source: TrendInTech news
Amanda Porter-August 6, 2017 A team of University of Washington researchers, led by Peter Pauzauskie, an assistant professor of materials science and engineering, developed a system for manufacturing* supercapacitor electrodes that is faster and cheaper than traditional methods.
Supercapacitors are similar to regular batteries in that they store and provide energy. However, they do so much faster and with more power, which is required for high tech devices like electric vehicles and high-powered lasers.
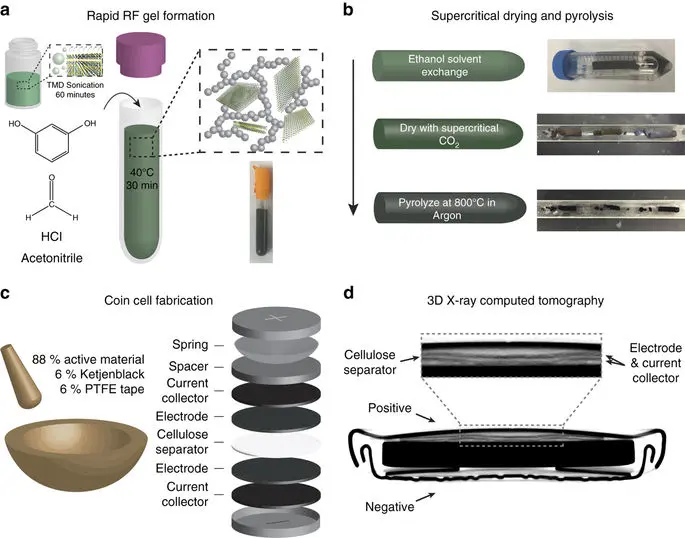
Outline of the nanomanufacturing process for composite TMD carbon aerogels. Initially, sonication-driven cavitation (a) drives TMD sheets apart and enhances dispersion within acetonitrile. Resorcinol and formaldehyde are added to this solution, which causes rapid sol-gel formation, catalyzed by hydrochloric acid. This gel is washed with ethanol to remove any unreacted species and dried with supercritical CO2 (b) to displace the solvent without destroying its pore structure before being pyrolyzed in argon. Finally, we process this material into a supercapacitor by grinding it with carbon black additive (Ketjenblack) and PTFE tape, rolling and punching it into electrodes that are assembled into a symmetric coin cell, and adding the resulting electrode to a full coin cell, using a cellulose separator, illustrated in (c). A three-dimensional X-ray computed tomography image of a coin cell after 10 000 charge–discharge cycles (d). source: Nature Microsystems and Nanoengineering
Currently, the manufacturing process for the electrodes required to make *supercapacitors work is time-consuming and expensive, two drawbacks that hinder widespread use. The UW electrode uses an aerogel infused with inexpensive carbon rich materials and only take a few days to create. The full details of the research are in a paper available in Nature Microsystems and Nanoengineering.
Aerogels start as wet, gel-like polymers that are processed to remove the moisture which is replaced with gas instead. The treatment maintains the three-dimensional structure, makes it lightweight, and significantly increases its surface area. According to Pauzauskie, a gram of aerogel has a surface area of 100 yards. Surface area is key because of a *supercapacitor stores energy by separating negative and positive charges across its surface, the more surface available, the more charge it can hold.
To make the electrodes, researchers combined aerogels made of formaldehyde and other carbon-based substance with molybdenum or tungsten disulfide, adhesives, and other materials until it resembles a ‘dough.’ The dough was then rolled out to millimeters of thickness and sliced into discs. Overall the process took a few hours.
After testing, they found the unique electrodes to have a capacitance 27 percent greater than an aerogel alone.
The team expects that more development of this type of electrode can lead to more powerful and refined capacitance, but initially they wanted to prove the method effective, quick, and cheap. They hope their electrodes and production method will improve not only supercapacitors but also batteries in general and hydrogen production.
featured image: Slice from x-ray computed tomography image of a supercapacitor coin cell assembled with the electrode materials. The thin layers — just below the coin cell lid — are layers of electrode materials and a separator.William Kuykendall