This article published by Rutronik discusses pre-charging of capacitors using pulse-withstanding resistors in drive circuits.
Electric motors are usually controlled using converters. Electrolytic capacitors are frequently used to stabilize and buffer the DC voltage in the DC link.
There are a number of issues to consider with switching these capacitors in and out of the circuit.
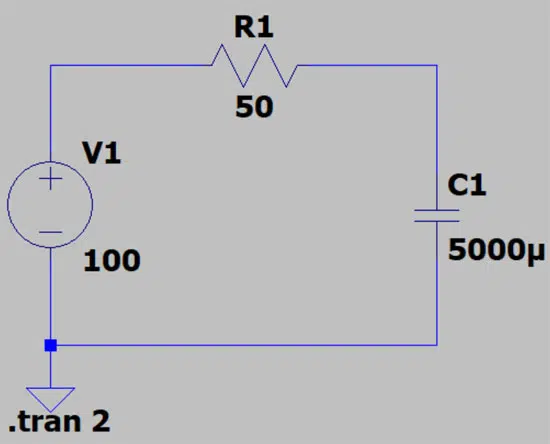
When a capacitor is charged through a resistor, the increase in voltage follows a curve in the form of a natural exponential function (Figure 1, blue line). The relevant charging current of the capacitor (green) on the other hand takes the form of a decaying natural exponential function.
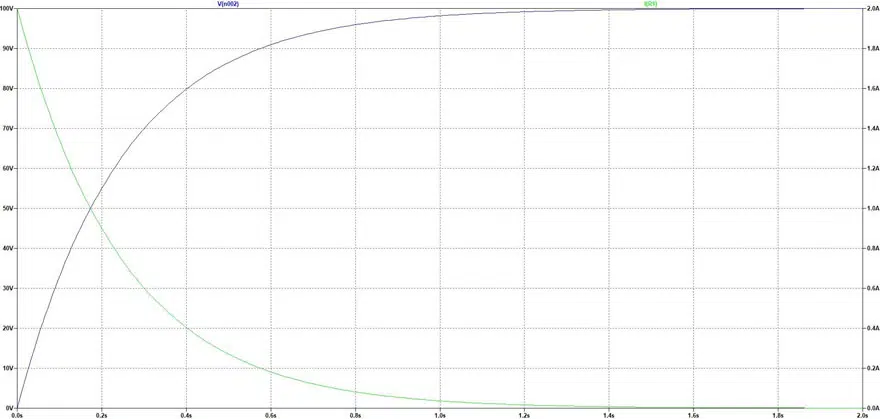
In an example of charging of 5000uF 100V capacitor through 50Ohm resistor (see Fig.2.) the maximum current flows right at the start of the charging process, at which point it is 100 V/50 Ω = 2 A. After around 1.5 seconds the capacitor reaches a voltage of close to 100 V, while the current is close to 0 A.
Let’s say this capacitor is charged without using a resistor, so that when the voltage is “hard switched,” there is only a very low specific resistance in the supply line—estimated to be 10 mΩ—in which case there is theoretically a current of up to 10,000 A at the first moment of charging!
However, in reality, in addition to the ohmic resistance of the connecting wire, there are other elements providing resistance:
- the ohmic resistance of the capacitor estimated at around 25 mΩ
- the internal resistance of the voltage source estimated at around 20 mΩ
- the transfer resistance of the connecting terminals, switching contacts, etc. of max. 5 mΩ
This means that a realistic total resistance would be around 50 mΩ. With this, there is a still a peak current of over 2,000 A (100 V/0.05 Ω = 2,000 A).
While this very high current would only be flowing for a very brief moment, you can still imagine what impact these current surges can have on other components — certainly so, when you remember that DC voltages of 800 V are commonplace in DC link solutions for converters nowadays.
Switch-On Processes in Consideration of Wire Inductance
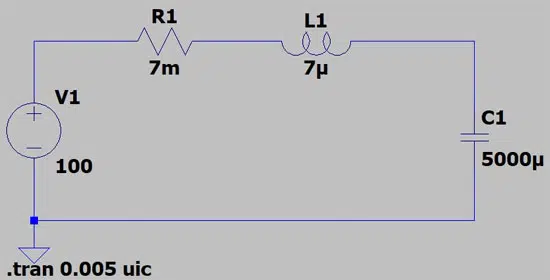
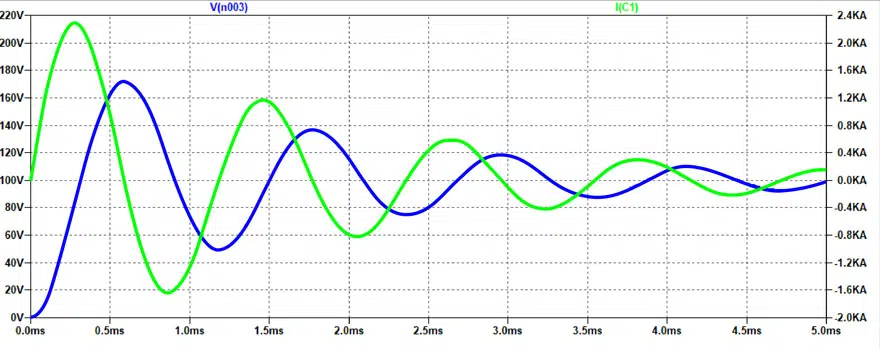
If we consider not only the capacitance but also any wire inductance as shown in Figure 3, we observe behavior such as that seen in Figure 4.
Without going into detail, the graph shows clearly that the voltage (blue curve) is no longer a natural exponential function, instead oscillating towards a value of around 100 V. Briefly, it will reach a value of up to 170 V, around 70% higher than the externally applied output voltage!
The current (green curve) also peaks at around 2,100 A just after switch-on due to the additional inductance.
In other words, the current reaches very high values and overvoltages with voltage surges of up to double the externally applied voltage possibly occurring even if all ohmic resistors, inductors, and capacitors to be charged in the charging circuit are accounted for.
This is why hard-switching a capacitor should always be avoided. Pre-charging a capacitor allows the aforementioned behavior to be almost entirely prevented.
Similar behavior occurs when discharging a capacitor, which is why it is also recommended to provide a resistor for the discharging process.
Pulse-Withstanding Pre-Charge Resistors
A very simple and cost-effective approach is provided here by pulse-withstanding charge resistors, which can be connected in series with the capacitor for a certain time. All that is needed here is a pre-charge branch connected in parallel to the main switch. This branch needs to fulfill the following requirements:
Use of the current-limiting effect of the resistor
Two-step switch-on process:
- The pulse-withstanding resistor is used to pre-charge the capacitor until it has almost entirely reached the externally applied voltage level
- The capacitor is directly connected by bridging the pre-charge branch connected in parallel with the main switch
A mechanical or electrical lock-out mechanism that prevents switch-on without a pre-charge.
A wide range of pre-charge resistors is offered by leading power resistor manufacturers. These include cement-coated wire resistors from 3 to 18 W and high-load resistors with aluminum housing from tenths to hundreds W. Customized solutions can be often ordered as well for special requirements. For example, increased voltage requirements, special geometric forms, and also enhanced cooling solutions can be implemented.