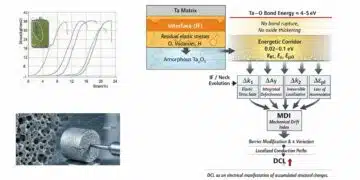
In this blog article Sotiris Zorbas, MSc, Frenetic Power Εlectronics Εngineer is explaining how to design a small integrated LLC transformer for 500W PSU application.
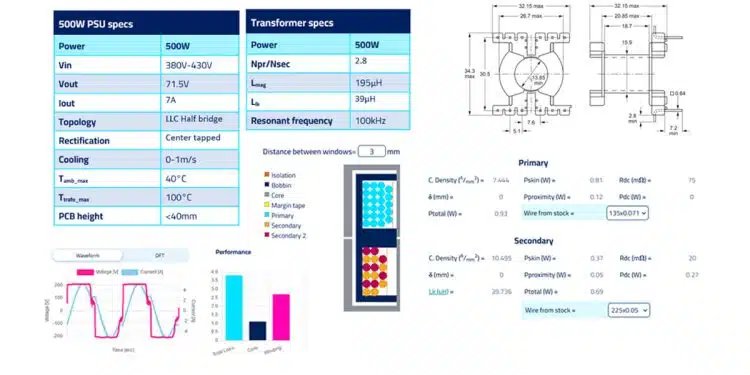
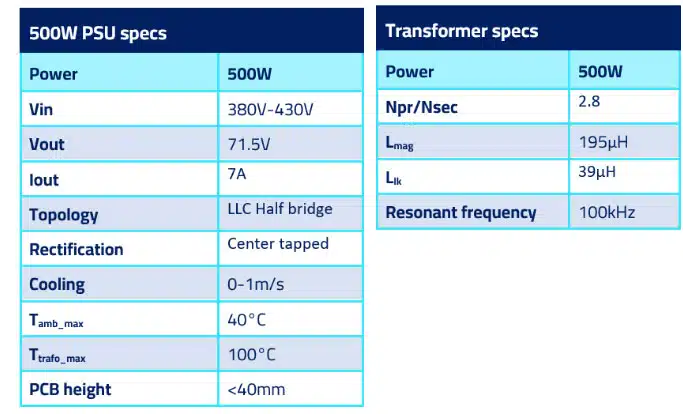
Let’s see the specs of this LLC center tapped PSU that we want to design Magnetics for. We are talking about a charger with 71.5V/7A output:
- Our cooling conditions can be either natural cooling or some forced cooling up to 1m/s, depending on the position of fan relative to the Magnetics.
- The intention is for the fan to be mounted on the enclosure, forcing air from the inside of the box to the environment outside. The ambient temperature inside the box is set at 40°C maximum. The fan speed will be controlled based on the core temperature of the Transformer, where a glued NTC inside an M3 bare ring terminal will be also glued to the Transformer core.
- Using the equations and methodology of the previous Newsletters, we derived the specifications for the Transformer inductances and turns ratio.
Based on the findings from previous blog
In previous blog, we built some nice 2-chamber Transformers from 500W to 2kW. In all cases, the actual Transformer total losses amounted to approximately 0.6% of the total power delivered to the load. That observation is in line with our experience in Frenetic, and we will use it to minimize our design iterations.
Also, the power density for naturally cooled designs to achieve approx. ~50°C of temperature rise is somewhere between 5-9kW/L. But in our case, we have some variable fan cooling when the Transformer gets hot. That said, we will push power density more than 50% to about 12-15kW/L. Of course, these are preliminary assumptions and should be treated as such.
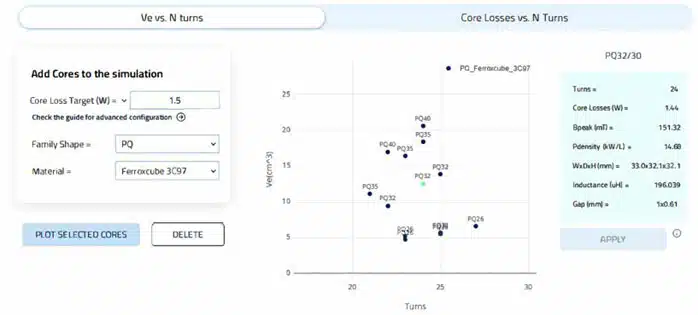
Plotting PQ core sets I quickly found a match for my specifications:
- As mentioned, 0.6% out of the 500W are set aside for the Transformer losses, and that is 3W. Given a 50-50% split between core-winding losses we set a 1.5W core loss target.
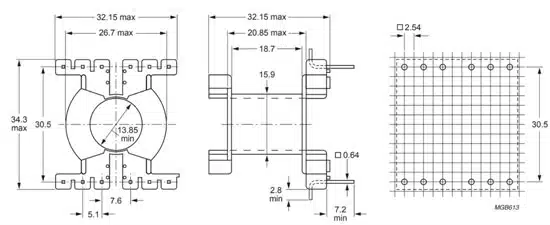
- From the results shown a PQ32/30 core has a power density of 14.7kW and height at 32mm which if one counts a 1.6mm FR4 and 5mm standoffs is less than the 40mm PCB height that was specified.
- Also, instead of 24 turns suggested from the tool, 23 turns were selected to better match the turns ratio, given that the secondary turns should be a round number. In this case 7 turns for each secondary.
The windings part
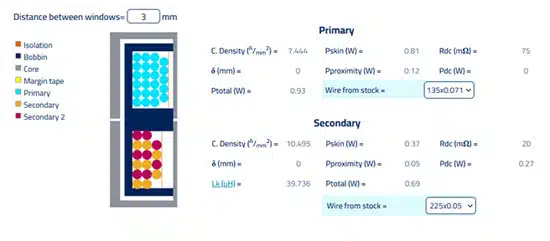
All necessary info for the Winding is here. As you can see in Figure 4., we predict a 39-40 μH of leakage with 3mm of separation. The wires used are simple in stock Litz wires with different strand diameters, and my comment here is that this is a manufacturable design with the necessary margins as far as fitting goes, in place.
The worst case condition
- Assuming natural cooling only.
- The PFC outputs 380V (input voltage of the LLC converter)
- Frequency moves down to 84kHz (100kHz is the resonant freq.)
- The rms currents increase.
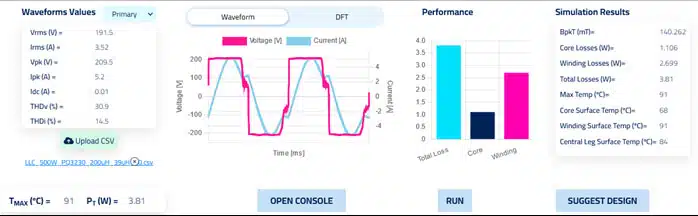
We get the following performance:
✅ Tmax at 91°C below 100°C
✅ Pmax = 3.8W in line with our 3W prediction.
✅ Integrated 40μH of leakage inductance
Of course, with air cooling or higher input voltages (close to 400V) the Transformer may as well operate at 50°C under full load!
And the best part: design time, just 2hr!