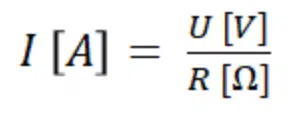This article explains very basic definition of What is electrical resistance, What is a Resistor ? as passive electronic components and its main application and technologies.
The very basic definitions:
What is Electrical Resistance ?
Physical property in conductor or of a component which transforms electrical energy into heat
What is Electrical Resistor ?
Resistors are passive electrical components that limits the flow of electric current.
Component R that has no significant distortion of phase at an applied voltage U and the resulting flow of current I
Resistors, like inductors and capacitors, are passive electronic components which are quite simple in theory but rather more complex when the behaviors of real-world devices are considered. Any resistor that one can build or buy is non-ideal in some respect that renders it unsuitable for some purposes; the various products available offer different balances of imperfection in an effort to be found good enough for others..
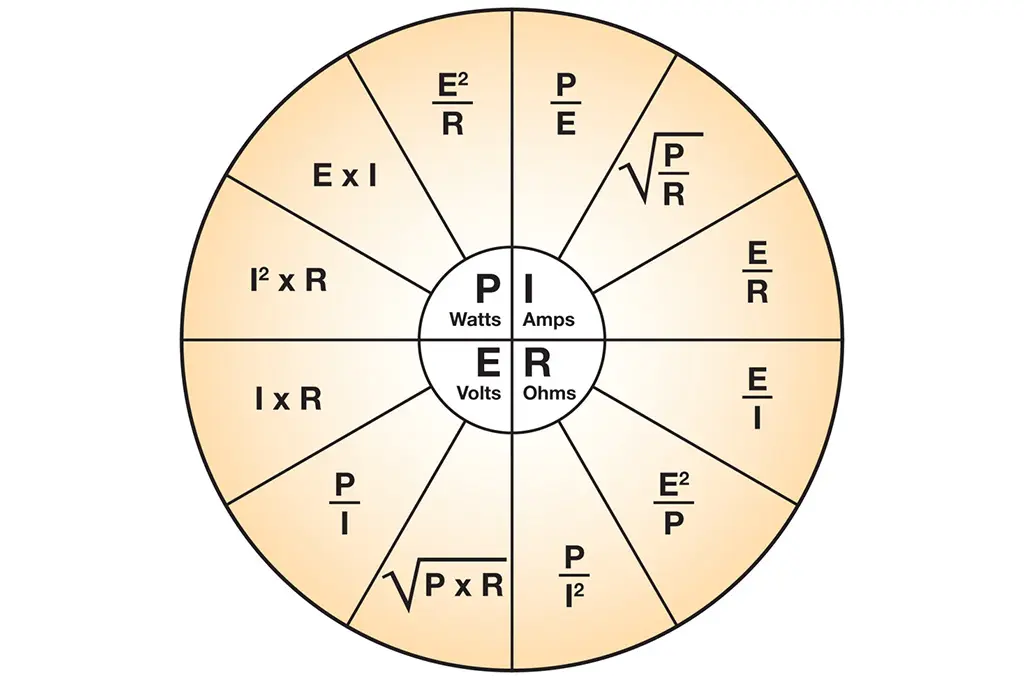
Resistors can be found in almost all electrical networks and electronic circuits. The resistance is measured in ohms. An ohm is the resistance that occurs when a current of one ampere passes through a resistor with a one volt drop across its terminals. The current is proportional to the voltage across the terminal ends. This ratio is represented by Ohm’s law basic equation [1] and related equations for power, current, voltage and resistance in Figure 1.:
Despite the Ohms’ law is one of the most frequent used relationship for components and circuits, there is some limitation for it validity at:
- high frequencies (relaxation, skin effect)
- high field strengths (flashovers at highly resistive materials)
- very low temperatures (superconductivity)
Resistors have several properties besides their rated resistance, such as their temperature coefficient, resistor noise and power rating. These resistor properties can be important to take into account depending on the application.
Resistors are used for many purposes. A few examples:
- delimit electric curren
- tvoltage division
- heat generation
- matching and loading circuit
- control gain
- fix time constants
- current measurements
They are commercially available with resistance values over a range of more than nine orders of magnitude. They can be used to as electric brakes to dissipate kinetic energy from trains, or be smaller than a square millimeter for electronics.
Resistor technologies differ in features, range of electrical parameters covered. Lets start our course to learn some basics about them and what technologies are available today.
Resistor Terms and Definitions
Nominal Resistance
Designed resistance value usually indicated on the resistor.
Power Rating
Maximum allowable power at rated temperature. Some of our chip resistor arrays and networks specify the whole power rating as a package.
Rated Temperature
Maximum ambient temperature at which the power rating may be applied continuously. The rated ambient temperature refers to the temperature around the resistor mounted inside the equipment, not to the air temperature outside the equipment.
Rated Terminal Part Temperature
Maximum terminal part temperature of the surface mount resistor at which the power rating may be applied continuously. Includes the temperature rise by self heat generation.
Derating Curve
Curve that expresses the relation between ambient temperature and the maximum allowable power, which is generally expressed in percentage.
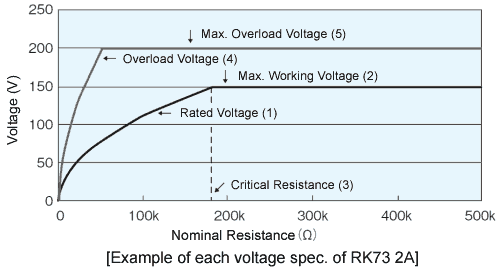
Rated Voltage
Maximum allowable D.C. or A.C. voltage (RMS), capable to be continuously applied to a resistor or a resistor element under the rated ambient temperature or terminal part temperature, which is calculated from the rated power and nominal resistance using the following formula.

Rated voltage shall not exceed the max. working voltage.
Critical Resistance
The maximum nominal resistance value at which the rated power can be applied without exceeding the maximum working voltage. The rated voltage is equal to the max. working voltage at the critical resistance value.
Max. Working Voltage
Maximum D.C. or A.C. voltage (RMS) that can be continuously applied to the terminations of a resistor. However, the maximum value of the applicable voltage is the rated voltage at the critical resistance value or lower.
Maximum working voltage and rated voltage are calculated direct-current voltages based on rated power. Sine wave is assumed for the alternate-current so the peak voltage should be √2 times the maximum working voltage. When the wave form is not a sine wave, or when the resistance value exceeds the critical resistance, please contact manufacturer/consult the product datasheet for the applicable peak voltage.
Overload Voltage
Allowable voltage which is applied in 5 sec. under short time overload test. Overload voltage shall be 2.5 times of rated voltage or max. overload voltage, whichever is lower.
Max. Overload Voltage
Dielectric Withstanding Voltage
A.C. voltage (RMS) that can be applied to a designated spot between the electrode and the outer coating in one minute, in the voltage proof test (JIS C5201-1 4.7).
Temperature Coefficient of Resistance(T.C.R.)
Relative variation of resistance between two given temperatures when temperature is changed by 1K.