solutions
As the saying goes, a “rising tide raises all boats.” Evolution in solar energy and energy storage solutions is driving progress in adjacent technologies, like PV-powered charging stations for electric vehicles (EVs). With EVs in higher demand, there’s a push for more abundant and efficient charging stations. To accommodate, energy storage systems like BESS are evolving to smooth peaks in electricity generation profiles for PV generation and in the electricity demand profiles from EV charging stations.
HVDC transmission is also achieving greater heights. With massive PV plants generating gigawatts of electrical energy far away from high-demand areas, HVDC grid solutions are poised to reduce energy loss over long-distance transmission.